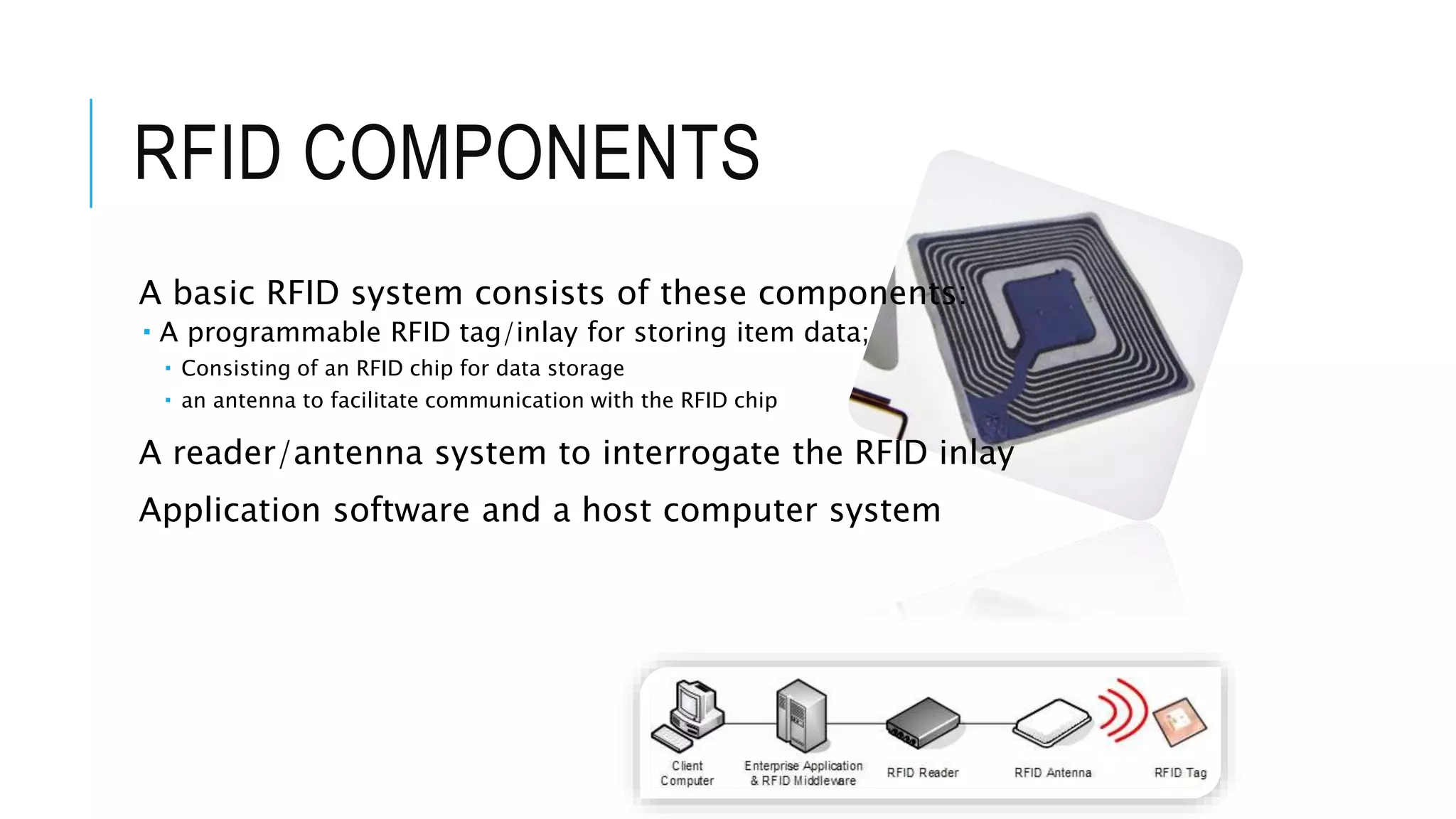
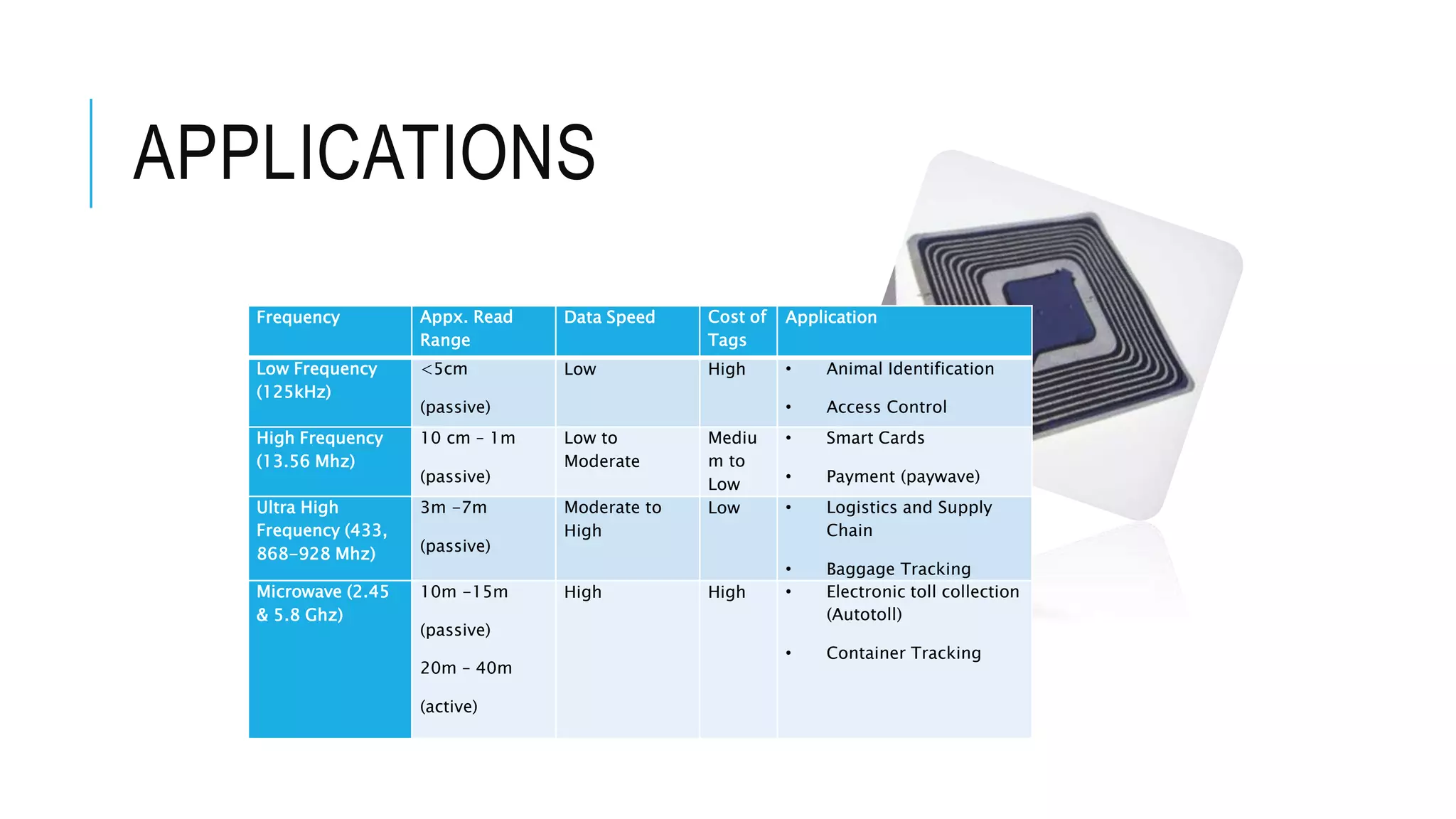
This document discusses RFID (radio frequency identification) technology and its applications. It begins with an introduction to RFID, describing its components and different tag types. Applications of RFID at various frequencies are then outlined, including for logistics, smart cards, electronic toll collection and more. The document also summarizes an online survey of SMEs that found most saw potential for RFID in logistics, libraries, and inventory control. It concludes by noting both benefits of RFID like contactless reading but also challenges around costs and standardization.