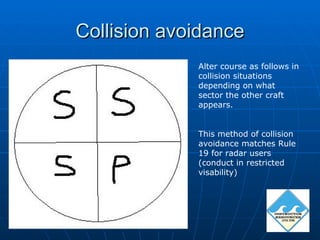
Radar is used for collision avoidance, navigation, and pilotage. The radar screen displays range rings and a ship's head marker. International regulations require proper use of radar if fitted, including long-range scanning to obtain early warning of risk of collision and radar plotting. Assumptions should not be made based on limited radar information. Regulations also specify radar reflector size requirements. Collision avoidance using radar follows the rules to alter course depending on sector of detected vessels. Different radar display modes like head-up and north-up have benefits and drawbacks. Factors like range, target size and material, and false or interference echoes must be considered when using radar. Attending an RYA radar course is recommended prior to use.