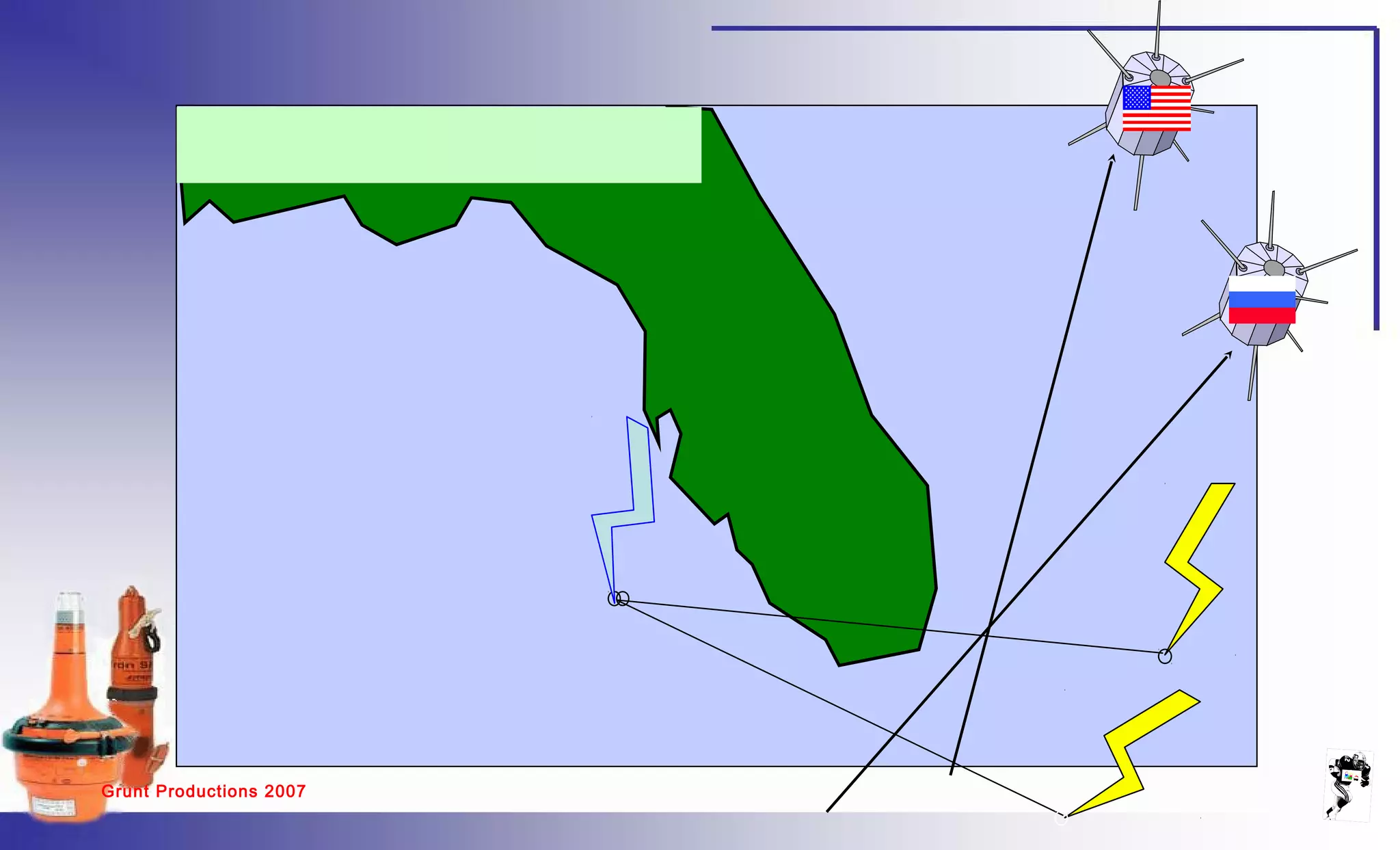
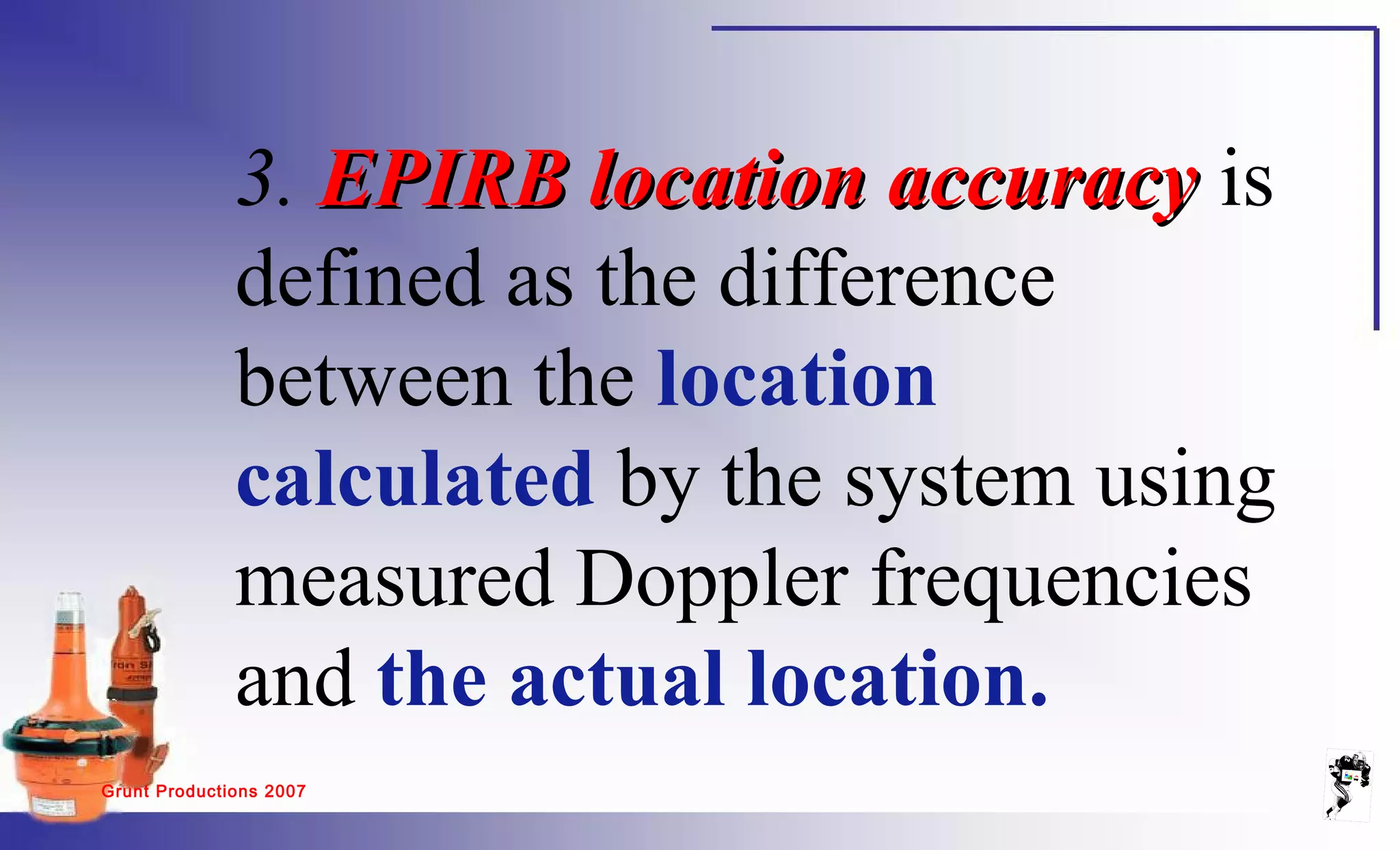
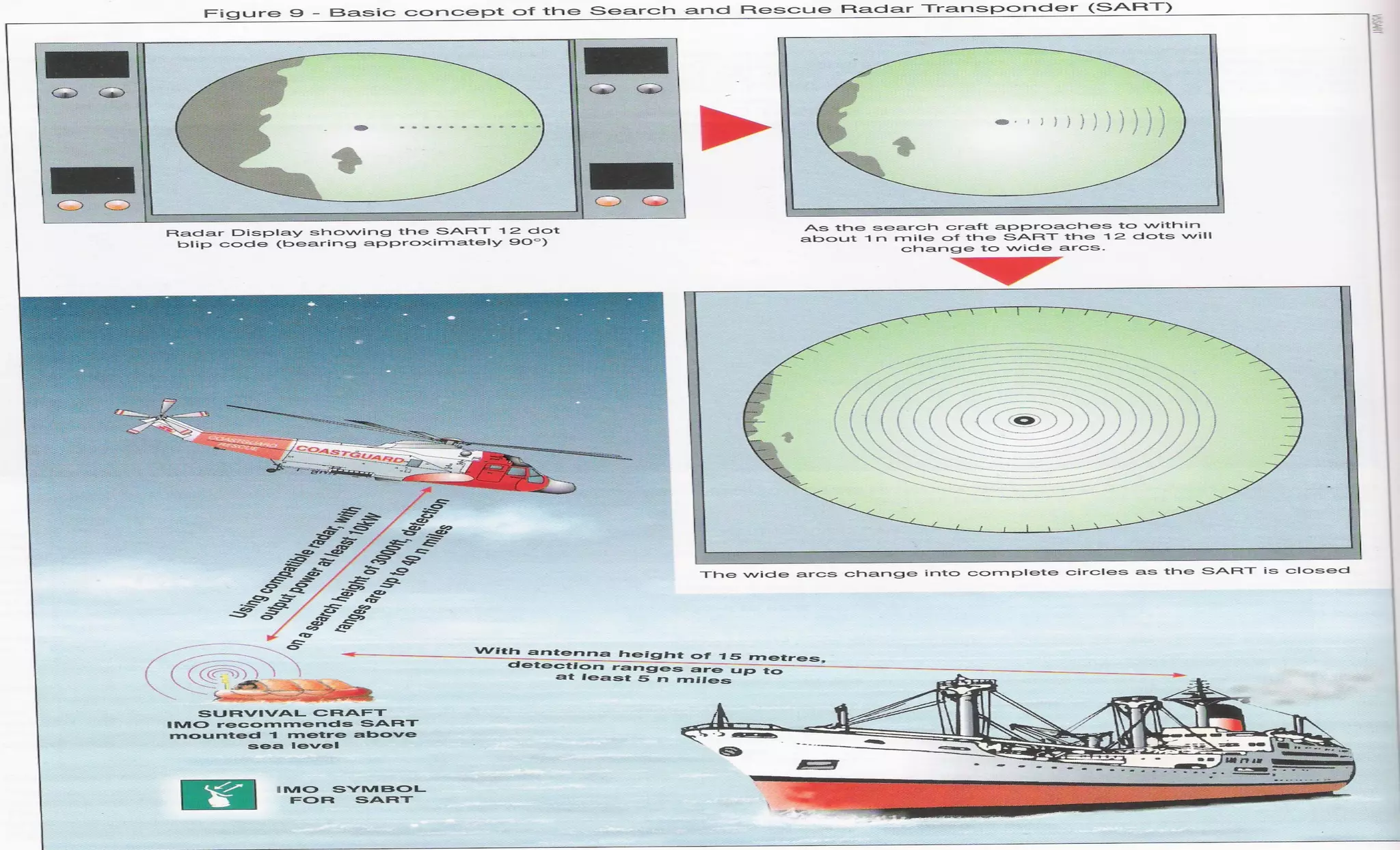
The document discusses emergency position indicating radio beacons (EPIRBs) and search and radar transponders (SARTs) that are used in search and rescue operations. It describes how 406 MHz satellite EPIRBs transmit a radio signal every 50 seconds that includes a digitally encoded message with information to help locate the vessel in distress. SARTs generate a response signal when interrogated by ship or aircraft radar to help rescuers locate survivors in the water even in poor visibility. The document outlines key performance parameters for EPIRBs such as detection probability, location accuracy, ambiguity resolution, system capacity, coverage area, and notification times.