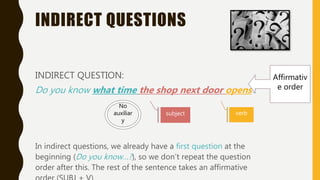
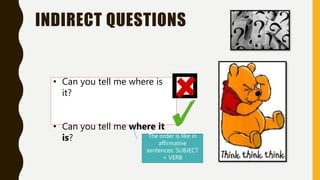
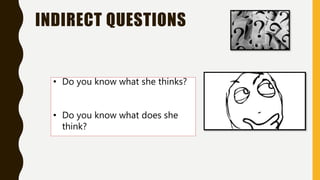
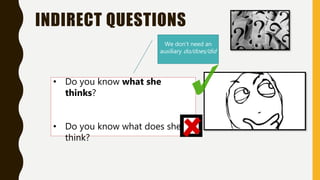
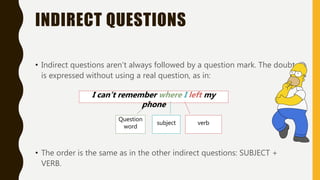
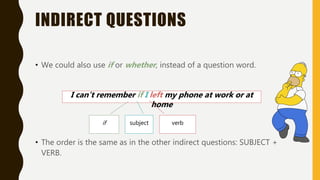
The document discusses different types of questions in English, including direct and indirect questions. It explains that direct questions follow subject-auxiliary inversion order, while indirect questions take the form of statements and do not require inversion. The document also covers question words, negative questions, questions with prepositions, and using "if/whether" in indirect questions.