The document discusses nuclear stability and binding energy. It provides three key points:
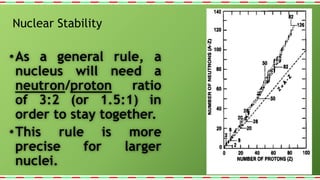
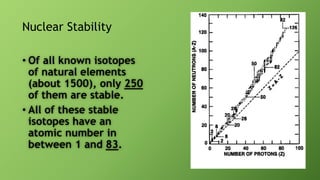
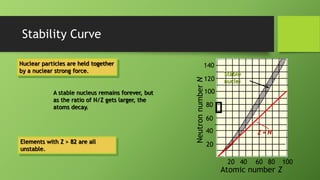
1) Nuclear stability is determined by the ratio of neutrons to protons in the nucleus, with a ratio around 1.5:1 being most stable. Only about 250 of over 1500 known isotopes are stable.
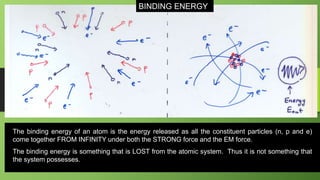
2) Nuclear binding energy is the energy required to separate nucleons in the nucleus. It is measured by the mass defect, which is the difference between the actual nuclear mass and the predicted mass of its constituents.
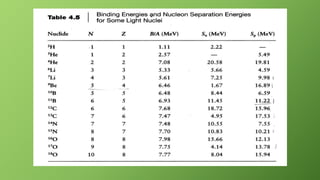
3) Binding energy per nucleon indicates the stability of a nucleus, with higher values corresponding to greater stability. For uranium-238, the binding energy per nucleon is calculated as 7.57













![SINGLE PROTON SEPARATION ENERGY
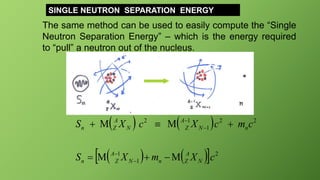
The same clever strategy applies to finding the “Single Proton Separation
Energy” Sp. But note here there is a difference – we must be careful in
counting electron mass.
2
2
2
1
1
2
M
M c
m
c
m
c
Y
c
X
S e
p
N
A
Z
N
A
Z
p
2
1
1
2
1
1
M
M
M
M
c
X
m
Y
c
X
m
m
Y
S
N
A
Z
H
N
A
Z
N
A
Z
e
p
N
A
Z
p
p
S [Mass of Final Products – Mass of Initial atom] c2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearstability-221110093848-d2f6da85/85/NUCLEAR-STABILITY-pptx-20-320.jpg)