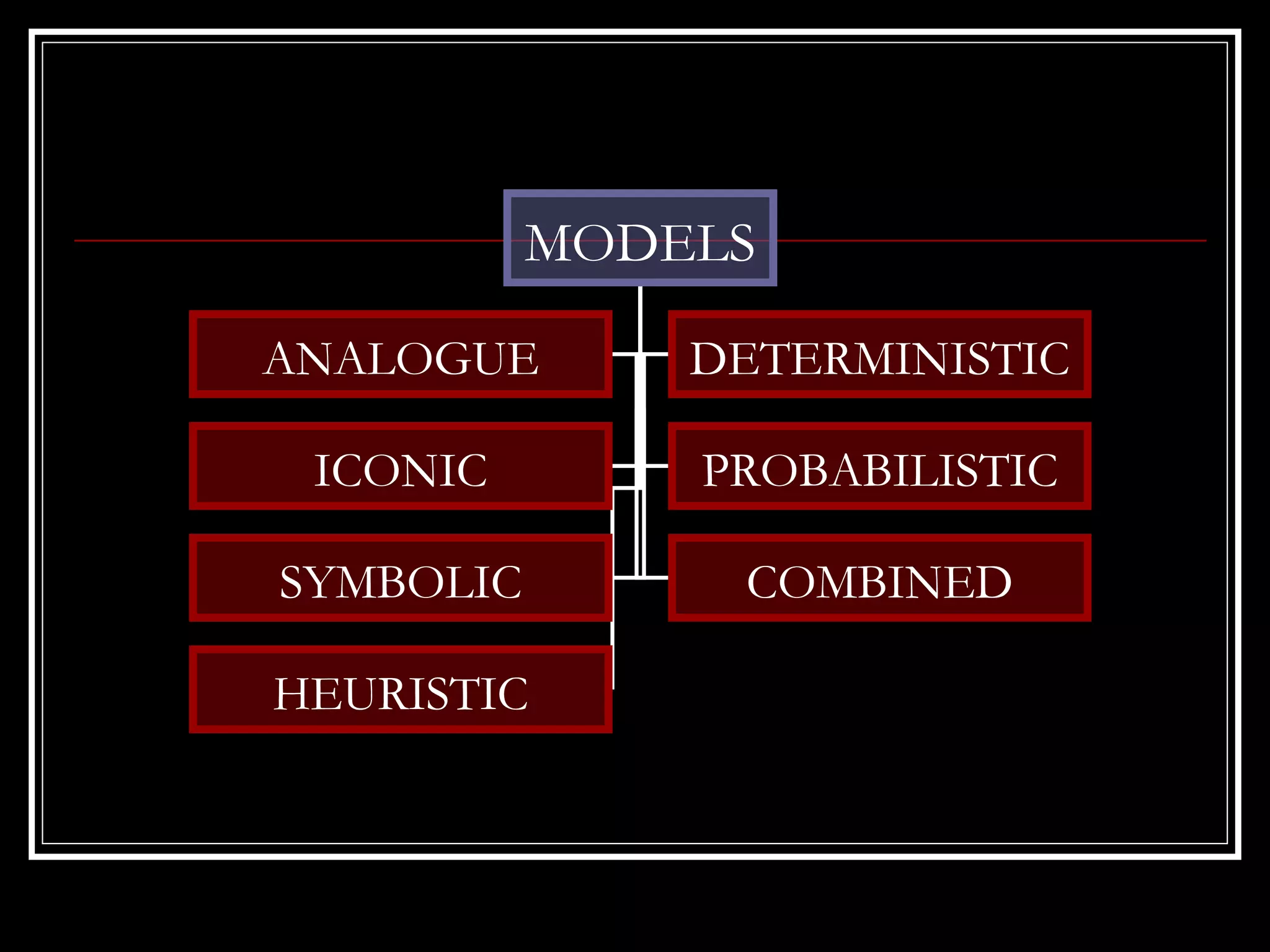
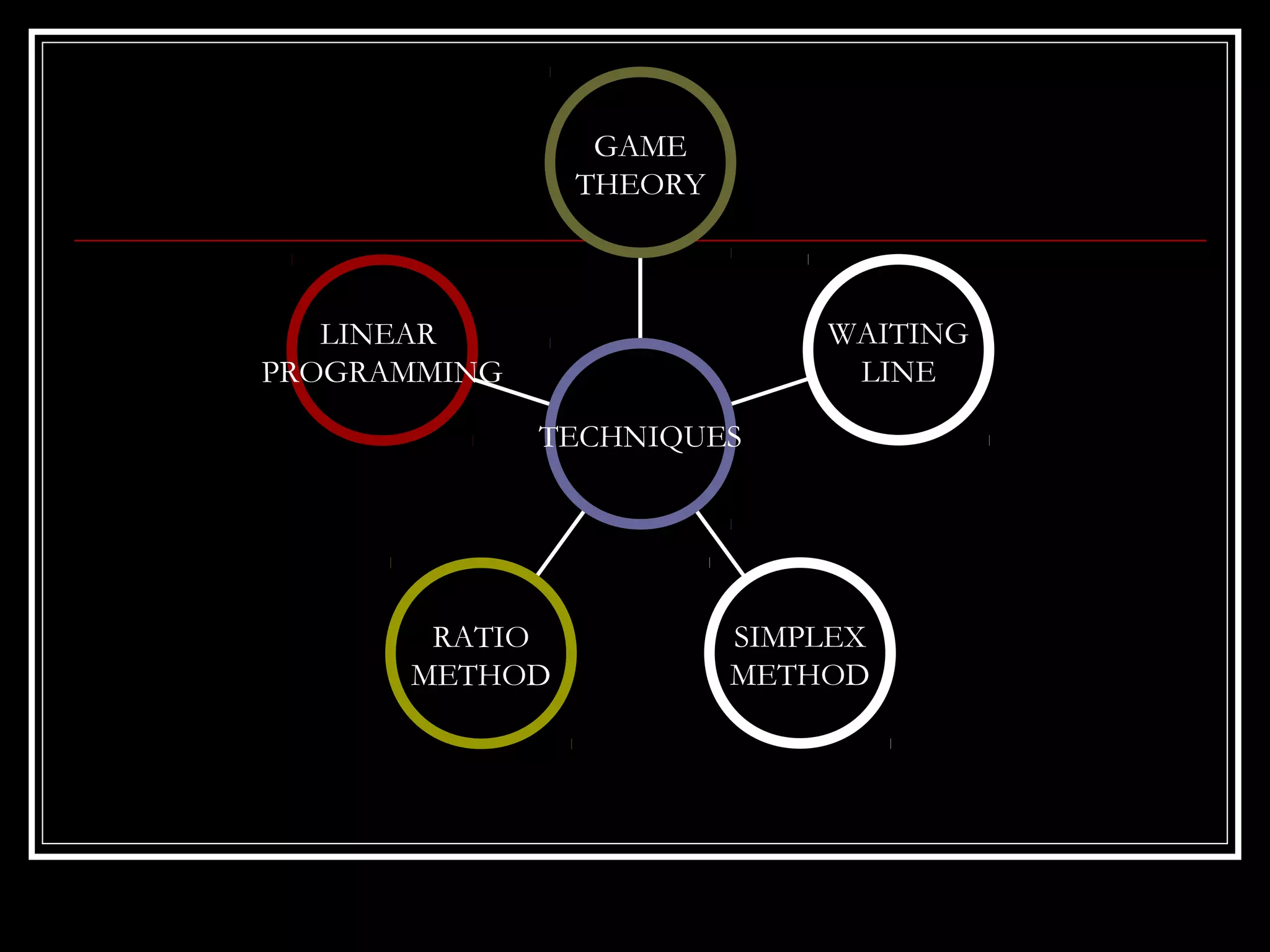
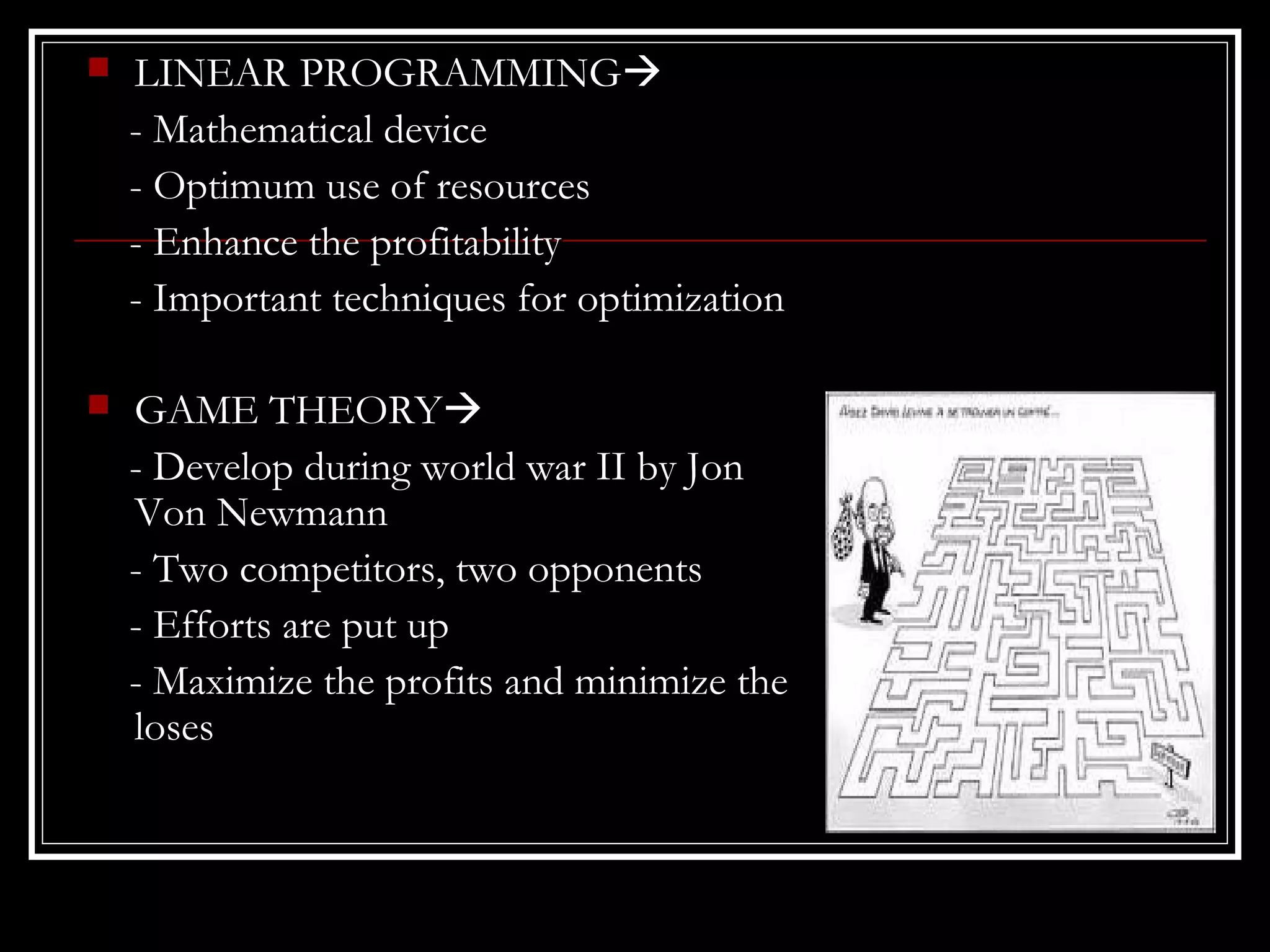
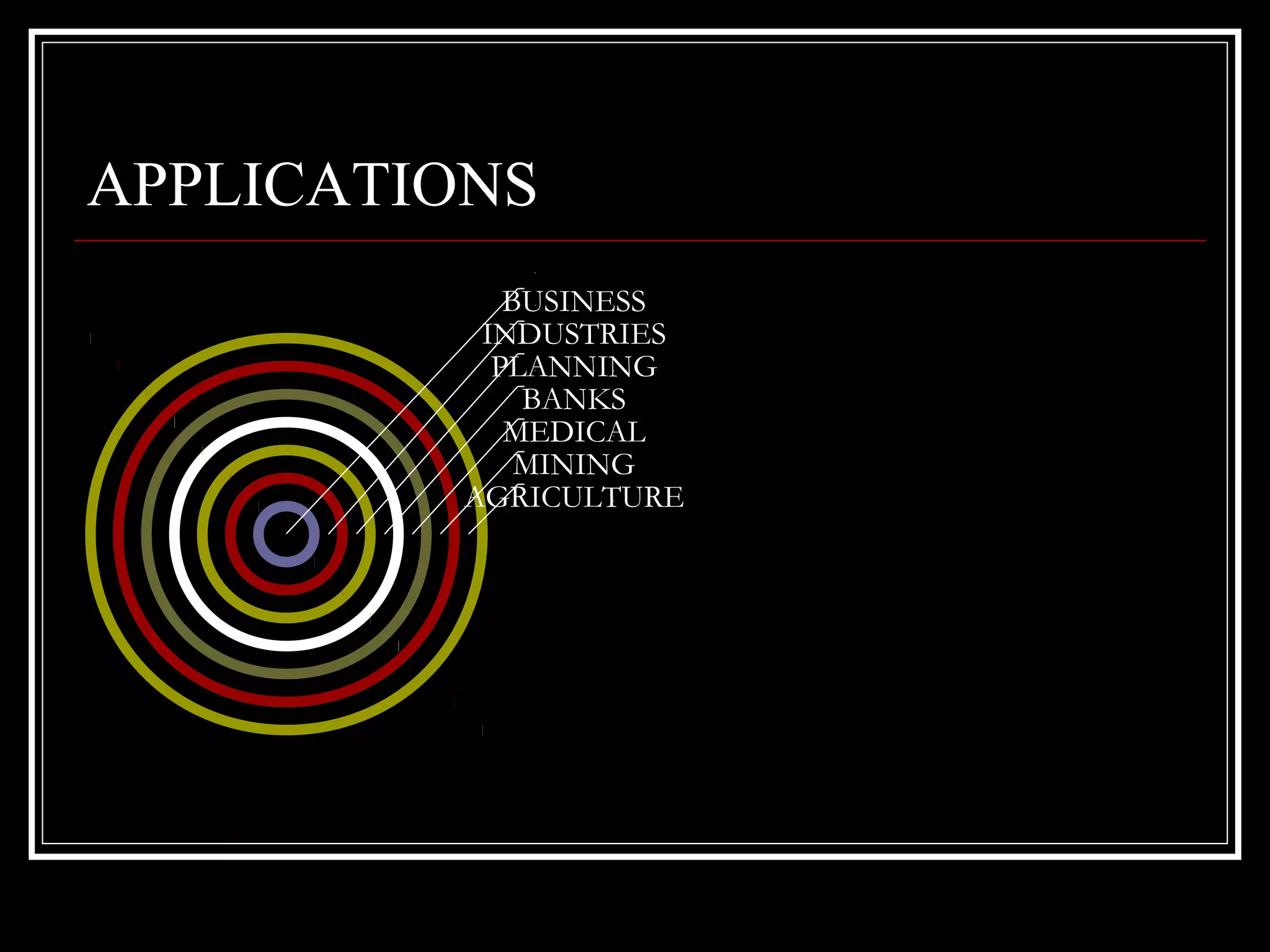
This document provides an overview of operational research techniques. It defines operational research as a scientific approach to problem solving for management. It describes several types of models used in operational research, including iconic, analogue, deterministic, symbolic, combined, heuristic, and probabilistic models. It also discusses common approaches and the significance of operational research for areas like profit maximization, cost minimization, and resource allocation. Specific techniques are outlined, such as linear programming, game theory, queuing theory, and the simplex method. Finally, potential applications and limitations of operational research are mentioned.