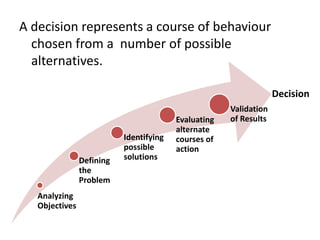
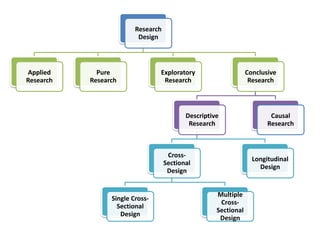
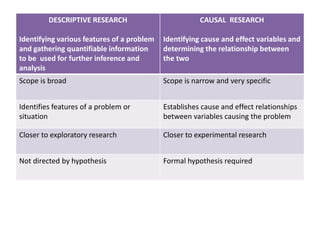
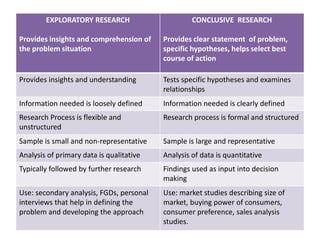
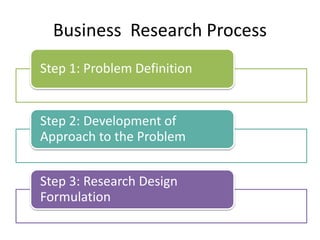
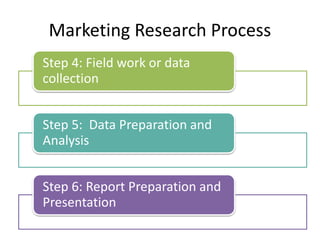
This document provides an overview of business research methodology. It defines research and its key features such as being systematic, objective, and aimed at discovering new information. The document outlines different types of research including exploratory research to gain insights, descriptive research to identify problem features, causal research to determine relationships, and conclusive research to test hypotheses. It also discusses research design approaches like cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Finally, it covers the significance and applications of research in business contexts like marketing, finance, production and human resources.