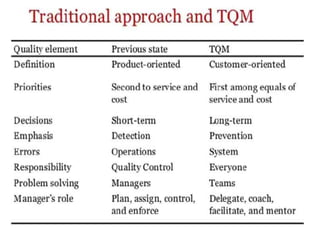
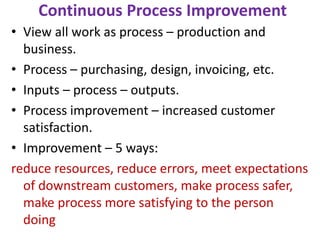
This document discusses key aspects of quality management in the pharmaceutical industry. It begins by defining quality management as a process that ensures quality throughout a product's lifecycle. It then outlines three main components: quality planning, quality control, and quality assurance. Quality planning involves setting goals and standards. Quality control inspects products for defects. Quality assurance reviews processes to prevent errors. The document also discusses quality improvement, total quality management (TQM), and principles of continuous improvement. TQM aims to achieve excellence through customer focus, employee involvement, and ongoing process refinement.