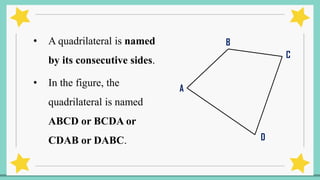
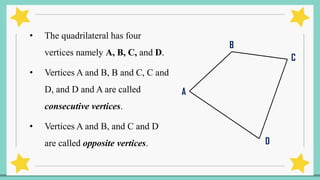
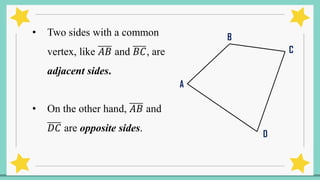
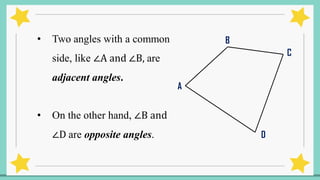
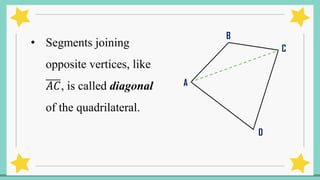
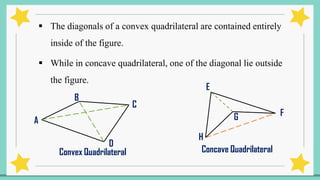
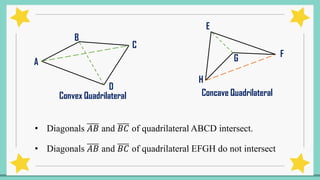
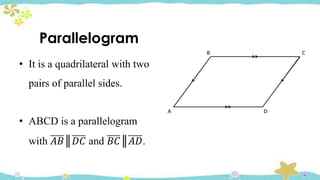
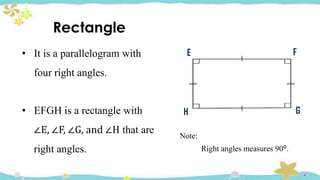
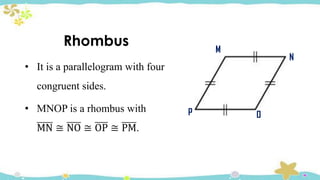
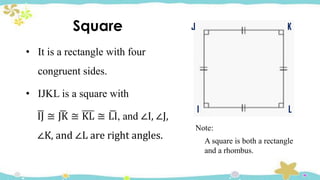
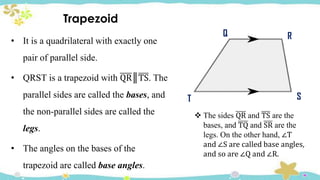
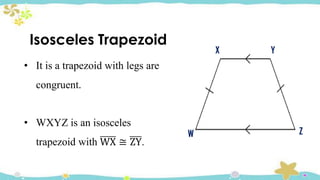
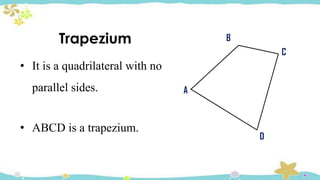
The document provides an introduction to quadrilaterals, defining them as polygons with four sides and describing their types, including parallelograms, rectangles, rhombuses, squares, trapezoids, isosceles trapezoids, and trapeziums. It explains key concepts such as vertices, sides, angles, and diagonals, as well as the properties that distinguish each type of quadrilateral. The material emphasizes the geometric relationships and classifications of quadrilaterals, suitable for learning mathematics.