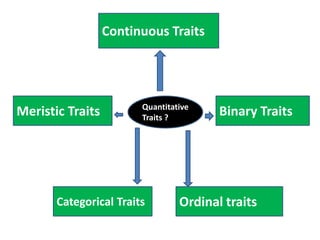
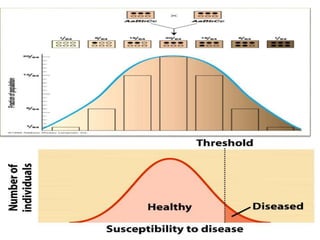
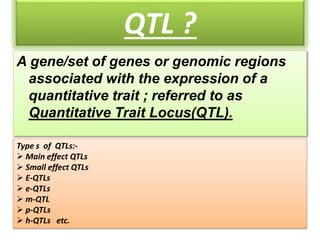
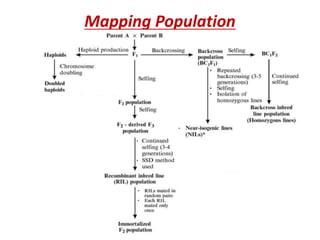
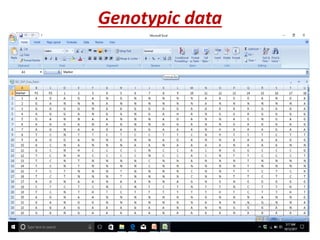
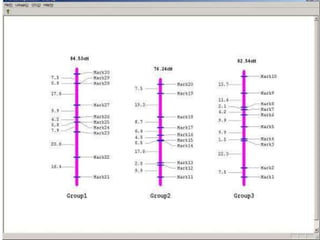
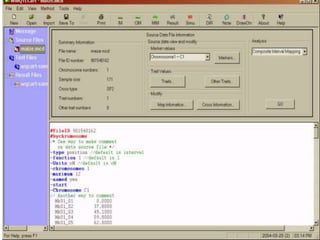
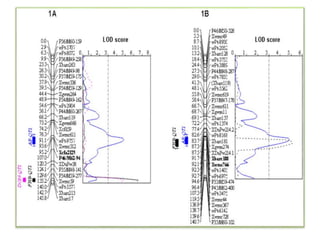
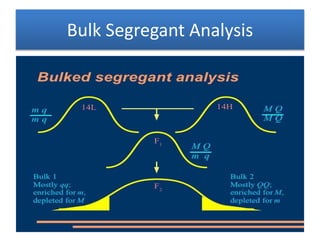
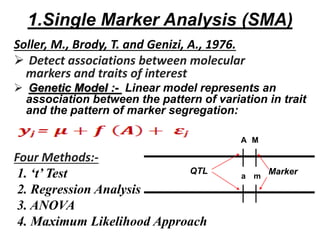
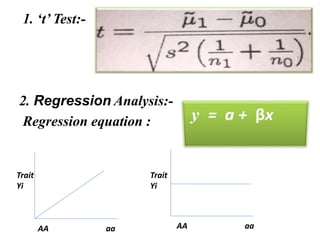
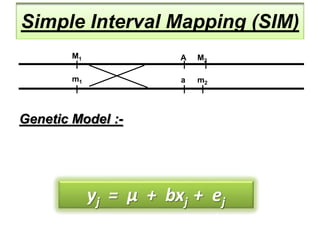
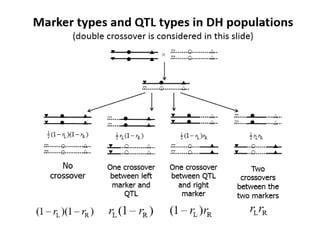
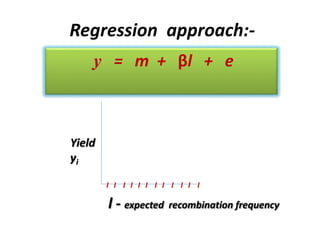
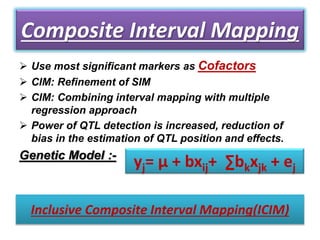
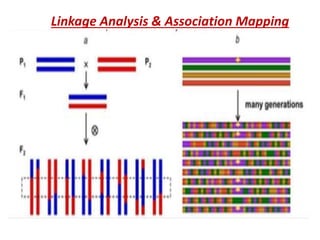
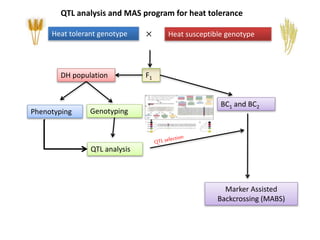
This document discusses QTL analysis for heat tolerance in wheat. It outlines the prerequisites for QTL analysis, which include a mapping population, phenotypic data, genotypic data, and a marker linkage map. Several methods for QTL analysis are described, including single marker analysis, interval mapping approaches like composite interval mapping, and association mapping. The document also provides details on using QTL analysis and marker-assisted selection to develop wheat varieties with improved heat tolerance.