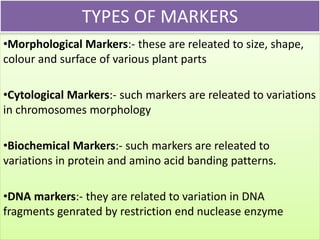
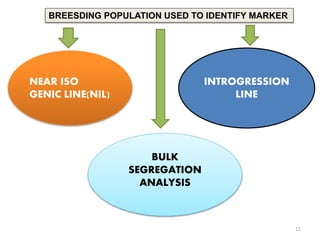
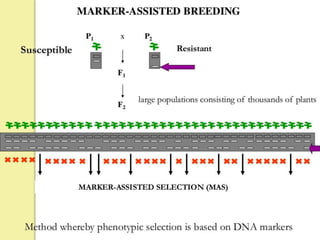
This presentation discusses marker assisted selection (MAS), a method for indirect plant breeding selection. MAS uses molecular markers linked to traits of interest, like disease resistance or yield, to select plants without observing the trait itself. The presentation defines MAS and different types of molecular markers like RFLPs, SSLPs, AFLPs. It outlines the steps of MAS, including selecting parents, developing breeding populations, isolating DNA, scoring markers, and correlating markers with traits. Benefits of MAS include high accuracy, allowing selection of traits affected by environment. Examples of using MAS in crops like barley, maize, rice and wheat are also provided.