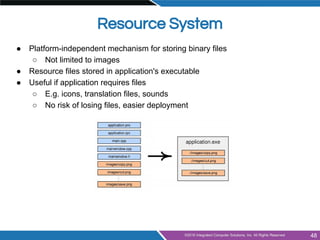
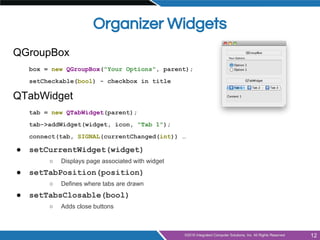
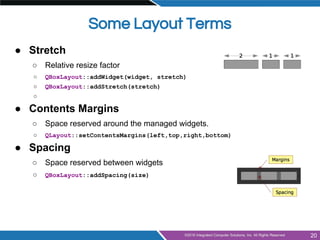
The document provides an overview of widgets in Qt, including:
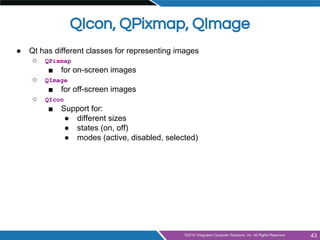
- Common widgets like labels, buttons, text inputs, sliders and organizers
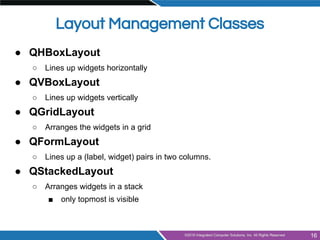
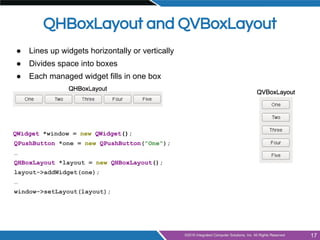
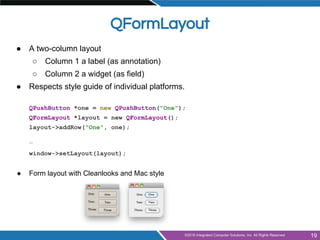
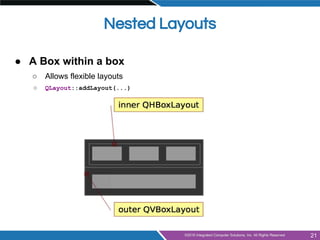
- Layout management using horizontal, vertical, grid and form layouts
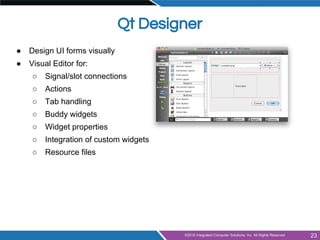
- Using Qt Designer for visually designing user interfaces
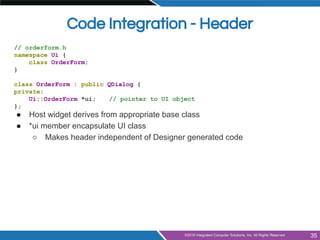
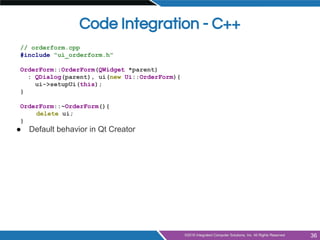
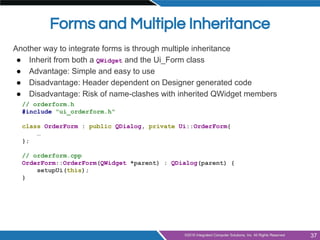
- Integrating designer forms into code using generated header and class files
- Creating common dialogs like file selection, messages and progress
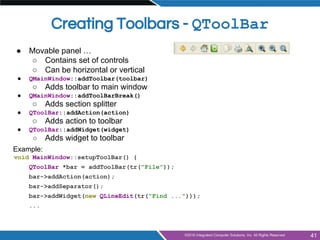
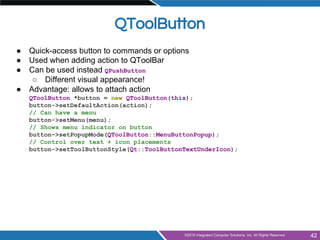
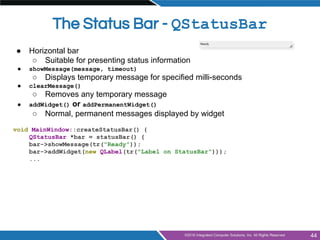
- Building applications with main windows, menus, toolbars, dock widgets and status bars





















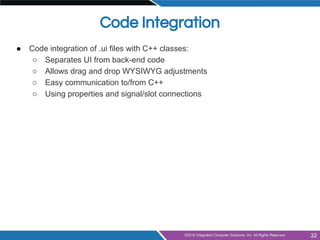

![From .ui to C++
34
OrderForm.ui
saves to
uic
Qt Designer
or
Design Mode in Qt Creator
class Ui_OrderForm { public:
QVBoxLayout *verticalLayout;
QLineEdit *lineEdit;
QDoubleSpinBox *doubleSpinBox;
QSpinBox *spinBox;
[...]
#include "orderform.h"
#include "ui_orderform.h"
OrderForm::OrderForm(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::OrderForm)
{ ui->setupUi(this);}
OrderForm::~OrderForm()
{ delete ui; }
produces
orderform.h
ui_orderform.
h
orderform.cpp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtforbeginnerspart2-widgets-160505195145/85/Qt-for-beginners-part-2-widgets-34-320.jpg)