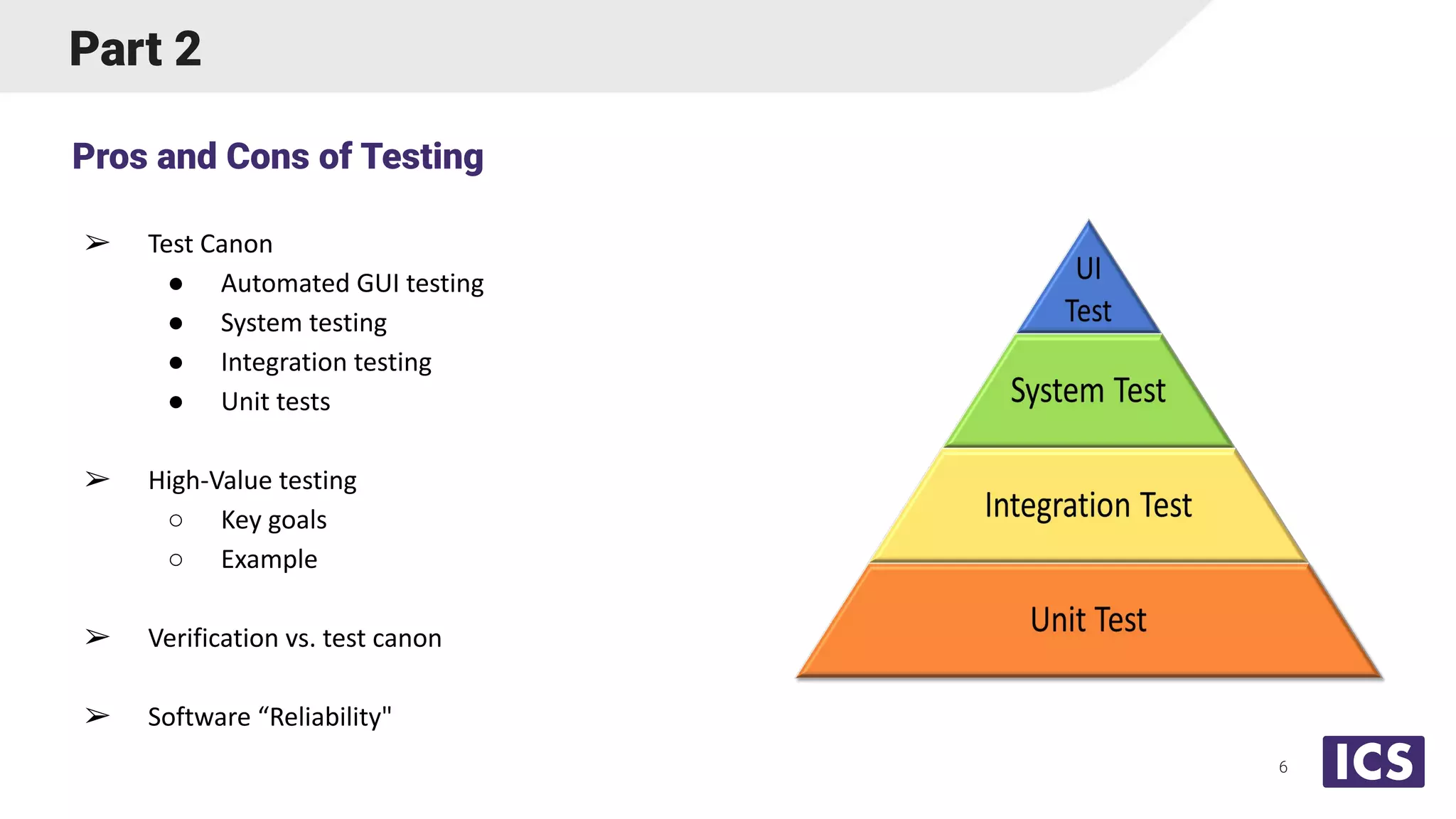
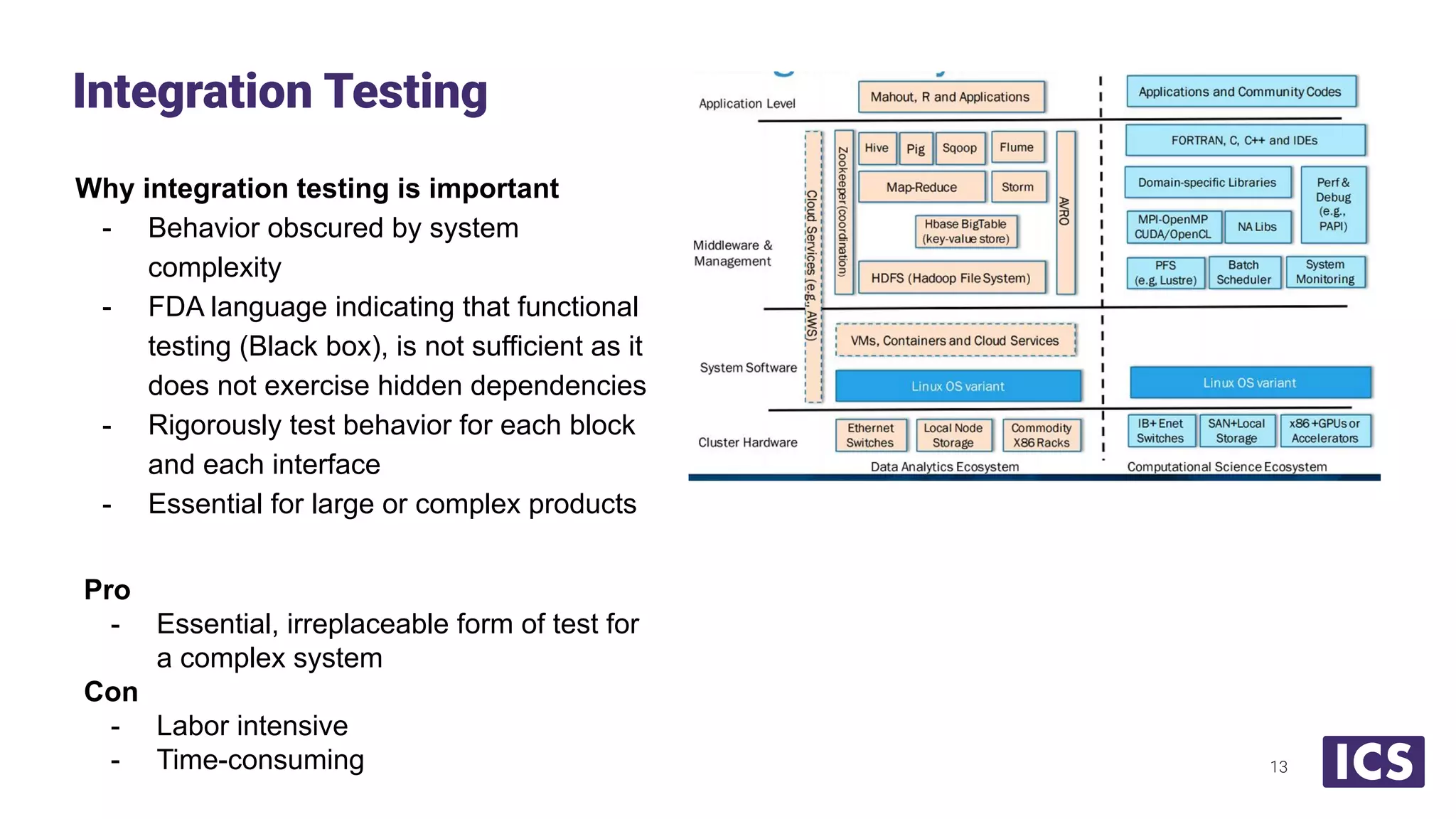
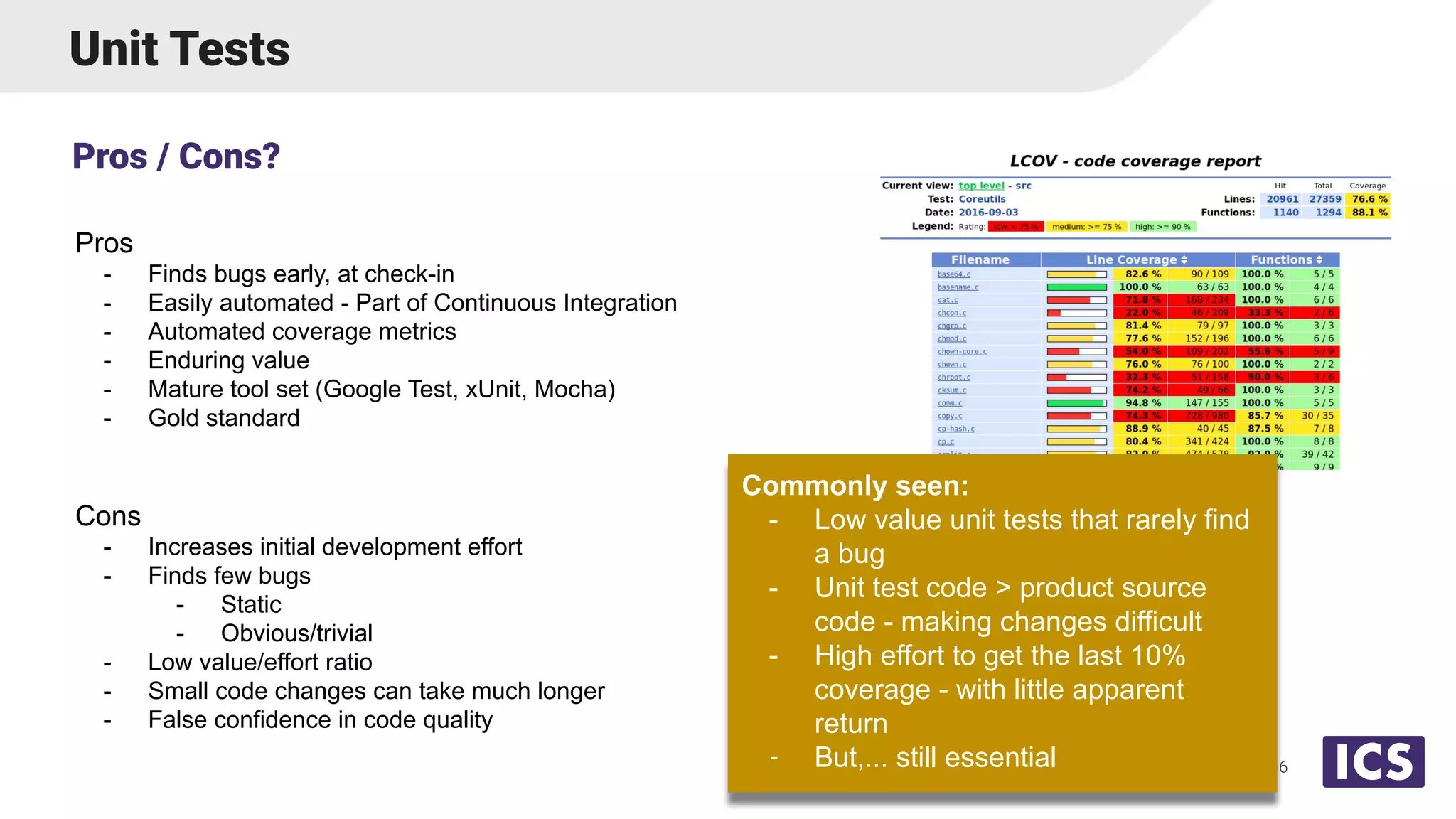
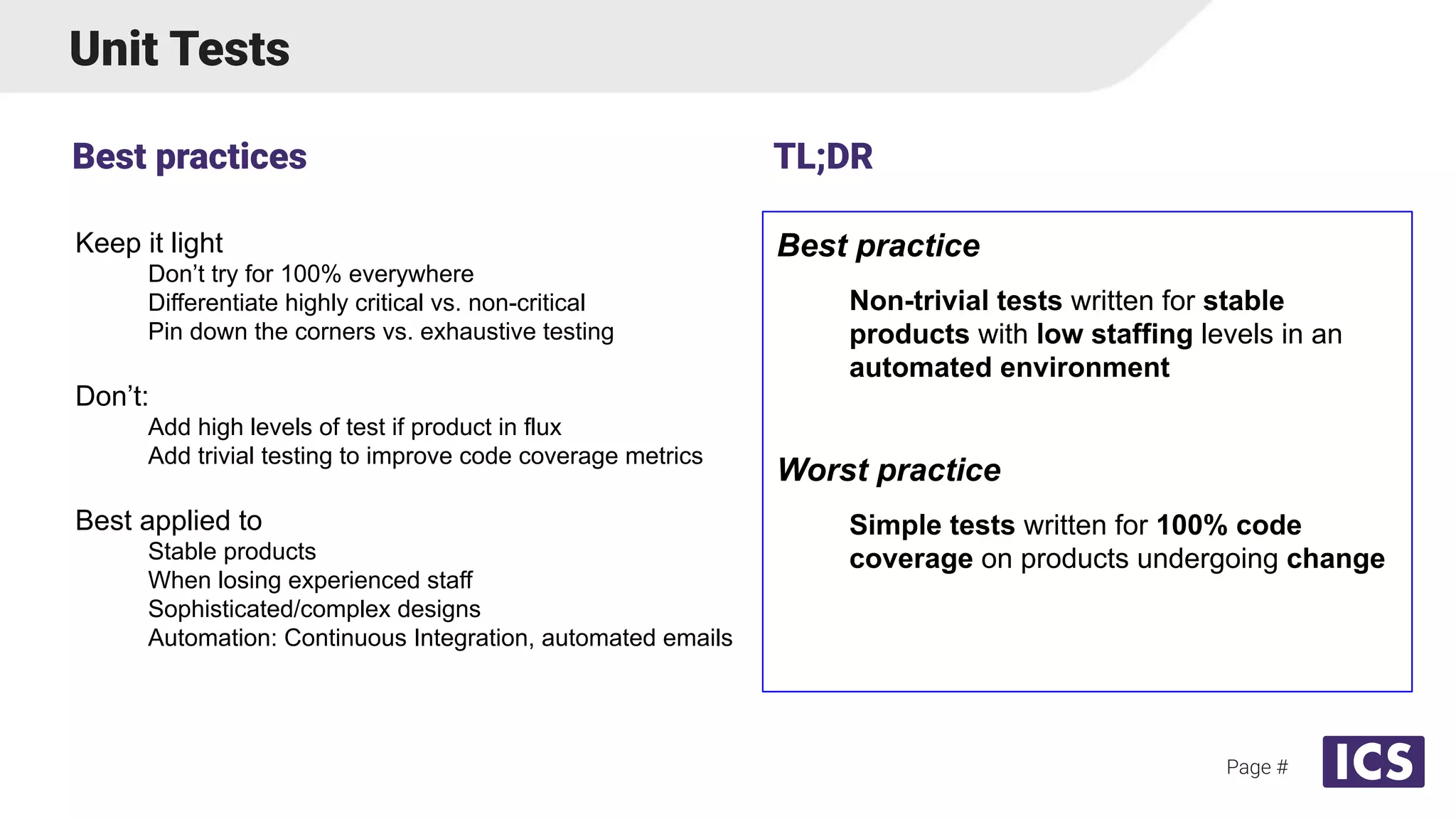
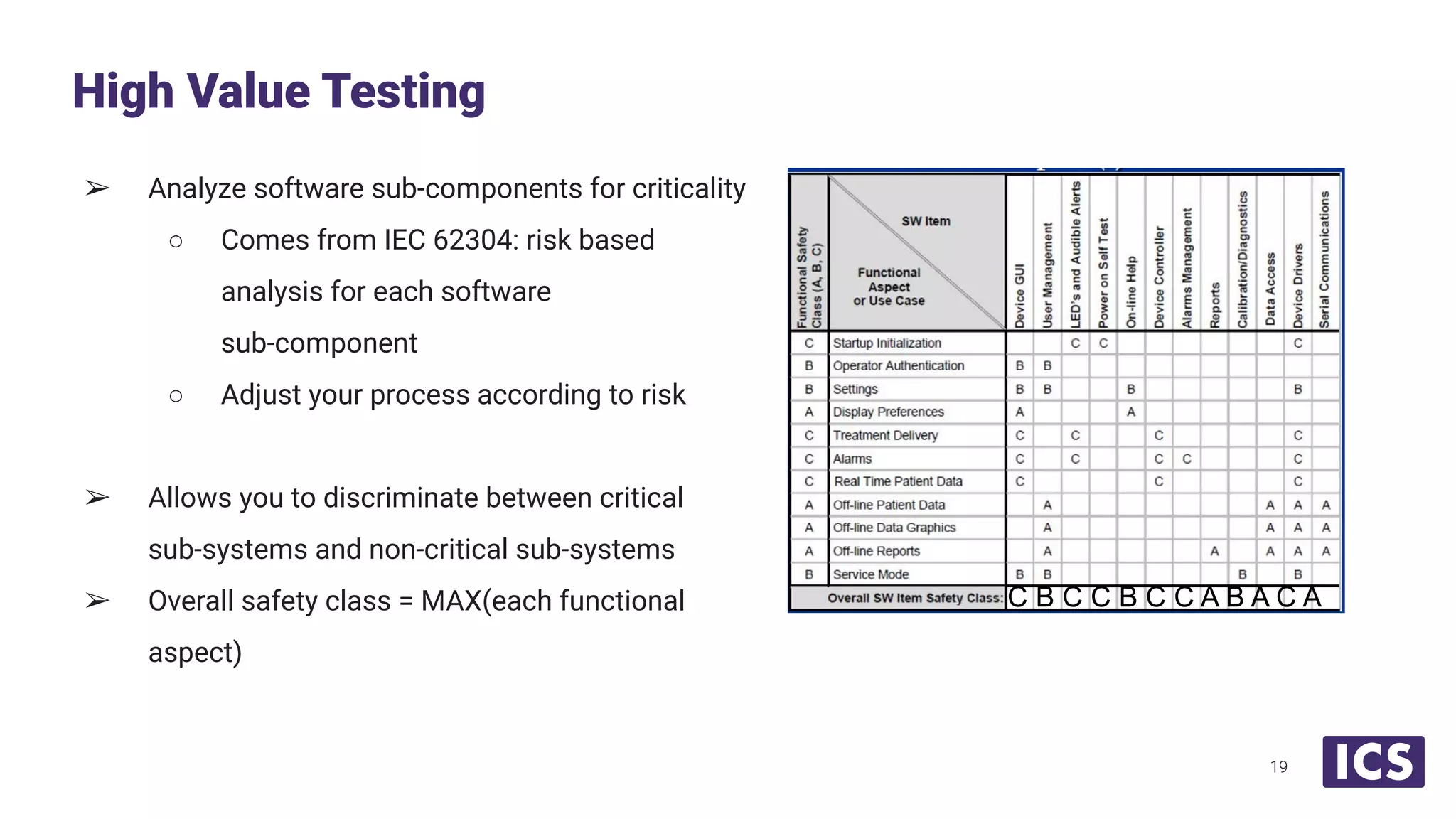
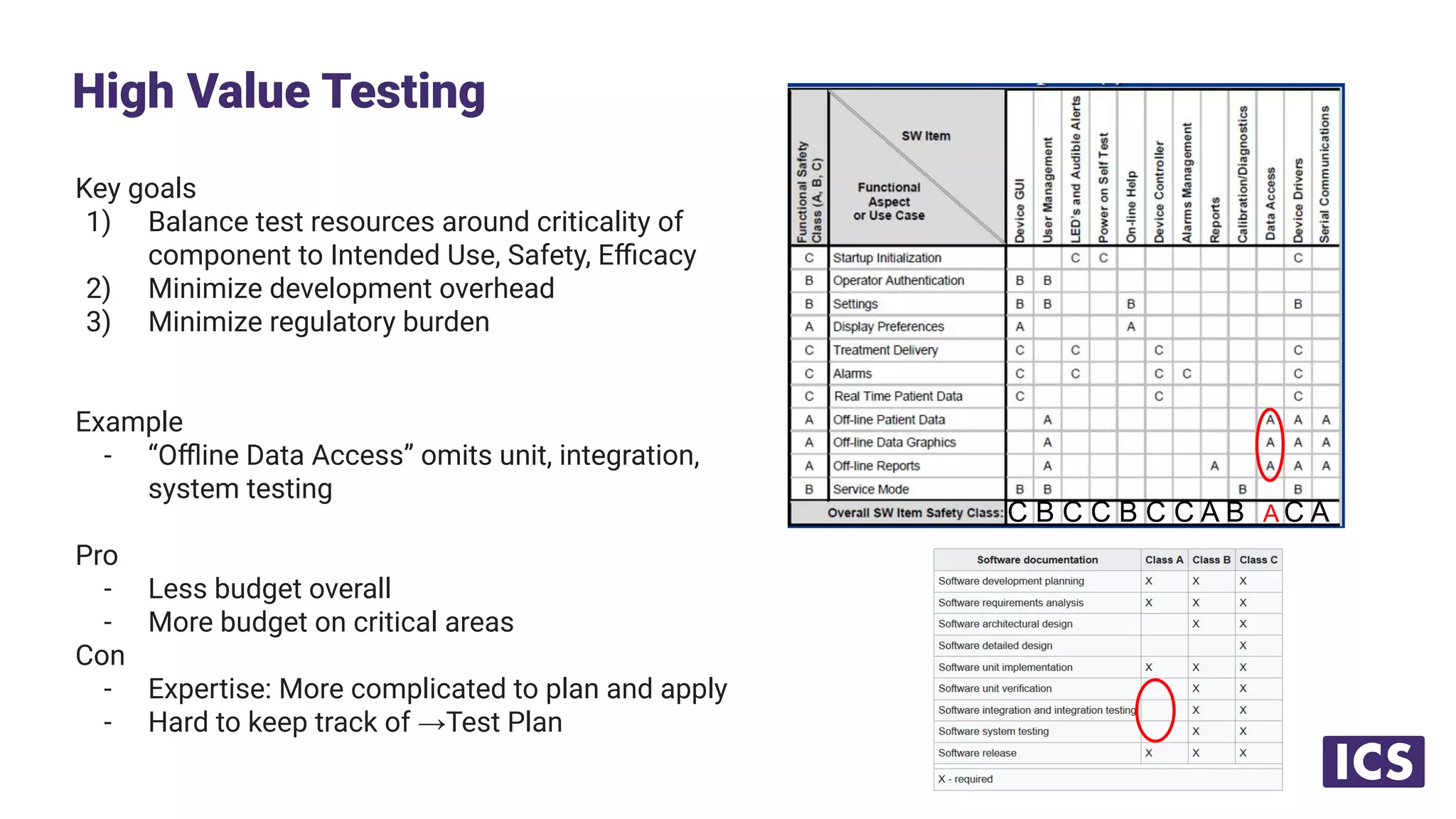
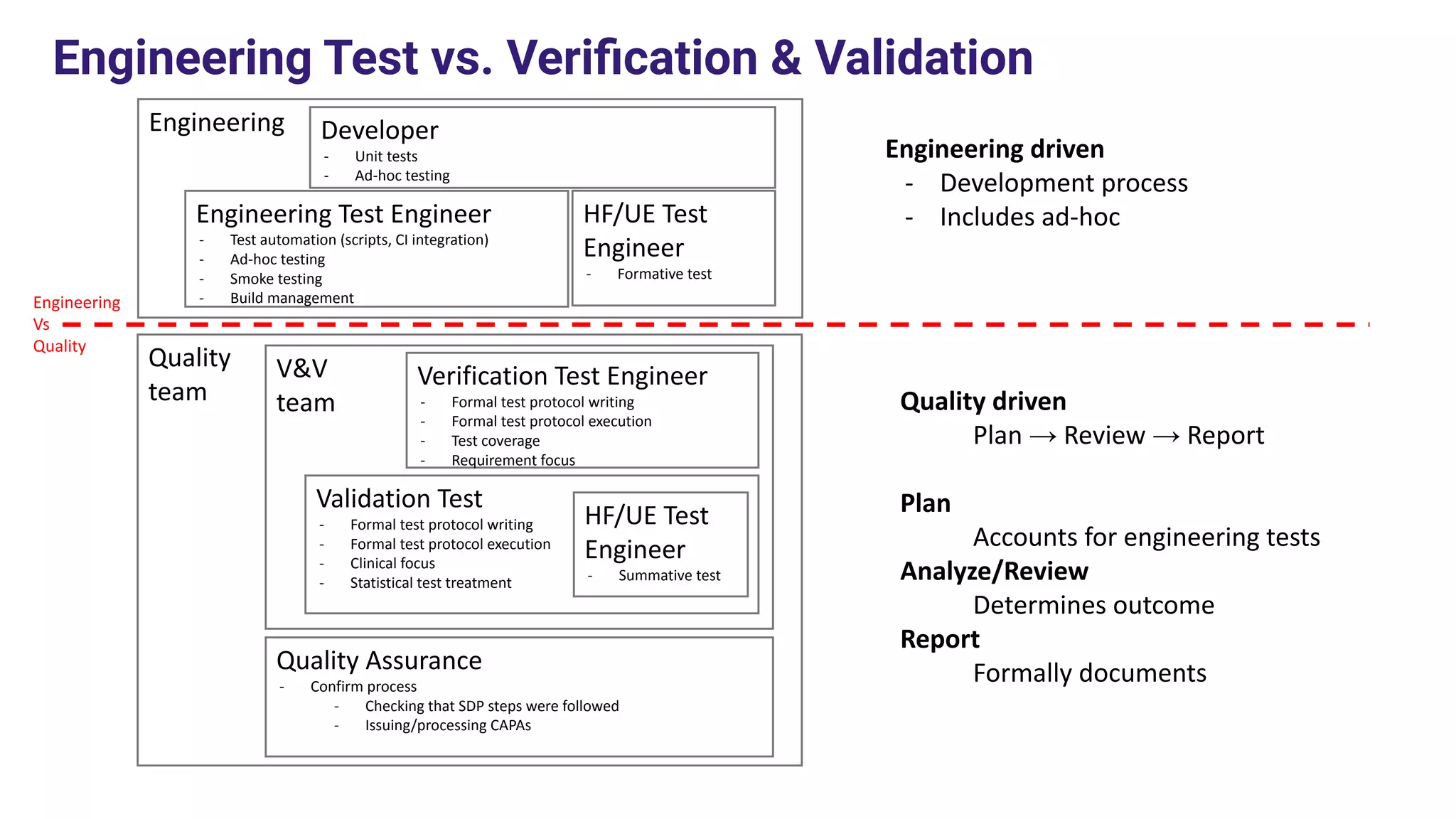
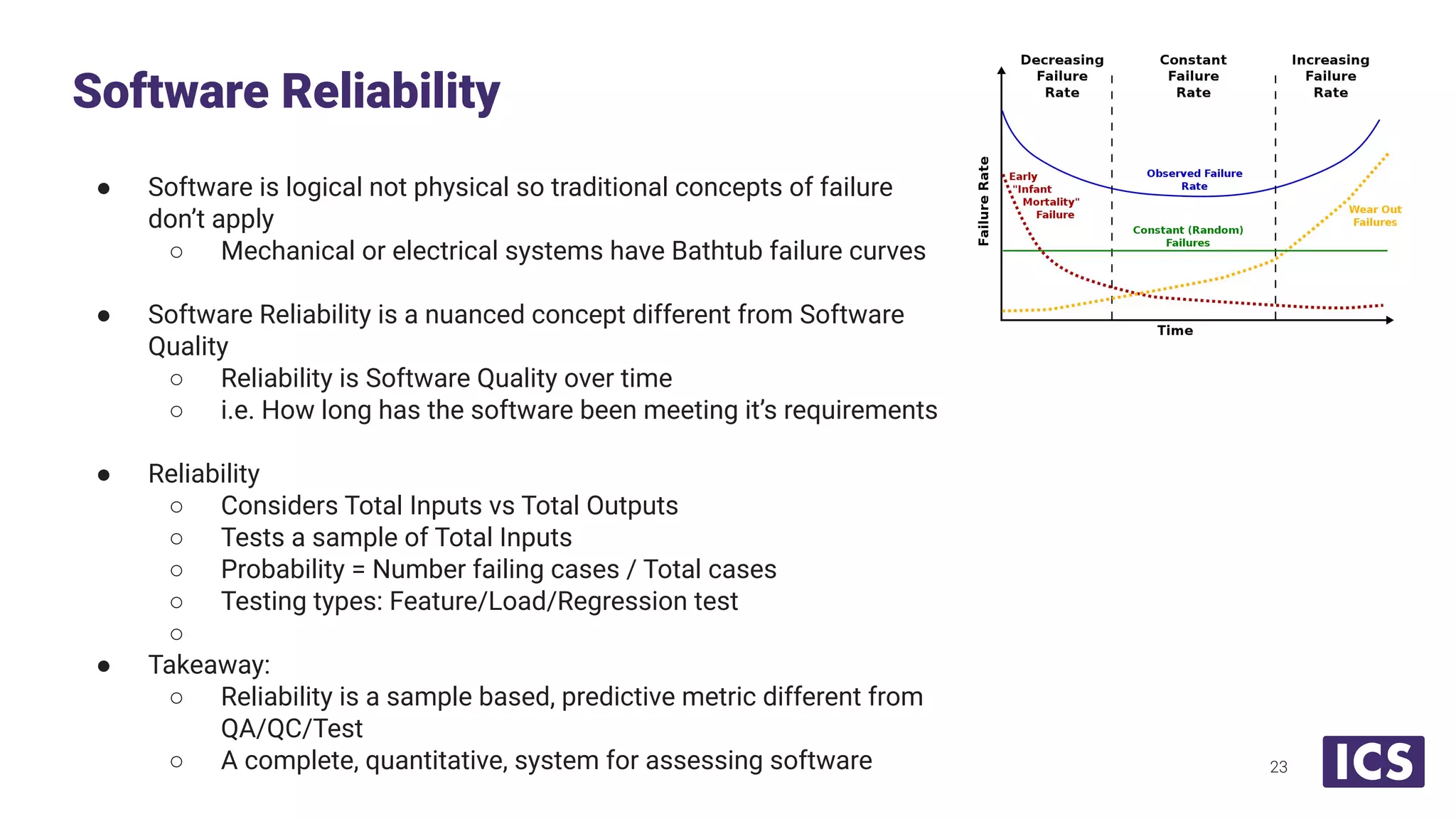
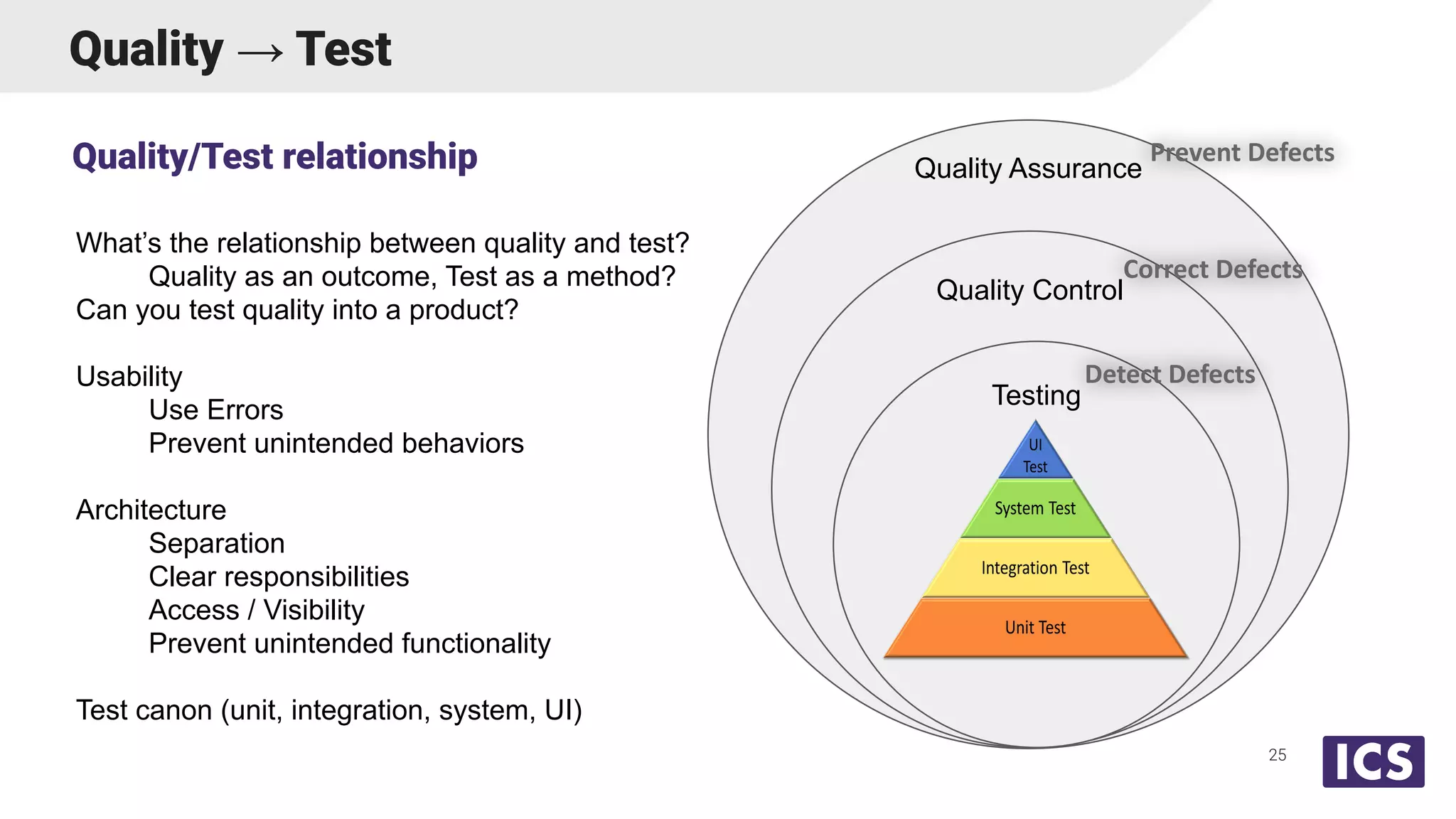
Integrated Computer Solutions, Inc. (ICS), established in 1987, specializes in software solutions for medical technology with services including software development, usability testing, and cybersecurity. The document discusses various testing methodologies such as automated testing, unit testing, and integration testing, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses while emphasizing a risk-based approach to quality assurance. It also outlines the distinct roles within quality and testing teams, ultimately underscoring the difference between software reliability and traditional quality concepts.