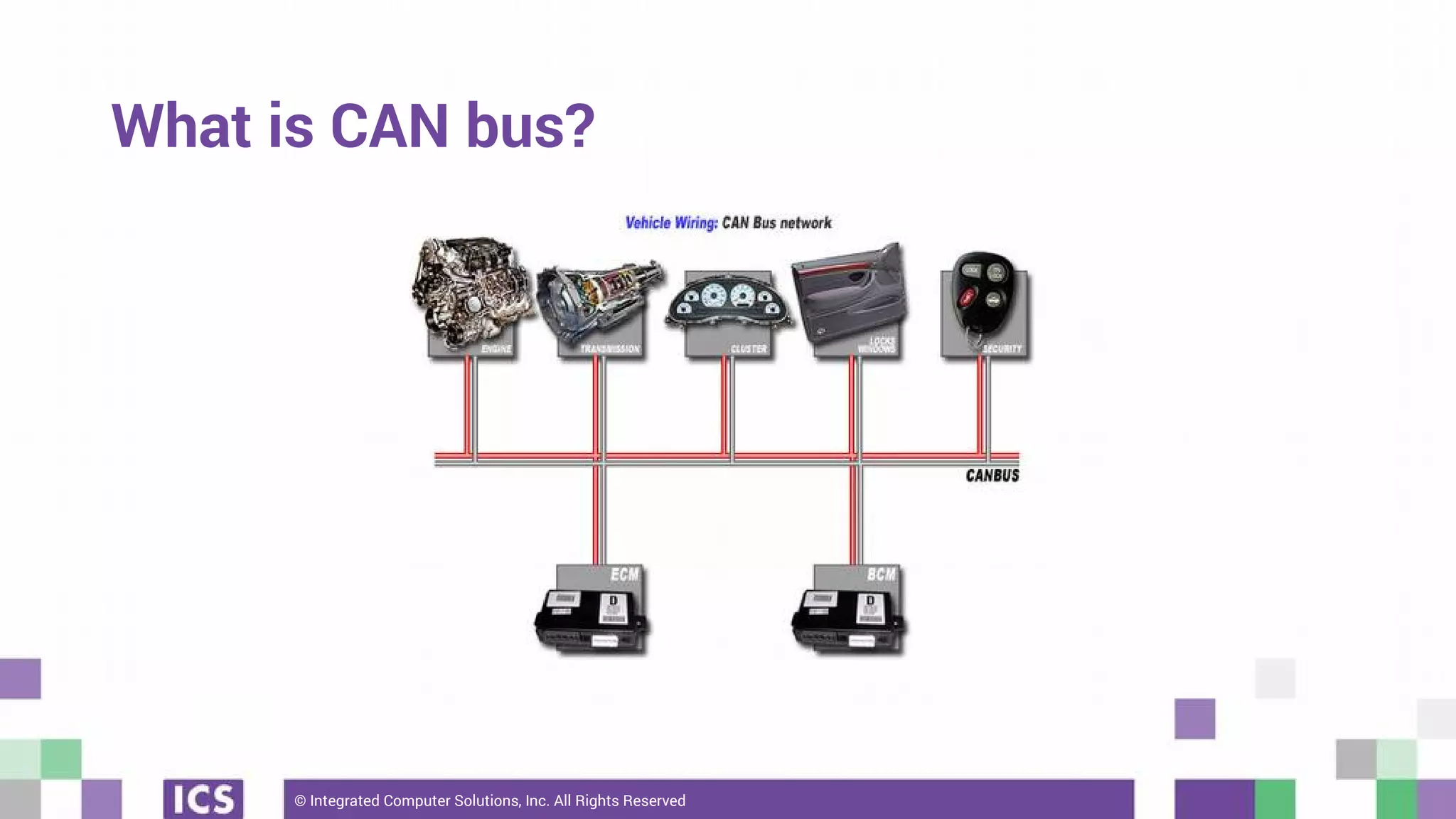
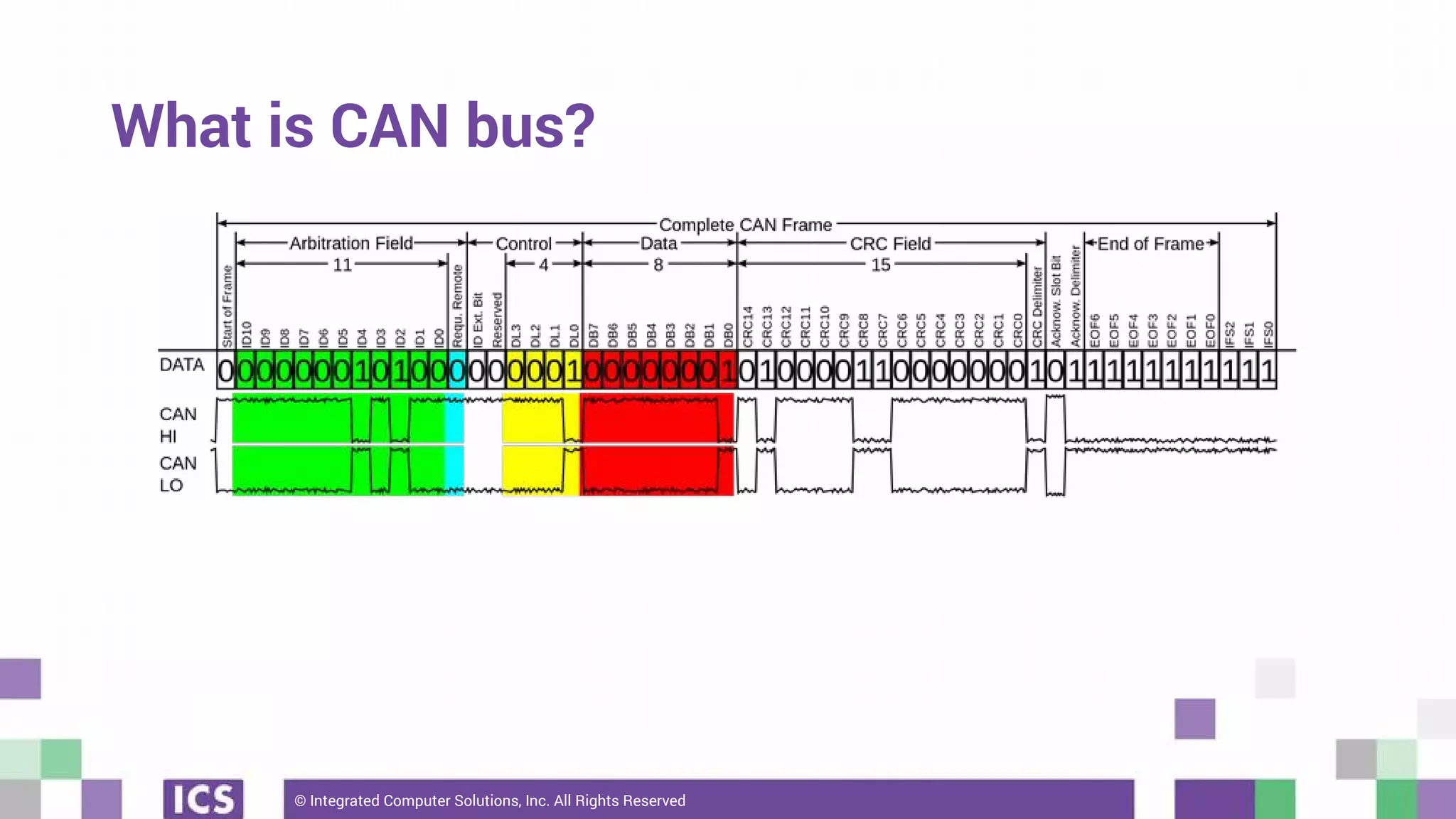
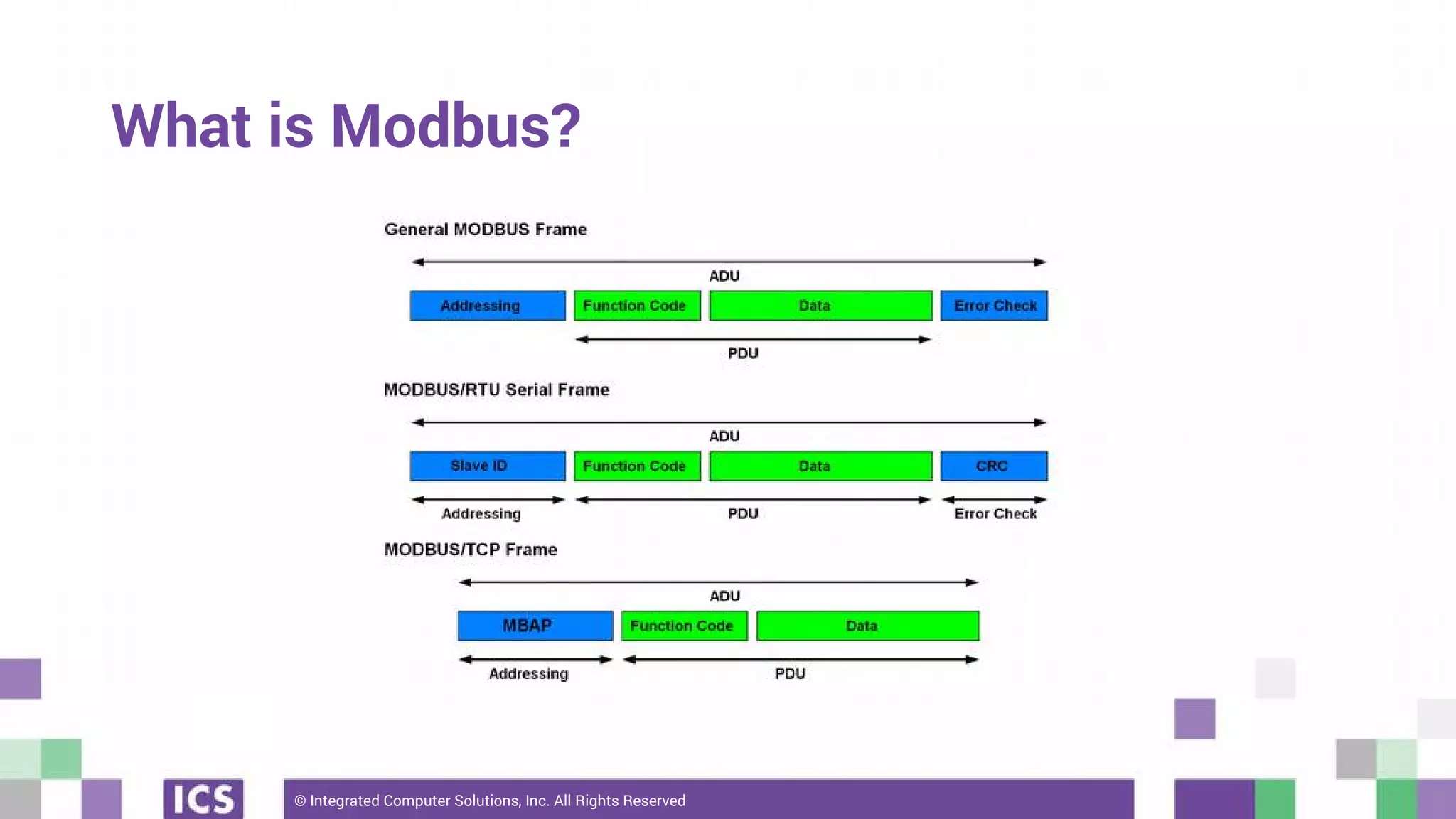
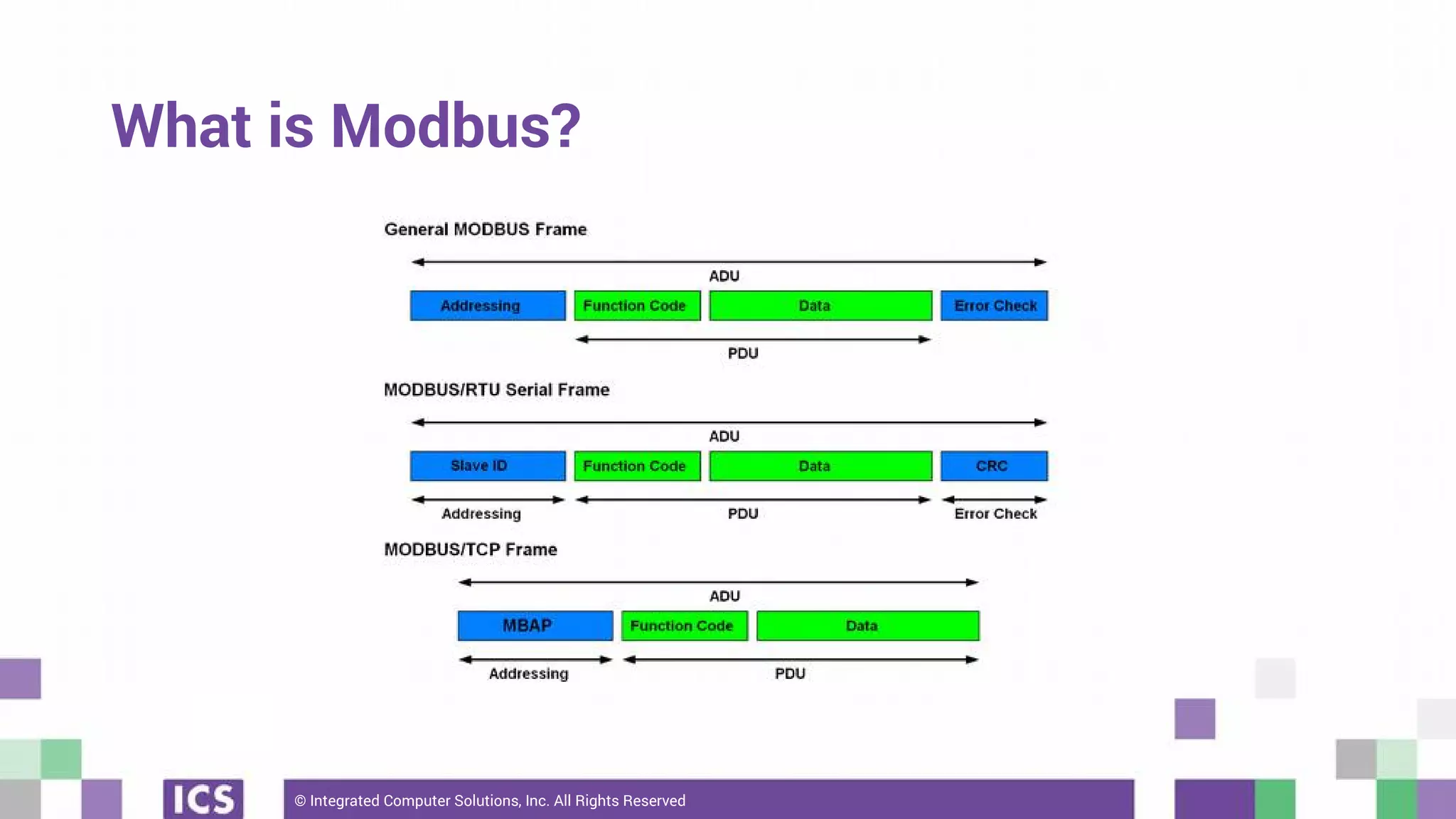
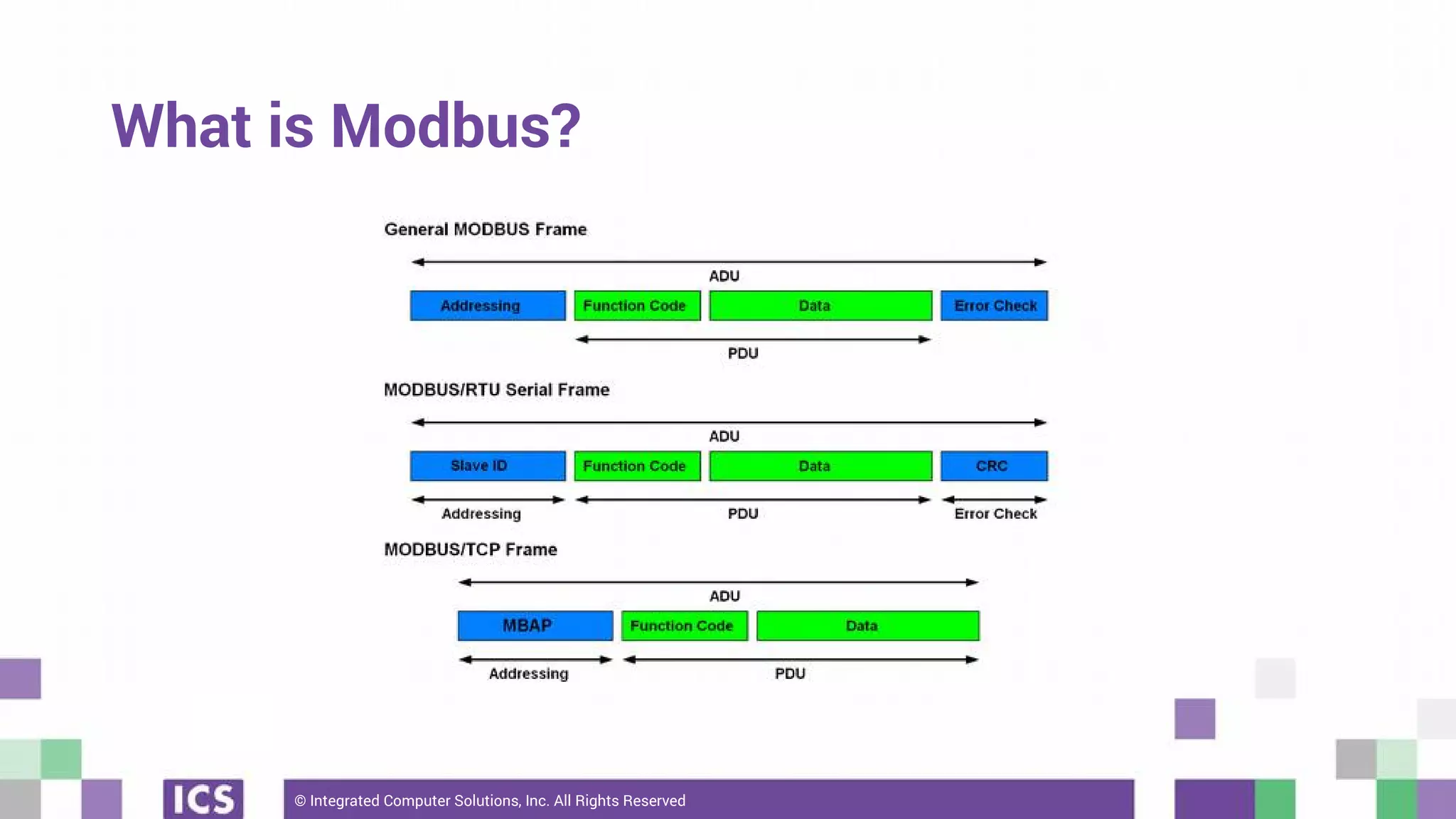
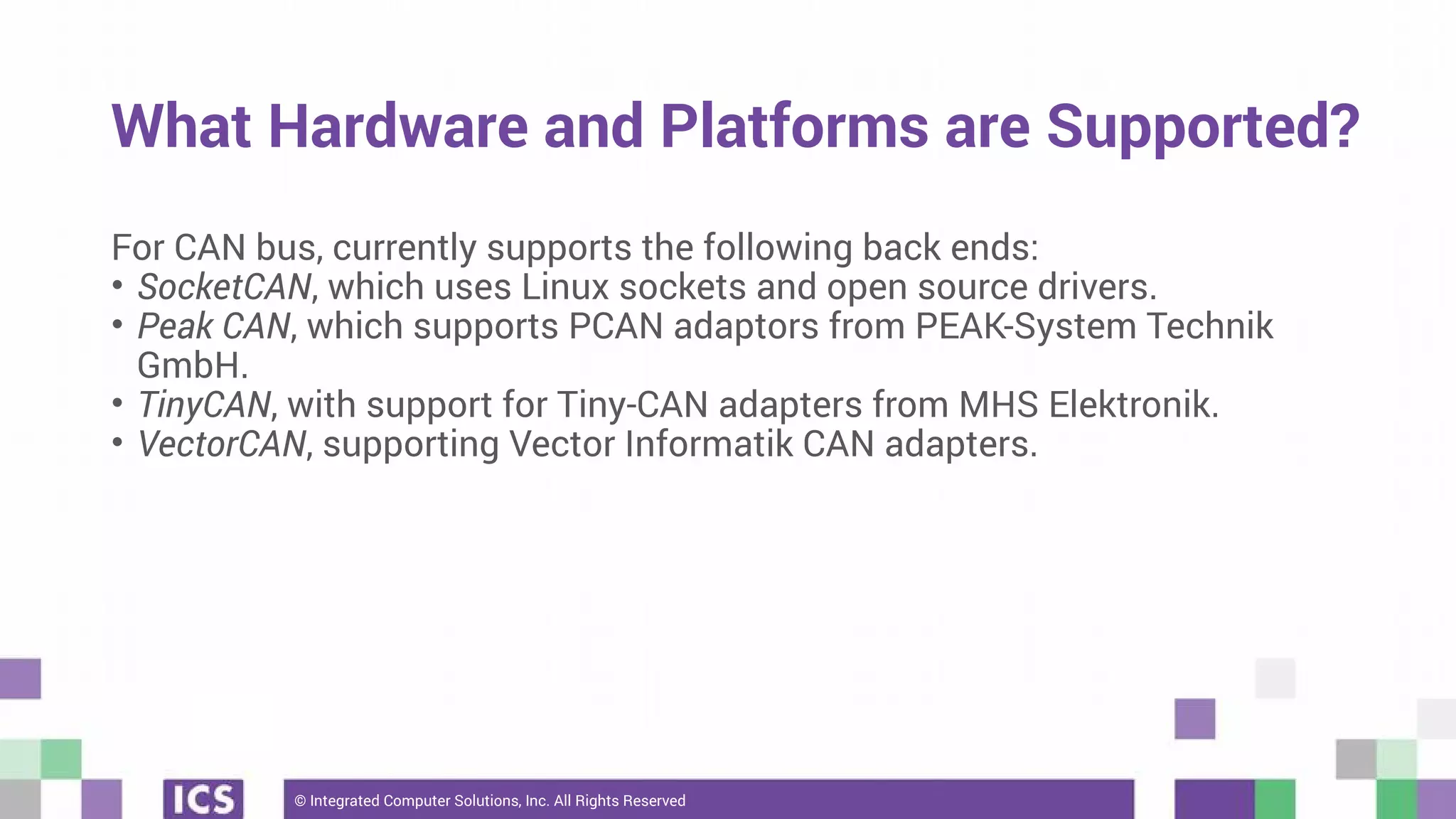
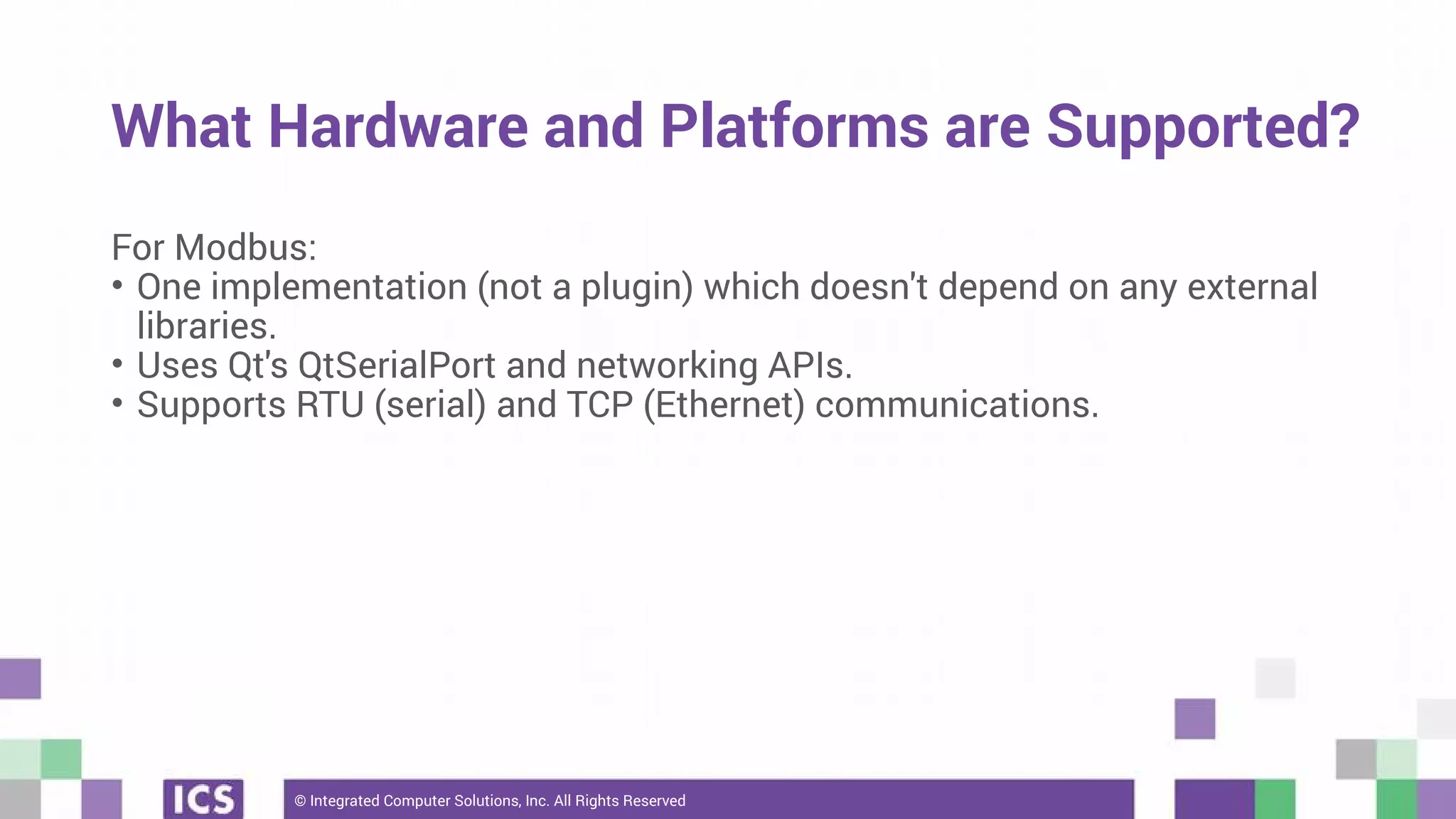
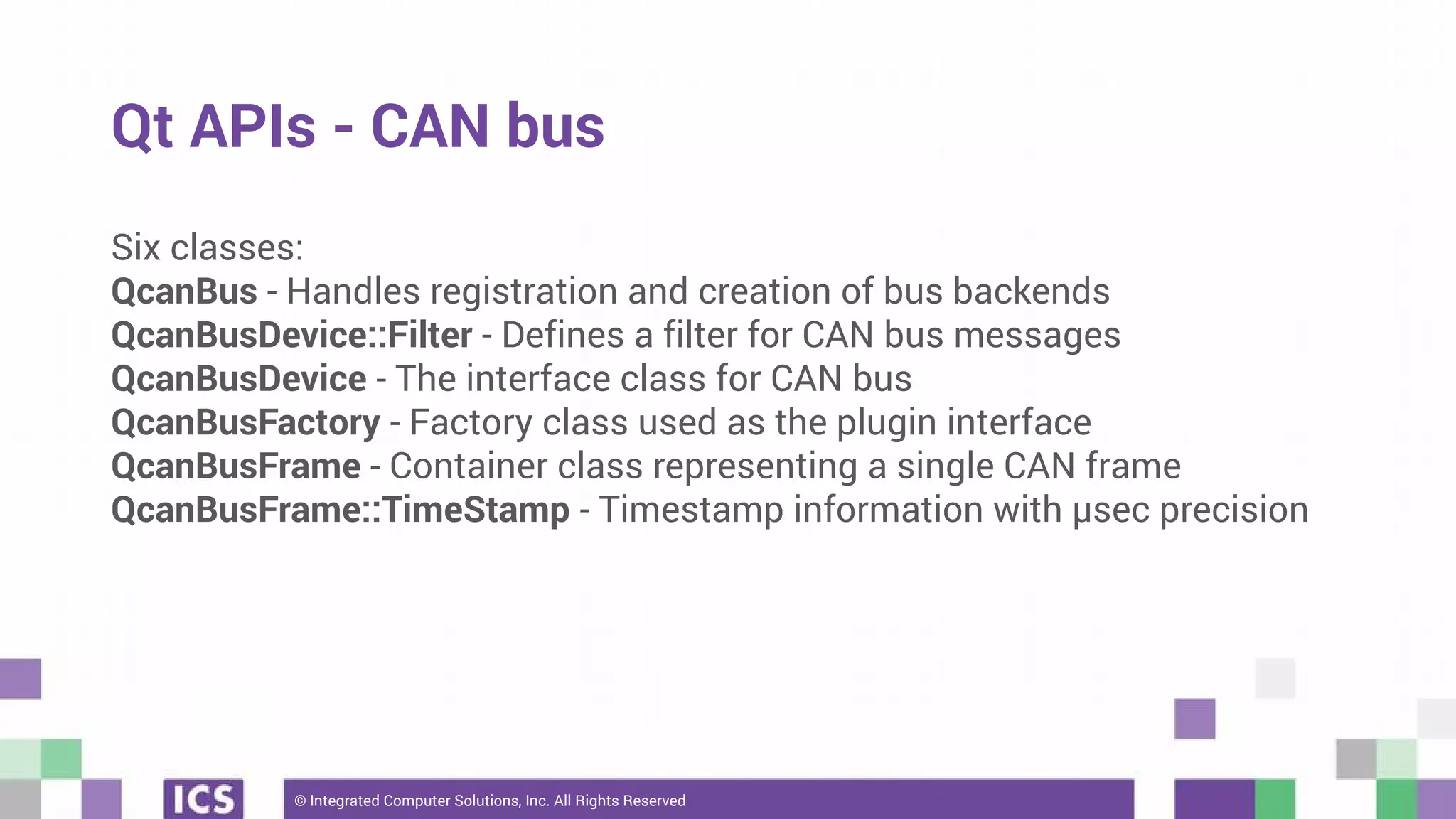
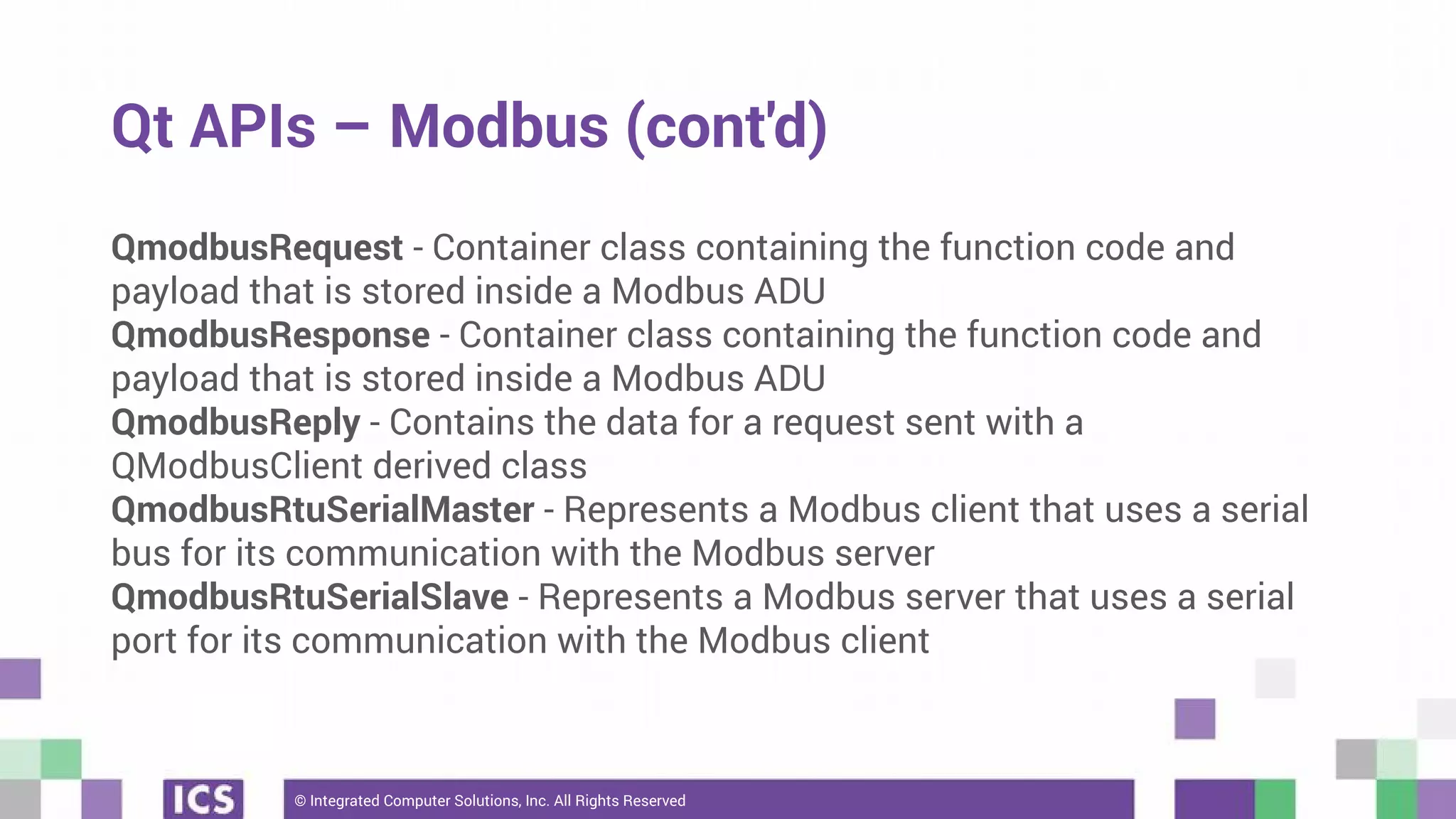
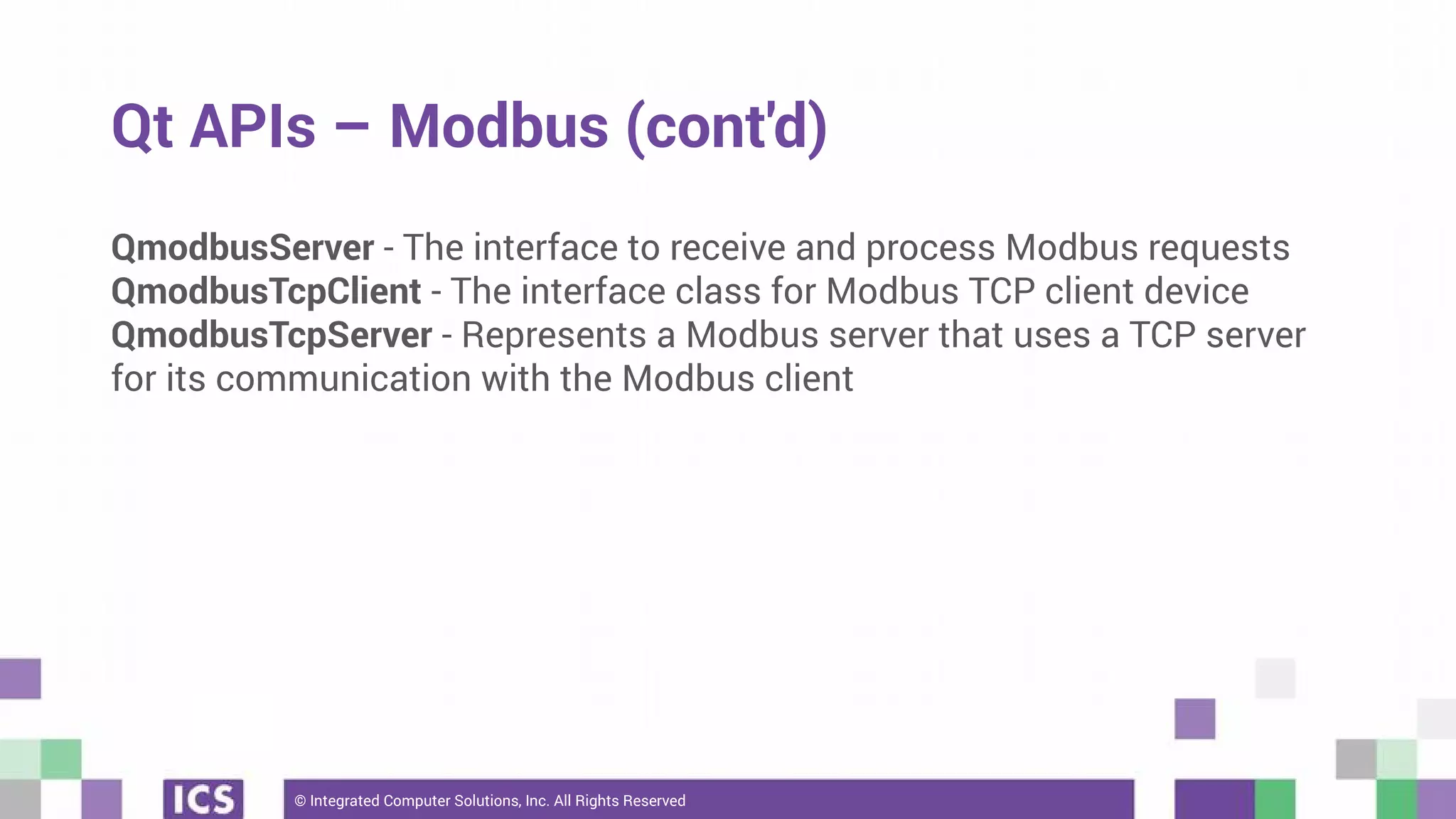
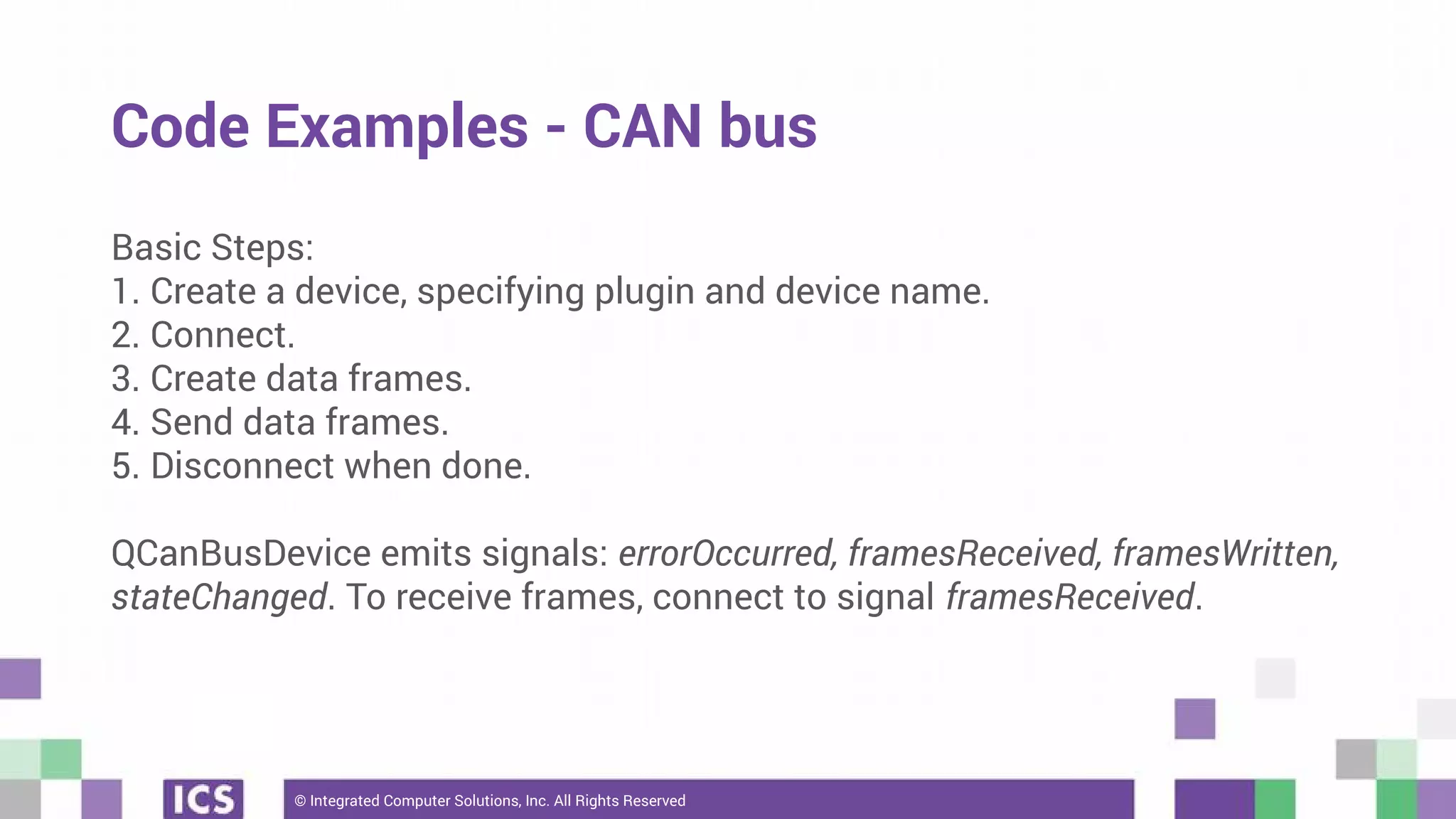
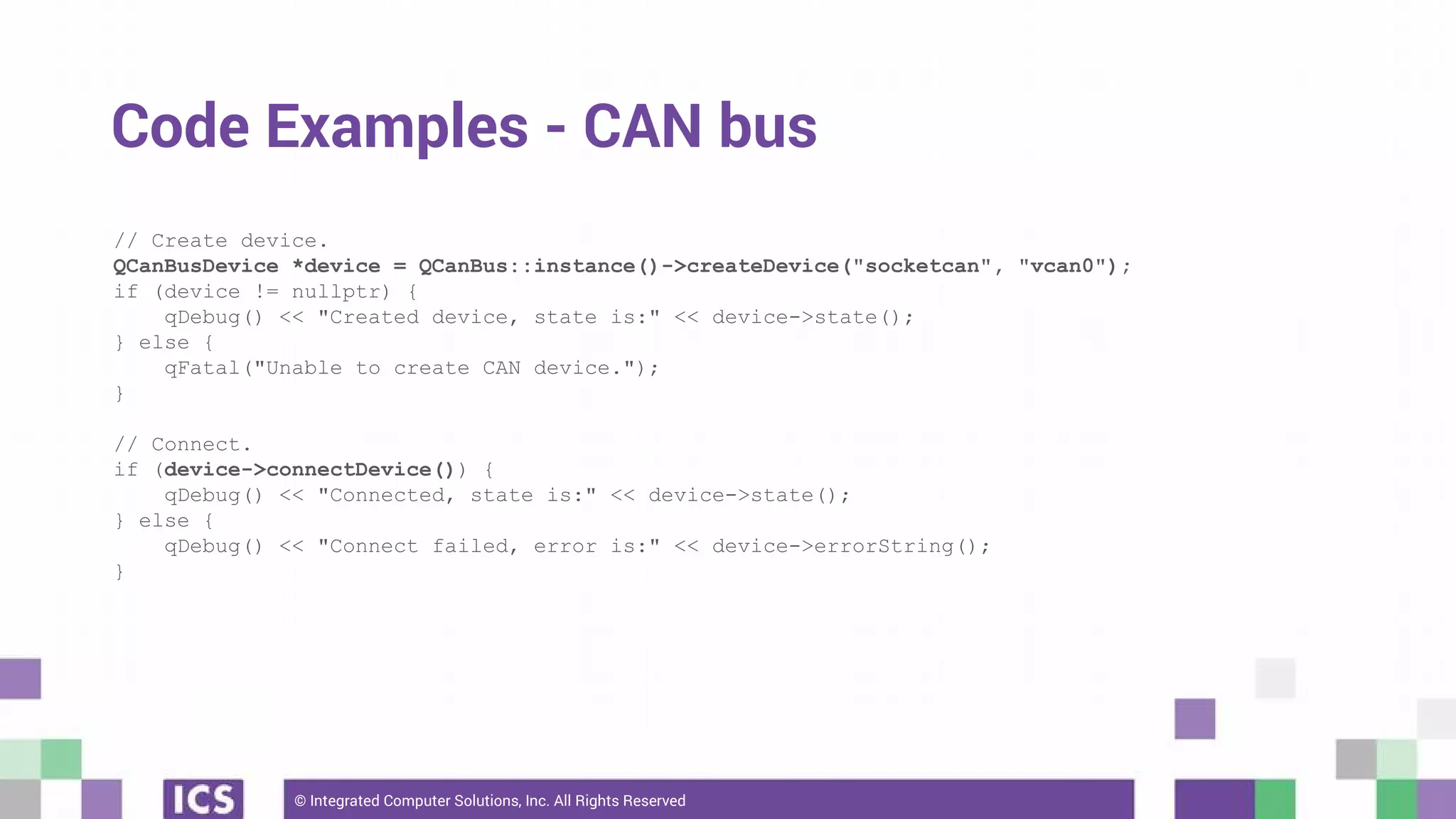
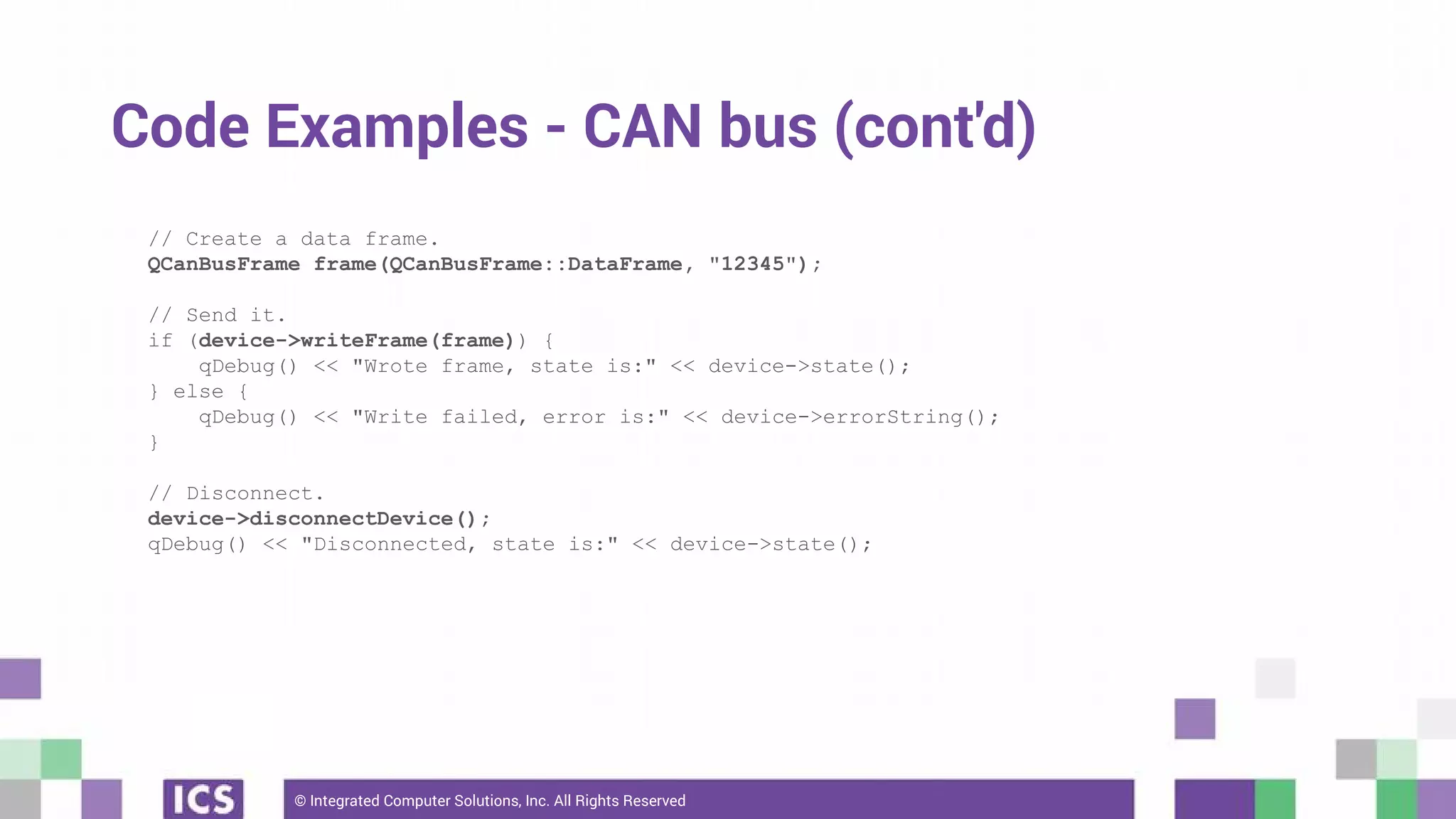
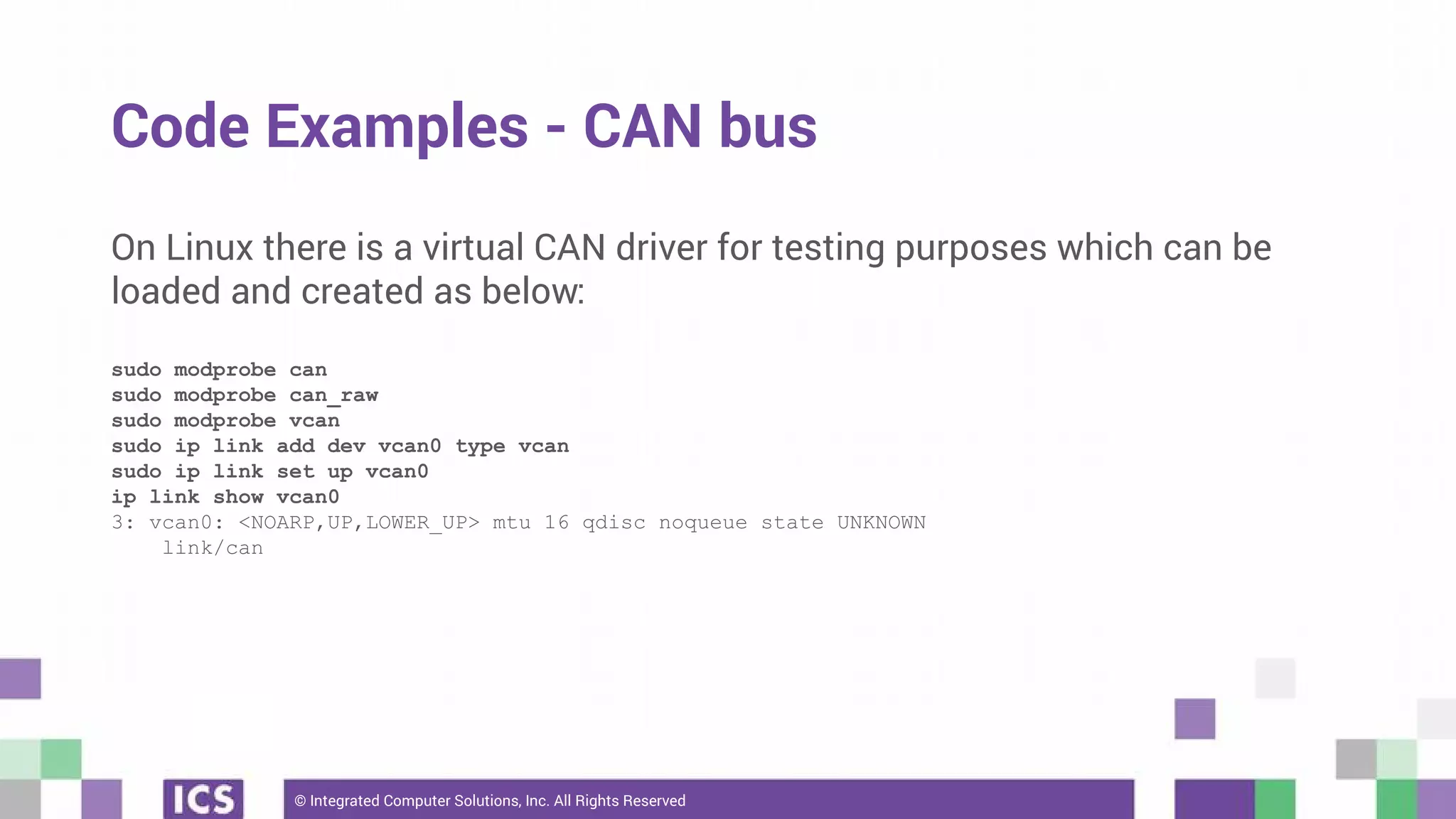
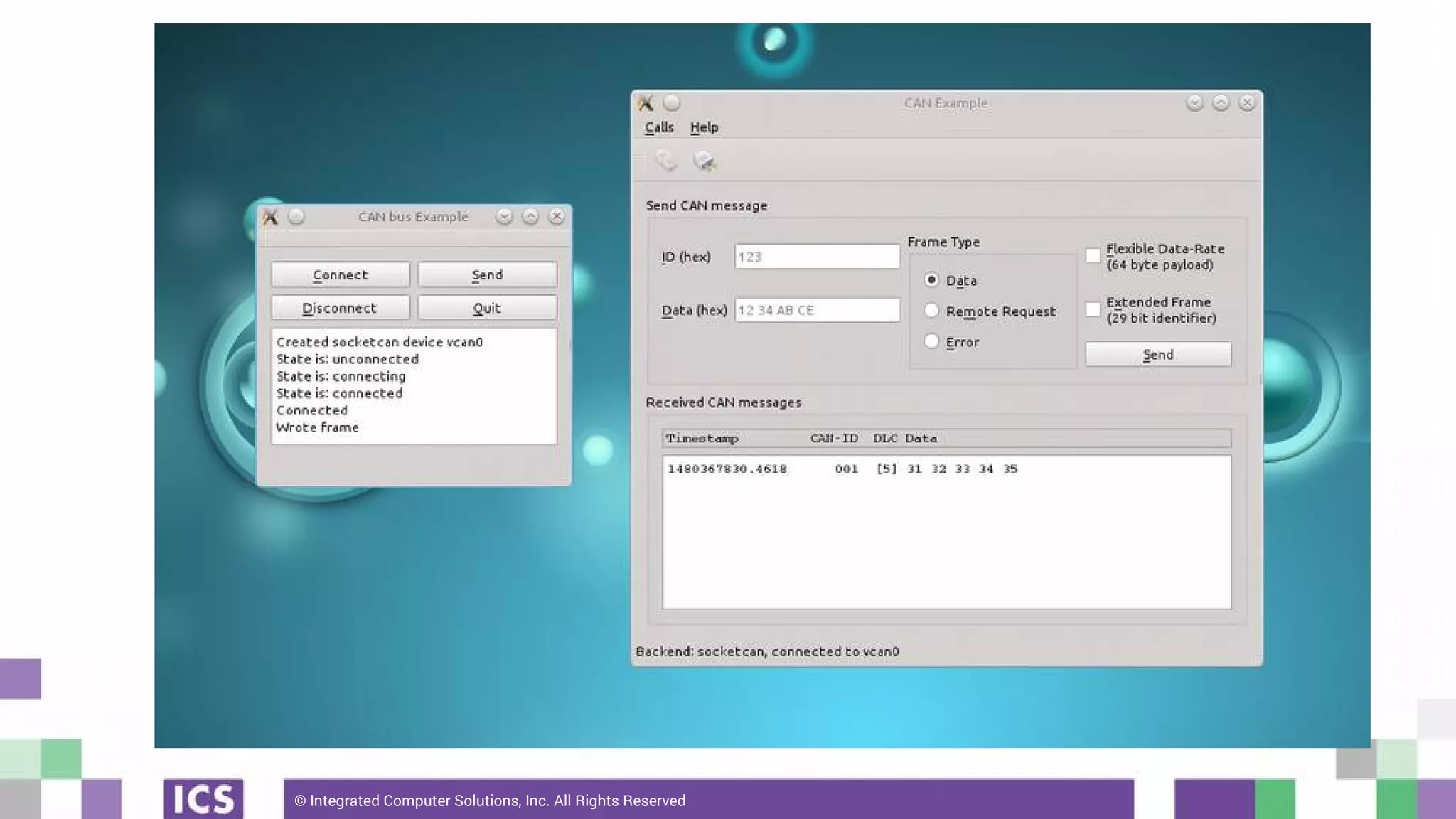
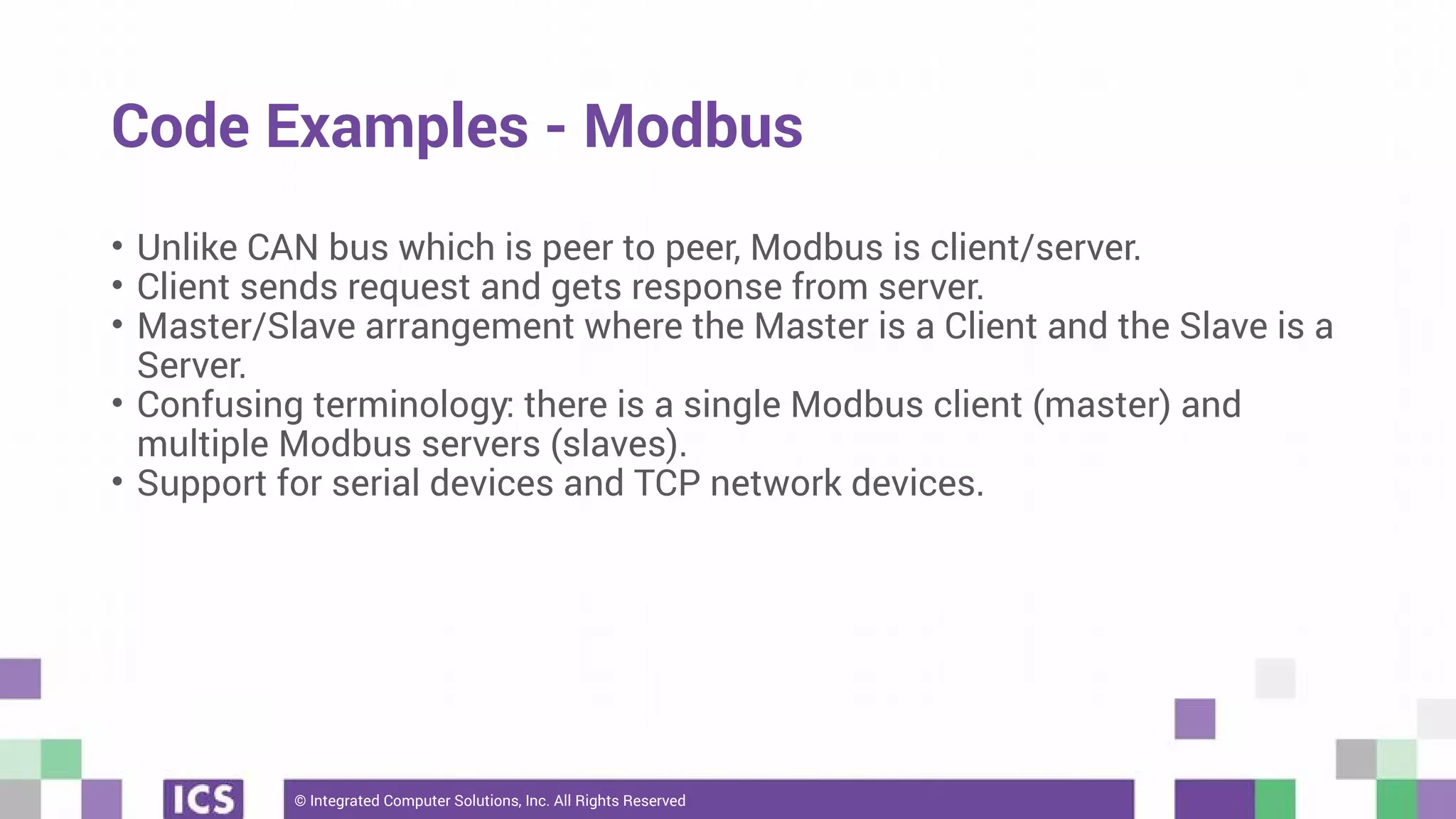
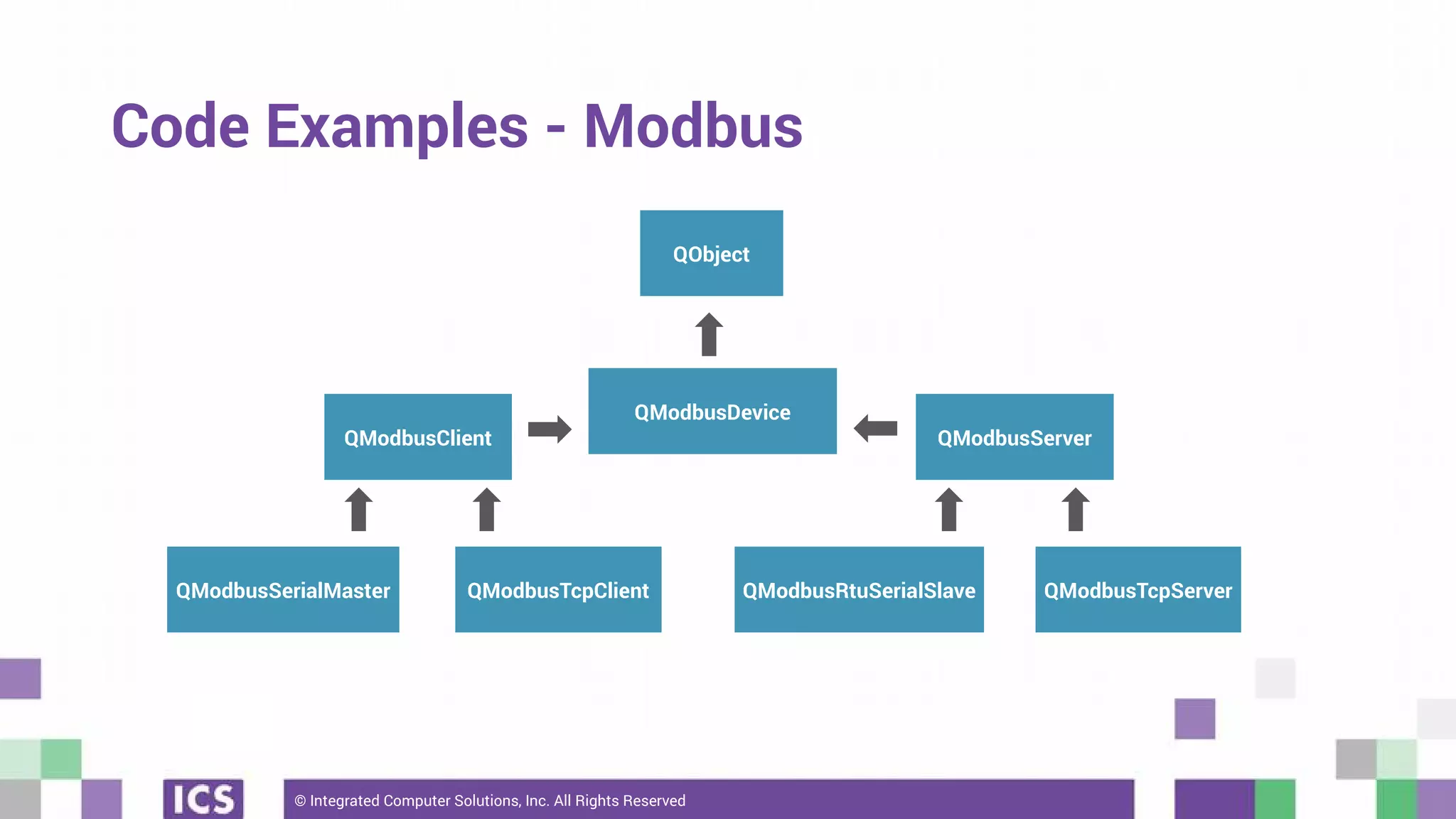
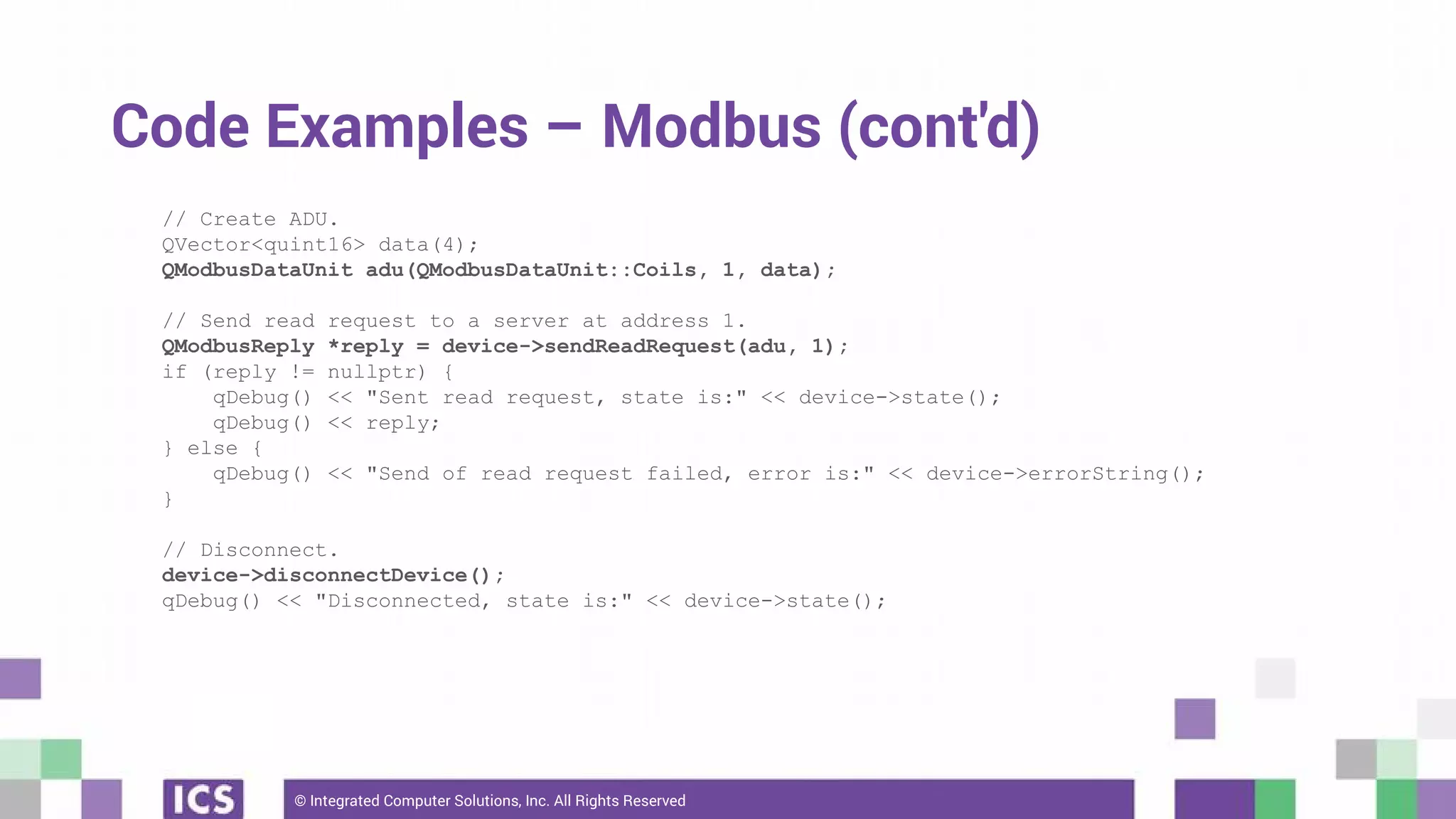
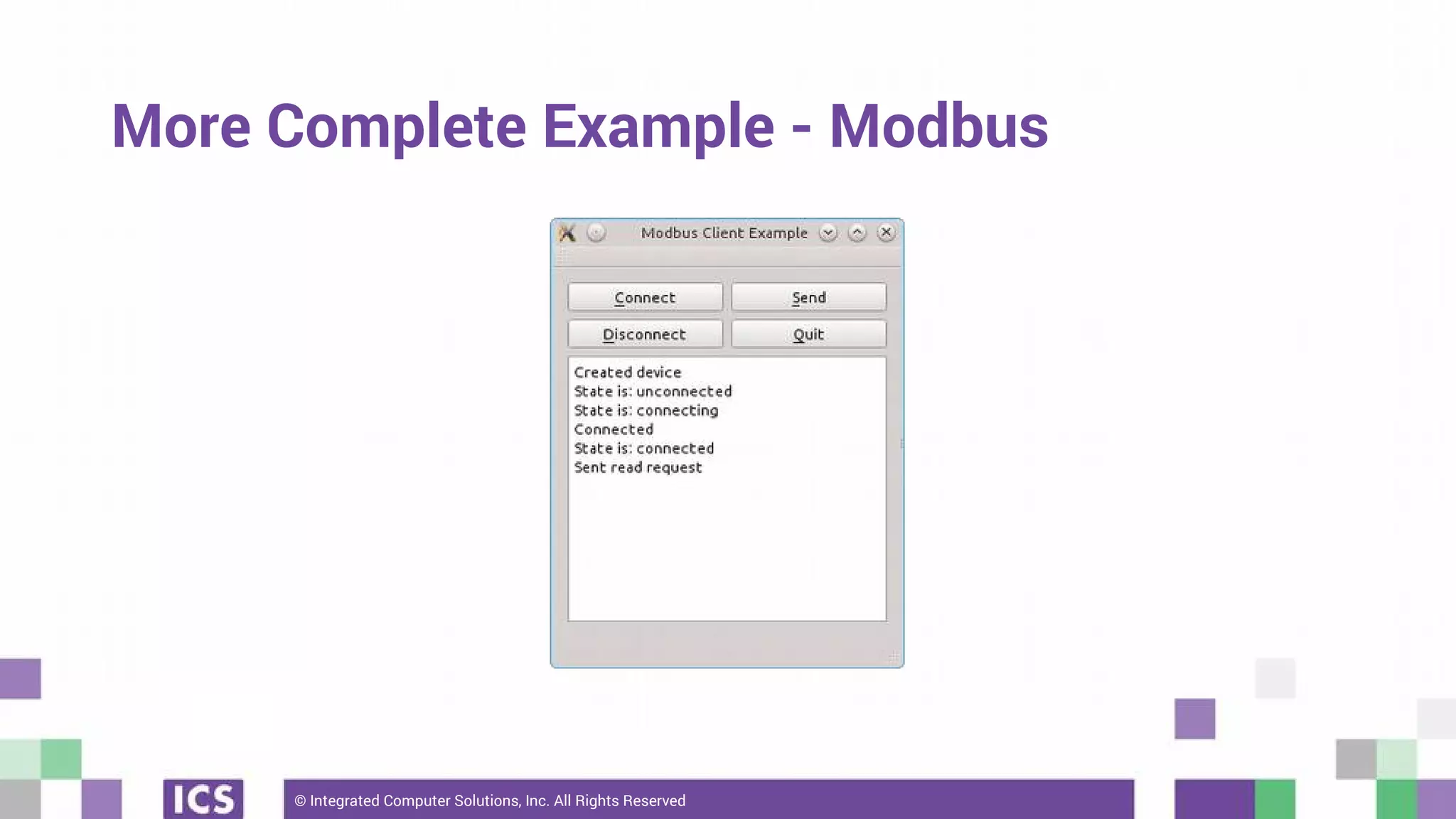
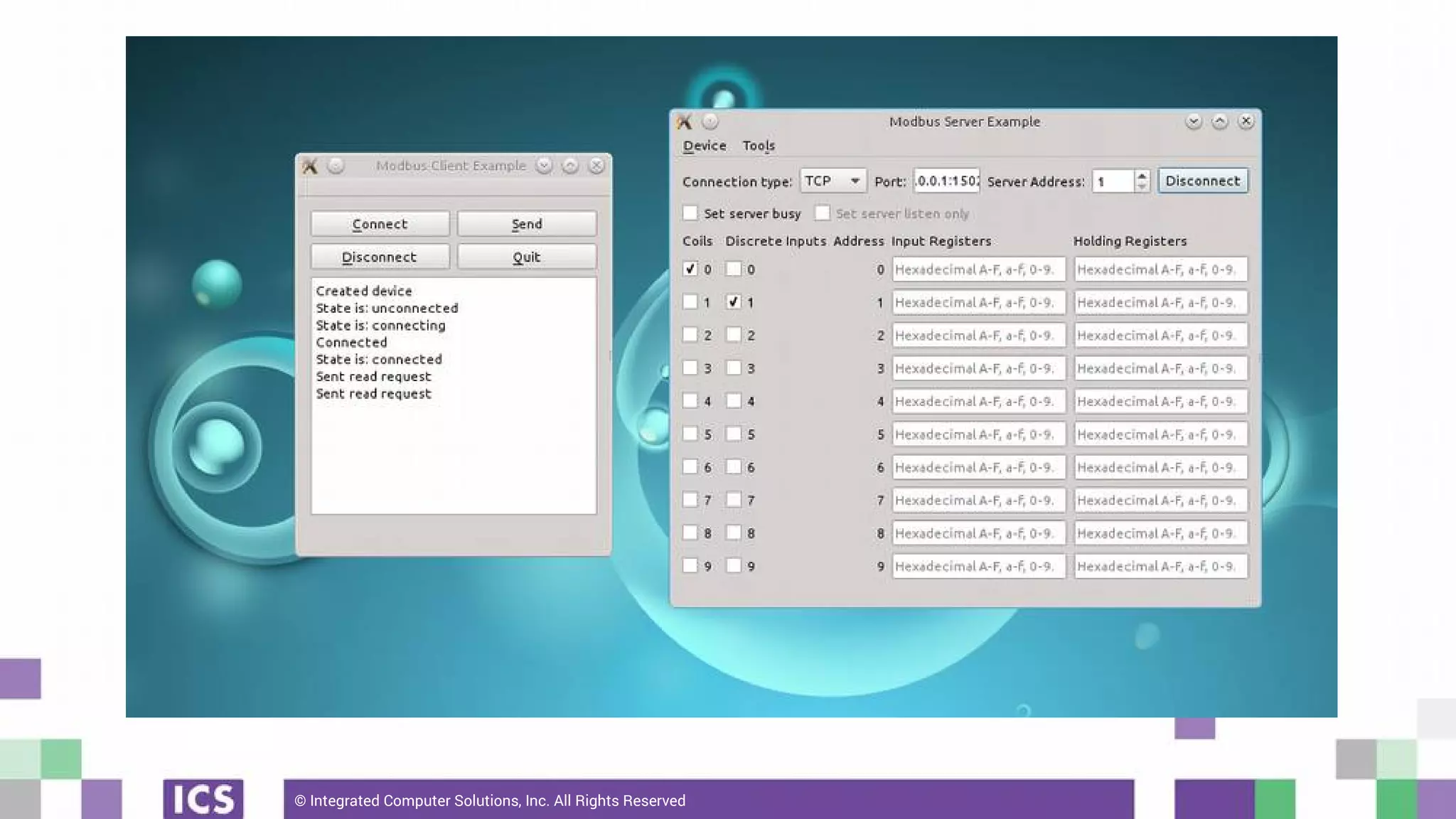
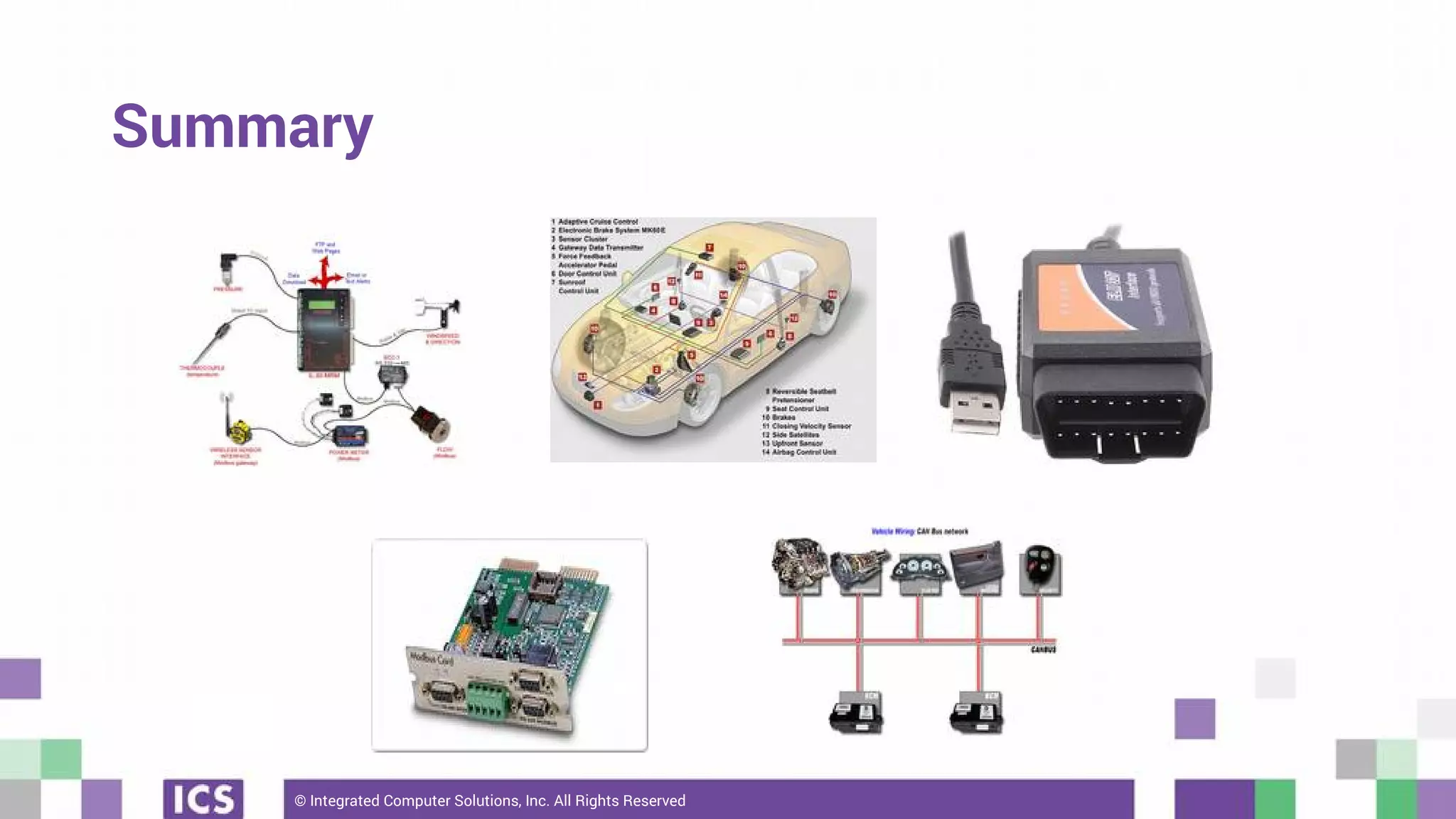
The document outlines the use of the QtSerialBus module to interface with CAN Bus and Modbus protocols for communication between electronic devices. It provides explanations of both protocols, code examples for implementing them in Qt, and discusses supported hardware and future enhancements for the module. Additionally, it addresses the API structure and includes references for further information.