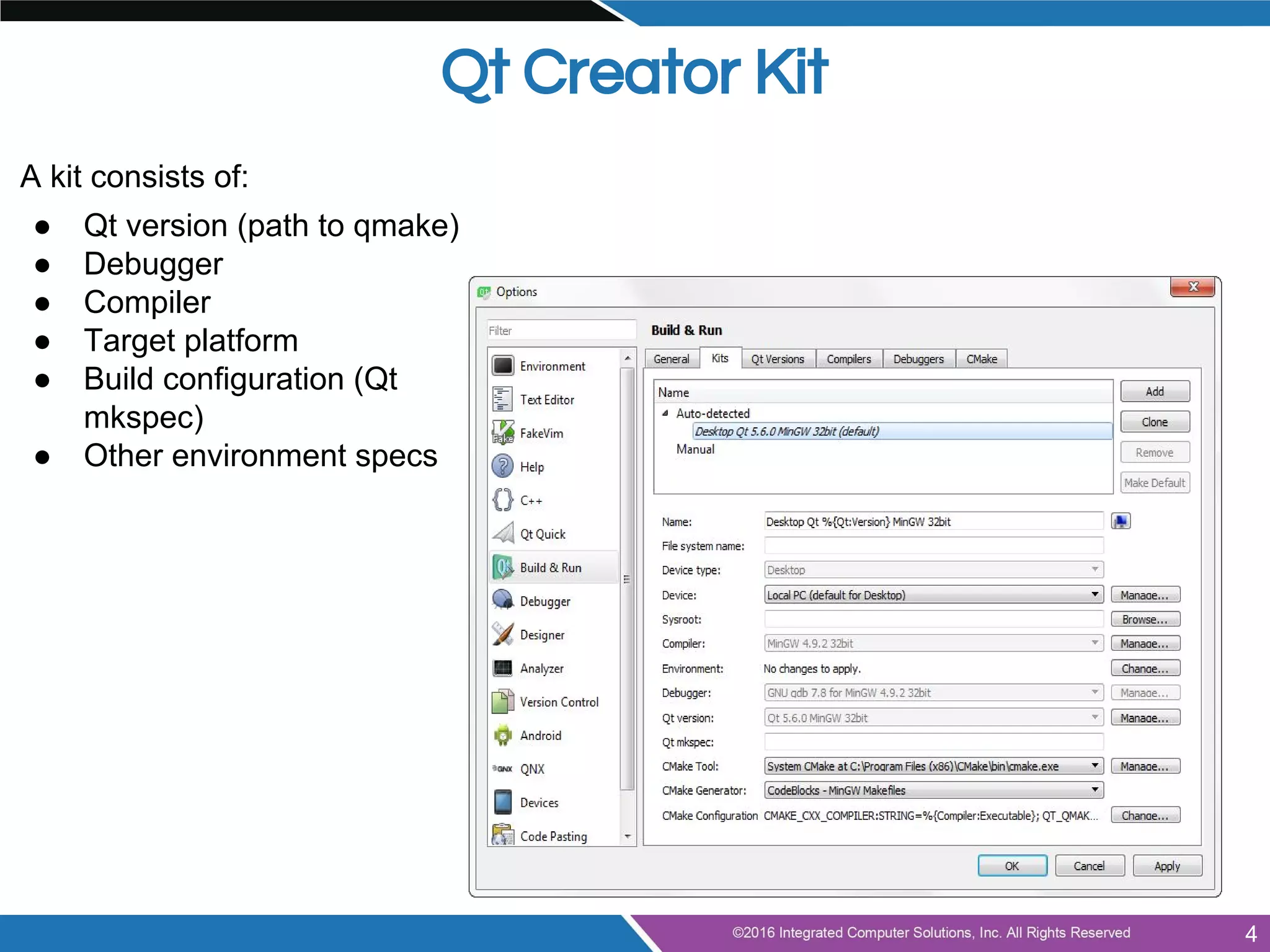
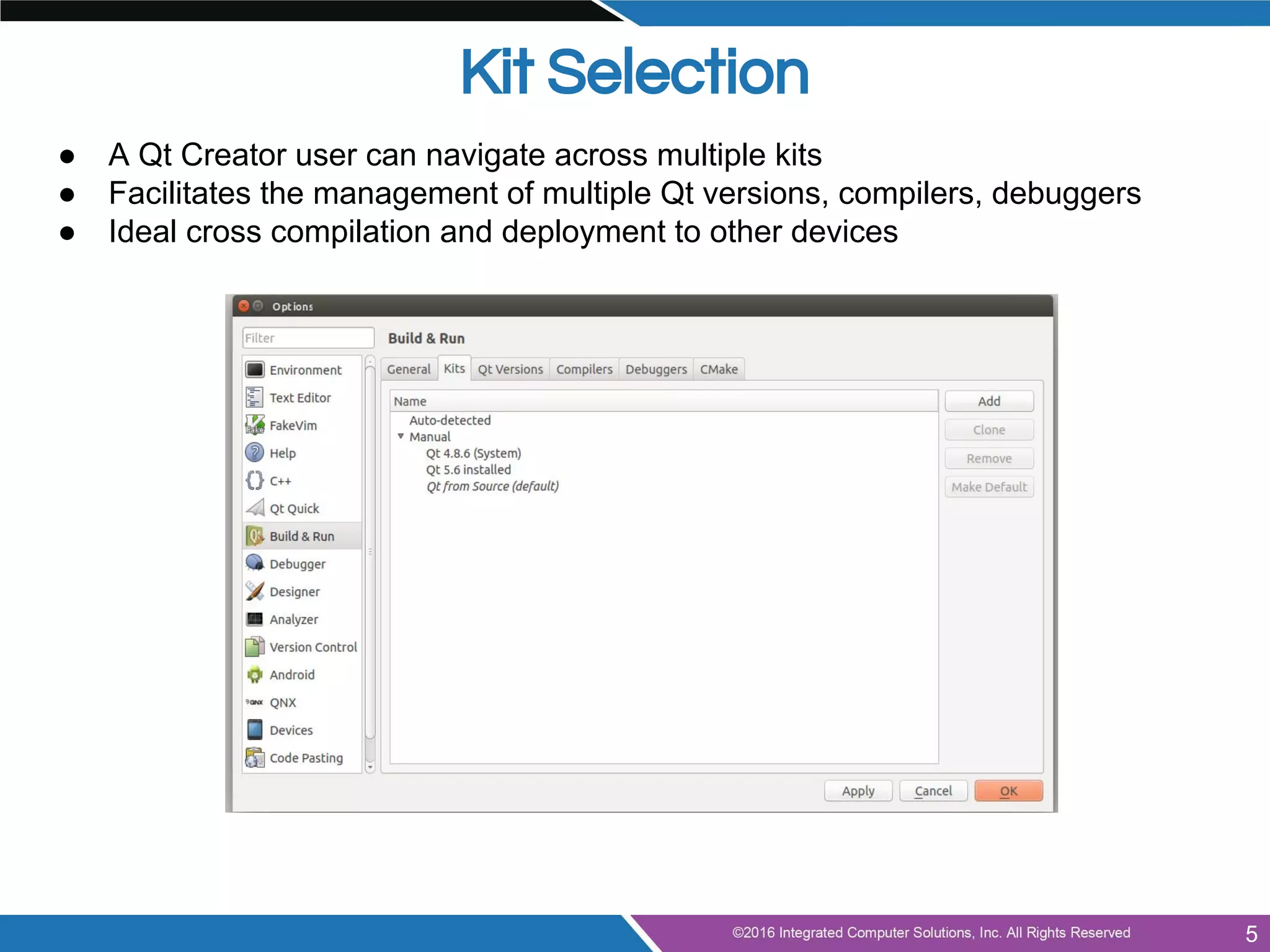
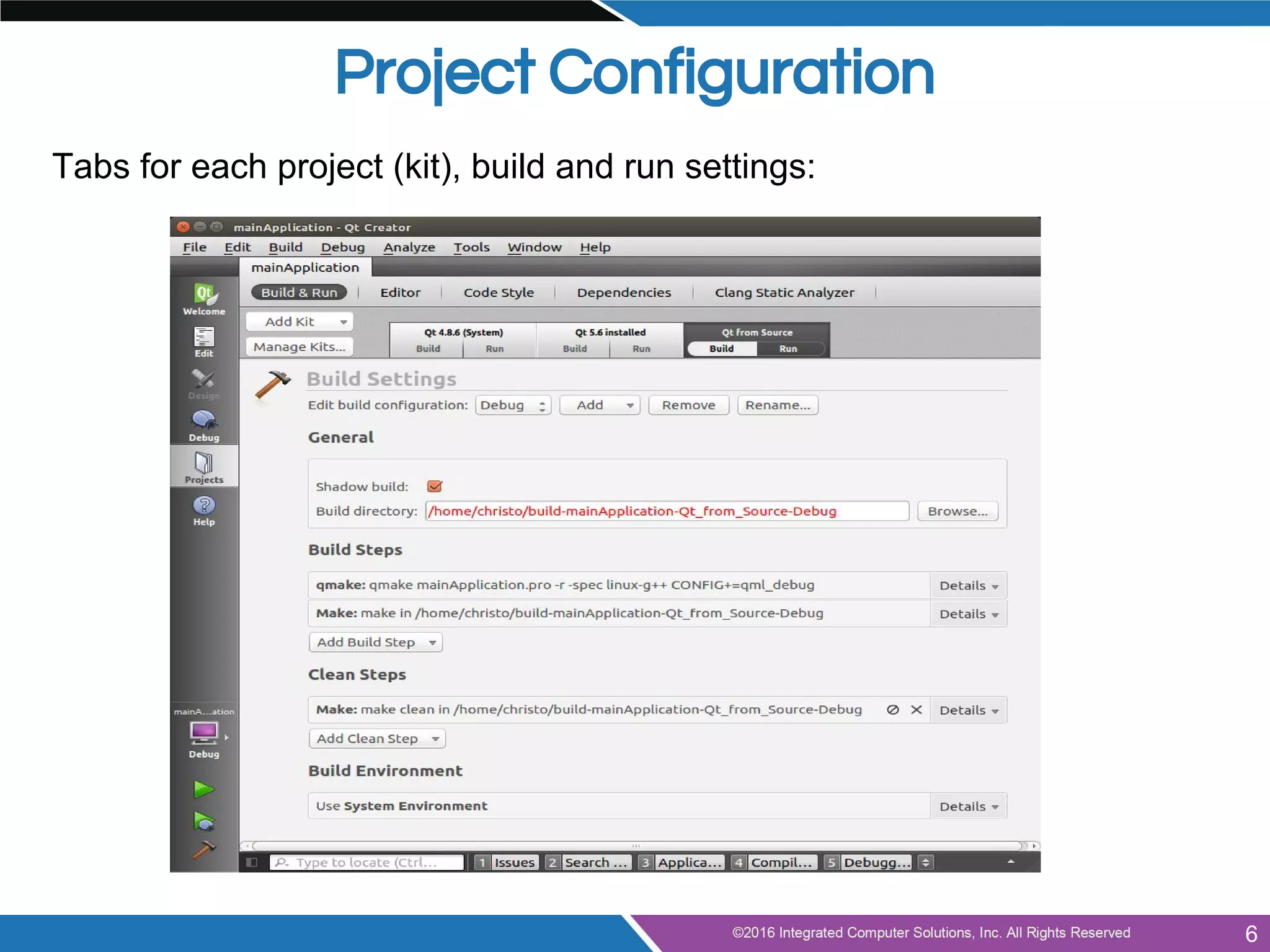
This document provides an agenda and overview for a presentation on doing more with Qt for beginners. The presentation covers advanced topics like using Qt Creator, model/view programming, localization, integrating QML and C++, best practices, tips and tricks. It also discusses next steps like exploring examples, documentation, tutorials, coding practice projects and getting involved with the Qt community through mailing lists and code reviews. The document concludes by inviting audience questions for a future Q&A session on Qt.



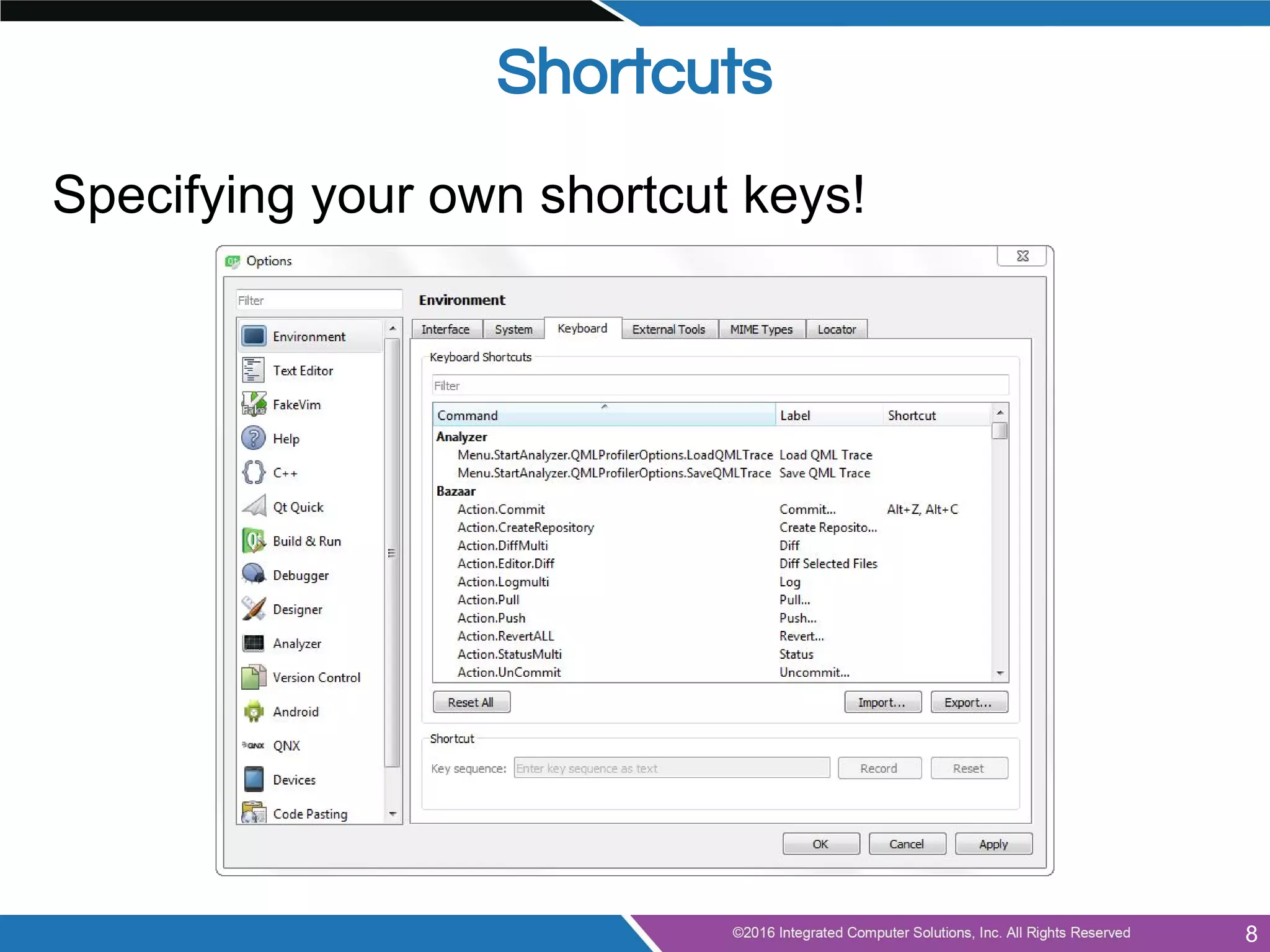
![Ctrl + [1-7]: Switch between various screens
● Welcome Screen
● Edit Mode
● Debug
● etc
Alt + [0-4]: Toggle which output panes are visible
● Sidebar
● Build Issues
● Search Results
● Application Output
● Compile Output
F2: Follow the highlighted symbol
Ctrl + i: Auto-indent selected code
Ctrl + /: Comment selected code
Ctrl + tab: Navigate through the files
Shortcuts
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtforbeginnerspart4-doingmore-160609202224/75/Qt-for-beginners-part-4-doing-more-7-2048.jpg)





![Loading the QML File
#include <QGuiApplication>
#include <QQmlApplicationEngine>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl("qrc:/main.qml"));
return app.exec();
}
23
QT += qml quick
CONFIG += c++11
SOURCES += main.cpp
RESOURCES += qml.qrc
In the .pro file...
In the main.cpp file...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtforbeginnerspart4-doingmore-160609202224/75/Qt-for-beginners-part-4-doing-more-23-2048.jpg)

![Alternate Way of Exporting C++ Object
#include "user.h"
#include <QApplication>
void main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
qmlRegisterType<User>("com.mycompany.qmlcomponents", 1, 0, "User");
User *currentUser = new User("Alice", 29);
QQuickView *view = new QQuickView;
QQmlContext *context = view->engine()->rootContext();
// Exporting of C++ object happens here
context->setContextProperty("_currentUser",currentUser);
}
25
Text {
text: _currentUser.name
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtforbeginnerspart4-doingmore-160609202224/75/Qt-for-beginners-part-4-doing-more-25-2048.jpg)





![Introspection Tip
QLabel aLabel;
aLabel.setText("hello world");
aLabel.show();
for (int i=aLabel.metaObject()->propertyOffset();
i < aLabel.metaObject()->propertyCount()
; i++) {
qDebug() << "Property Name :" <<
aLabel.metaObject()->property(i).name();
qDebug() << "Property Value :" <<
aLabel.property(aLabel.metaObject()->property(i).name());
}
35
// You can add properties to your QObject derived classes by using the //
following macro.
Q_PROPERTY(type name READ getFunction [WRITE setFunction])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtforbeginnerspart4-doingmore-160609202224/75/Qt-for-beginners-part-4-doing-more-35-2048.jpg)






