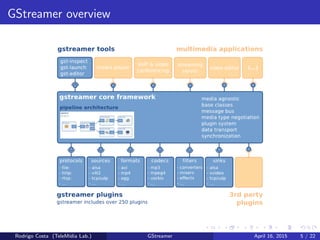
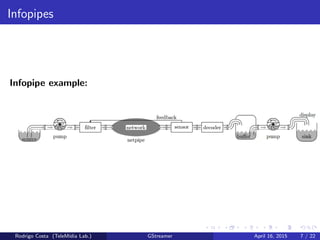
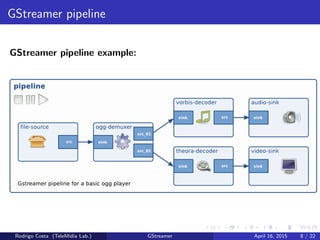
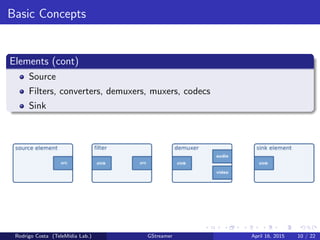
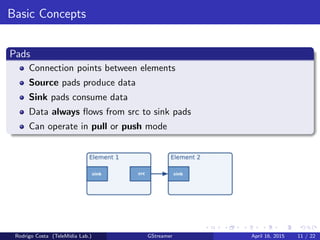
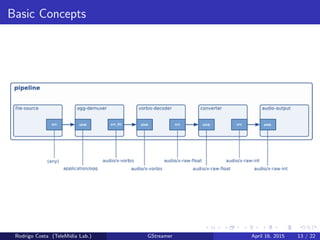
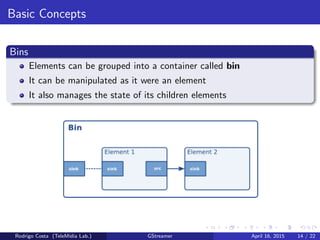
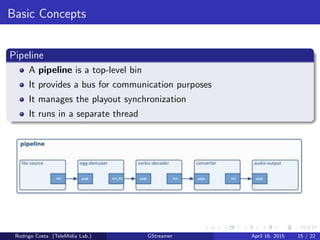
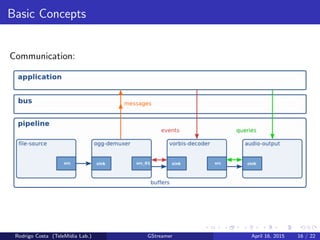
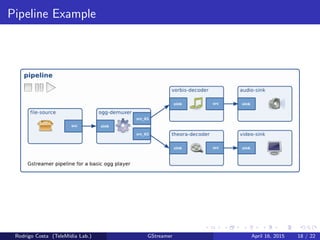
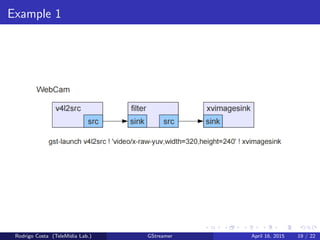
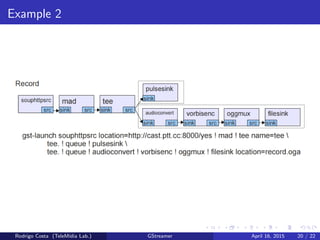
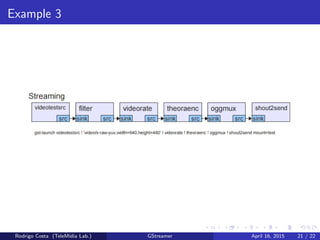
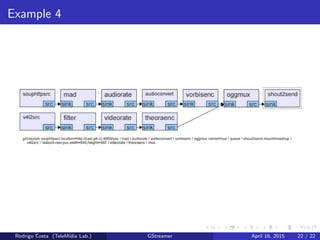
GStreamer is a multimedia framework for building applications that handle audio and video content. It provides reusable code modules called elements that can be linked together into pipelines to process multimedia. Elements include sources, filters, decoders, encoders and sinks. Pads connect elements and negotiate compatible data formats. Pipelines synchronize playback across elements and the framework supports integration with other projects and bindings to multiple programming languages.