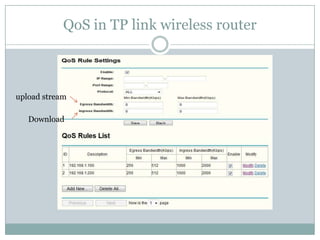
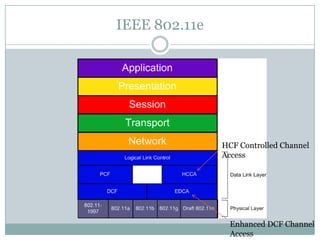
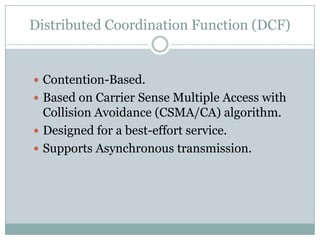
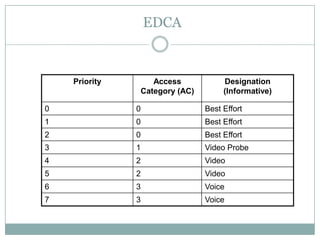
The document discusses quality of service (QoS) in wireless local area networks (WLANs). It describes the 802.11 medium access control schemes, including distributed coordination function (DCF) and point coordination function (PCF), and their limitations in providing QoS. It then introduces the 802.11e standard, which includes enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) and HCF controlled channel access (HCCA) to improve QoS support for real-time applications like voice and video.