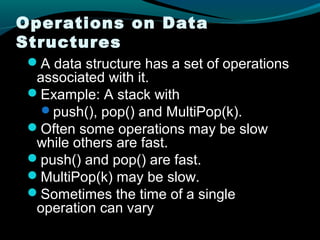
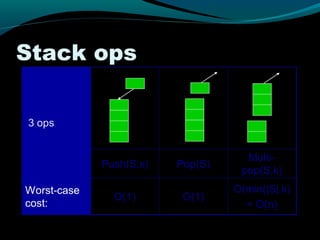
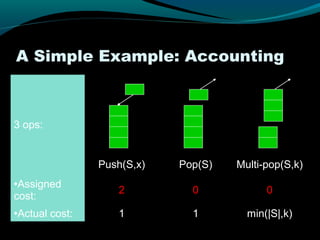
This document discusses amortized analysis, which analyzes the average cost per operation of a sequence of operations, even if some operations are individually expensive. It describes three methods for amortized analysis: aggregate, accounting, and potential. The aggregate method bounds the total cost of n operations to show the average cost per operation is small. The accounting method assigns different costs to operations, using credit from low-cost operations to pay for high-cost ones. The potential method associates potential energy with the data structure to pay for future expensive operations. Examples of applications like vectors and priority queues are also given.