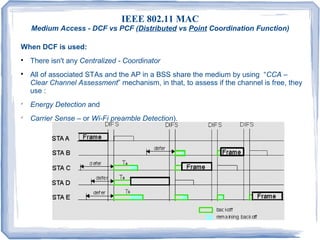
IEEE 802.11 defines two medium access methods - Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) where all stations share the medium equally using carrier sense and random backoffs, and Point Coordination Function (PCF) where a central point coordinator polls stations for transmission. DCF is more widely used. 802.11e introduced Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) to provide quality of service by prioritizing traffic categories, and HCF Controlled Channel Access (HCCA) which extends PCF with scheduled polling. Power saving modes allow stations to sleep and wake periodically to receive buffered frames from the access point.