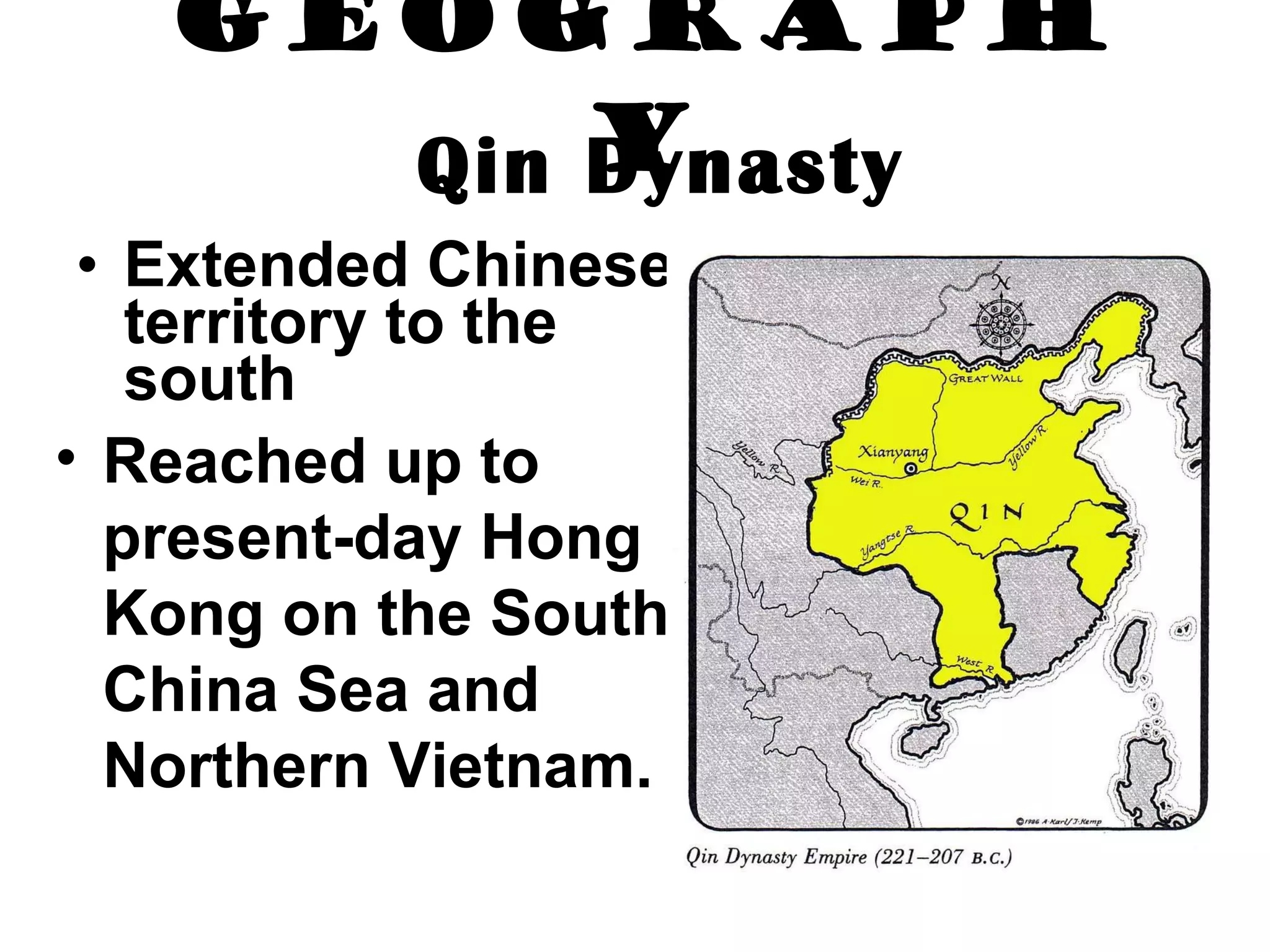
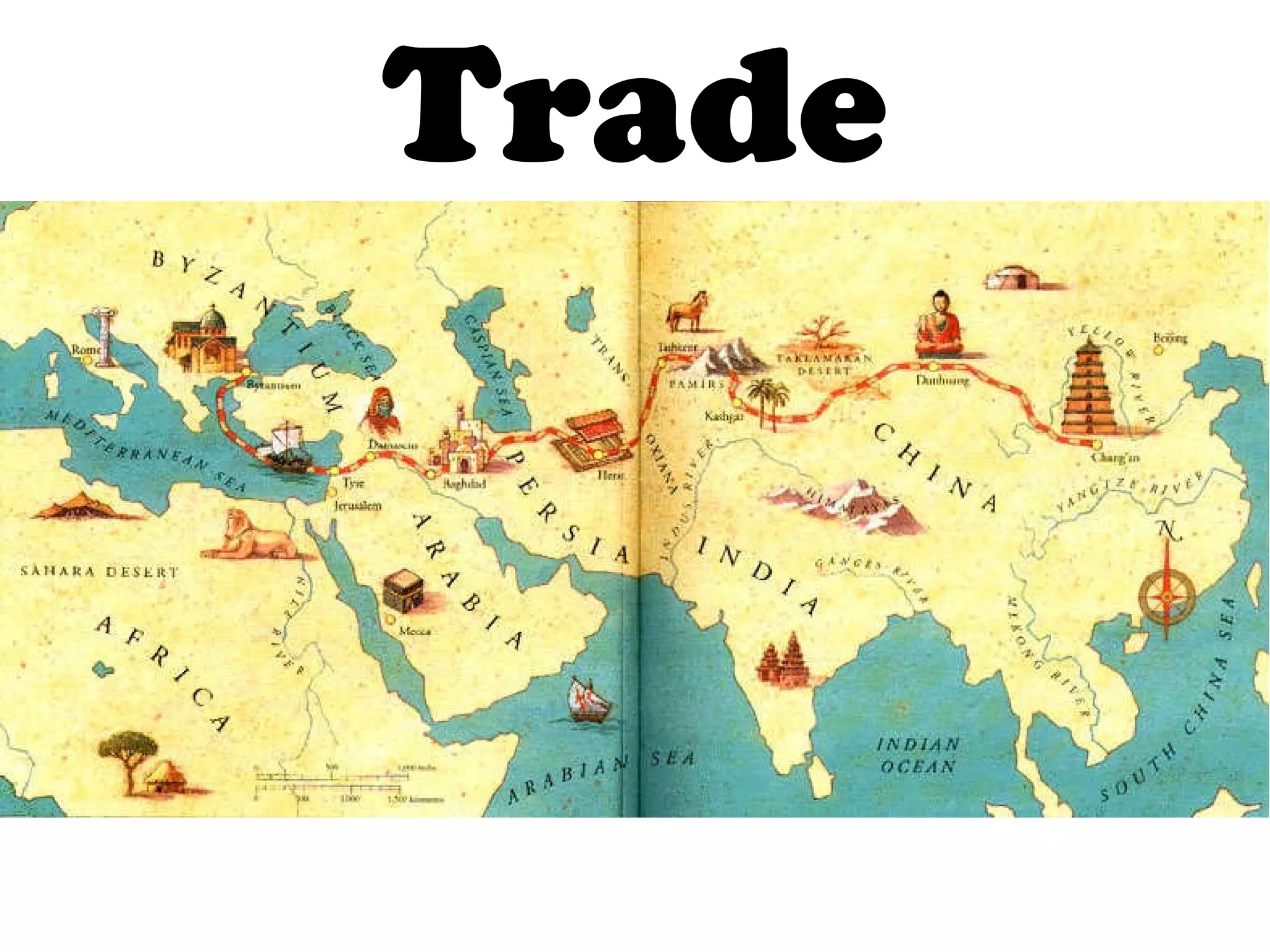
The Qin Dynasty lasted from 221 BC to 206 BC, unifying China under the First Emperor Qin Shi Huangdi. The Han Dynasty then ruled from 206 BC to 220 AD, being much longer lasting at over 400 years under the famous ruler Wu Ti. The Han expanded Chinese territory further south and west than the Qin, including reaching Korea, Indochina, and Central Asia. They also developed the Silk Road for international trade between China, Central Asia, India, and the Roman Empire. Confucian philosophy became emphasized under the Han in government and education.