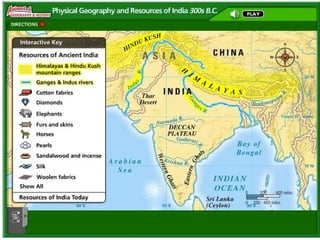
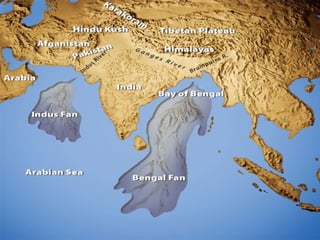
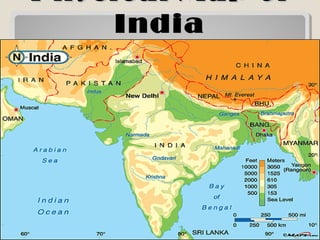
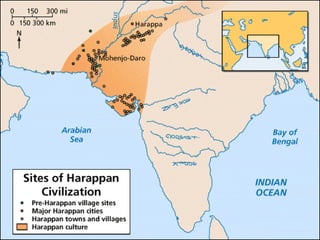
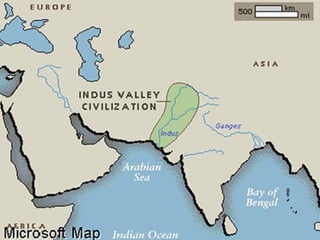
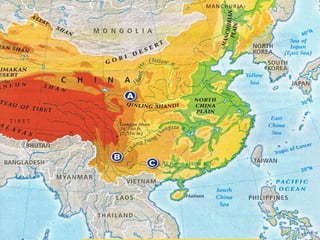
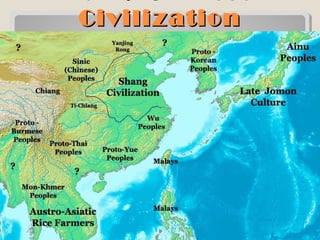
The document provides information on the geographic settings of ancient India and China. It discusses how India's location on a peninsula, surrounded by seas and mountains like the Himalayas, allowed early Indian civilization to develop with some isolation. The key features of India's landscape including the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra rivers are also noted. For ancient China, the document outlines how geographic barriers like mountains and deserts surrounded the central region, which the Chinese called the "Middle Kingdom." It then provides brief overviews of the Indus Valley and Harappa/Mohenjo-Daro civilizations in India as well as the Shang Dynasty in China.