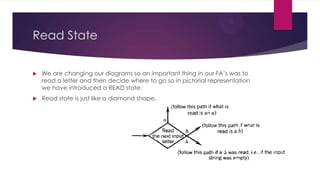
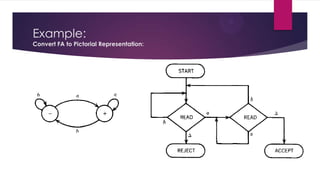
Pushdown automata are a new form of finite automata that have increased language recognition capabilities through the addition of a pushdown stack. A pushdown automaton is defined by an input alphabet, input tape, stack alphabet, pushdown stack, start state, halt states, push states, and read states. It can perform push and pop operations on the stack to recognize nested or hierarchical language structures that regular finite automata cannot. The addition of a stack allows pushdown automata to recognize context-free languages while retaining the intuitive graphical representation of finite automata.