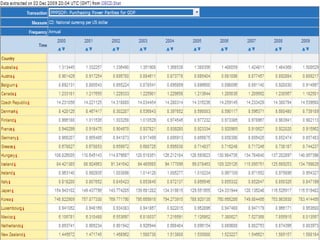
The purchasing power parity (PPP) theory compares the average costs of goods and services between countries using exchange rates. PPPs are useful for inter-country comparisons of GDP in real terms and economic data expressed in national currencies. PPPs are calculated at the product group level by comparing consumption baskets, then aggregated to GDP levels using weights. PPP exchange rates are meant to converge with actual exchange rates over the long run, though various factors can cause short-term deviations. PPPs are useful for output and productivity comparisons, while market exchange rates are better for trade-related analyses.










![How are PPPs calculated for GDP?Two stagesAt the product group level CB = P1Q1 + P2Q2 + P3Q3 + ... + PnQn PPP for Product group N between two country = (CB)country1/(CB)Country2 At the GDP or any aggregate levels X=[(PPP PG1)*W1 + ------- +(PPP PG N)*Wn] PPP GDP of two country = X country1/ X country2 Prices used in the calculation of PPPs are market Prices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/purchasingpowerparity1-12599342408666-phpapp01/85/Purchasing-Power-Parity1-12-320.jpg)



