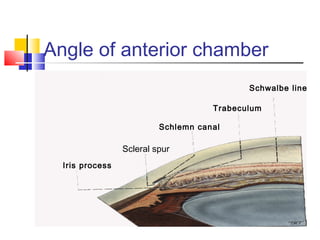
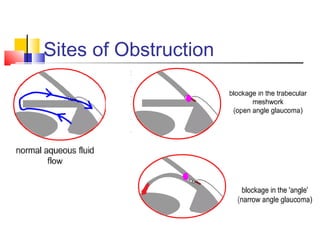
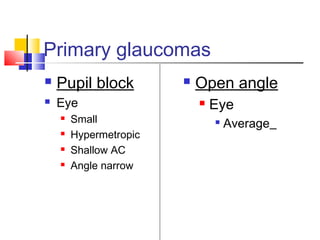
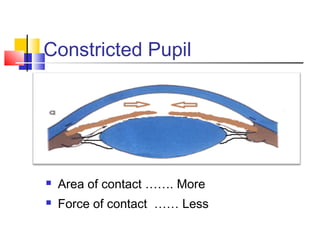
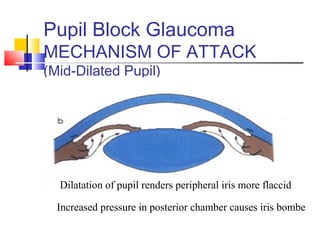
This document discusses pupil block glaucoma, describing the mechanism and stages of the condition. It begins by explaining how pupil block glaucoma occurs when the pupil is mid-dilated, causing the peripheral iris to obstruct the angle and increase intraocular pressure. The document then outlines the different stages of pupil block glaucoma from prodromal to acute congestive, and describes the signs, symptoms, and management approaches at each stage, including medical treatments to control pressure and surgical procedures like laser iridotomy or iridectomy to relieve the pupil block.