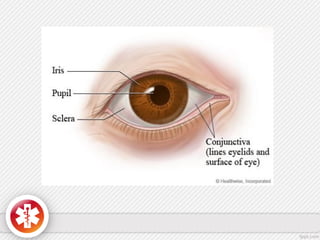
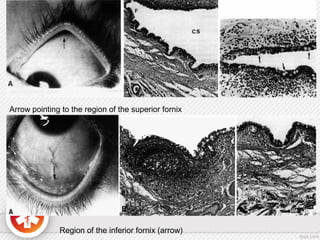
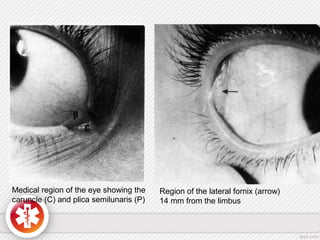
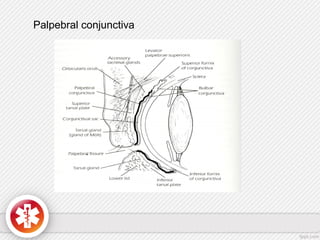
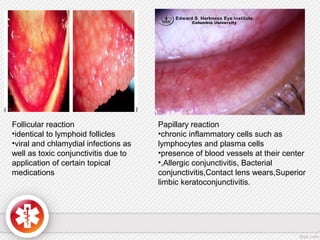
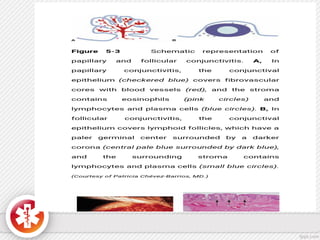
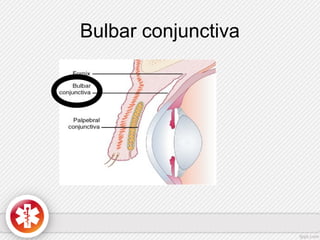
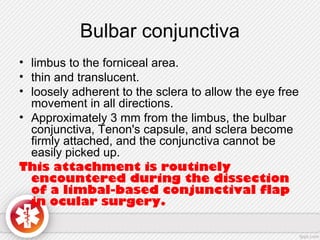
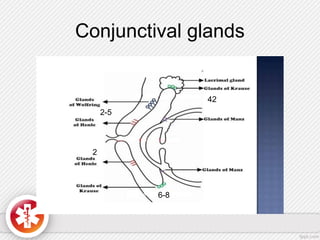
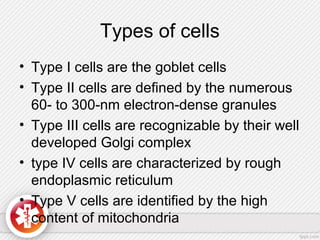
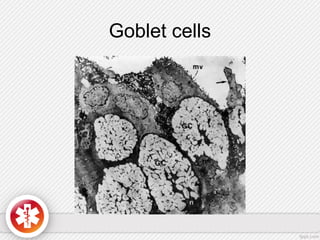
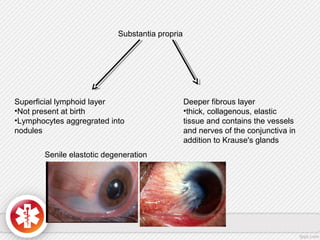
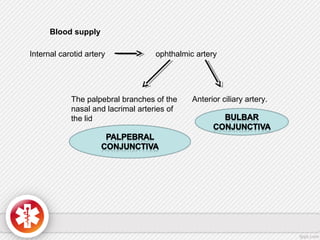
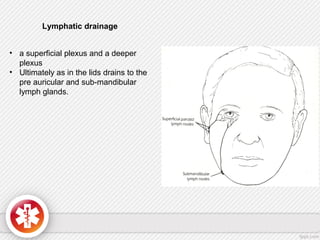
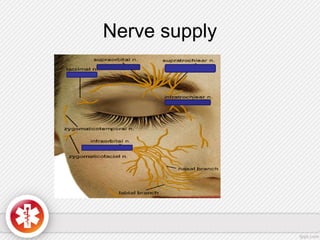
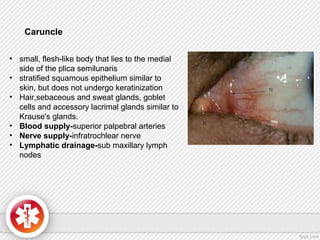
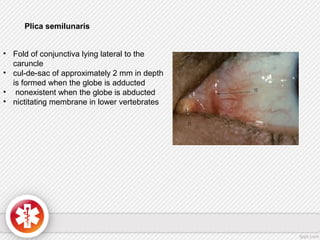
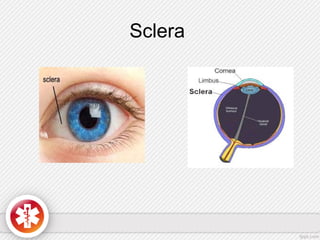
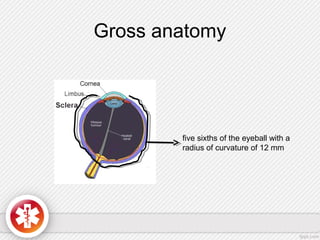
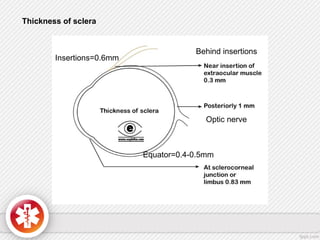
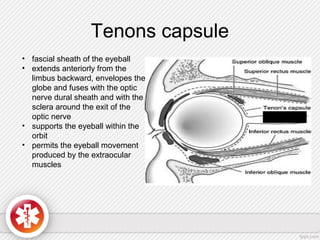
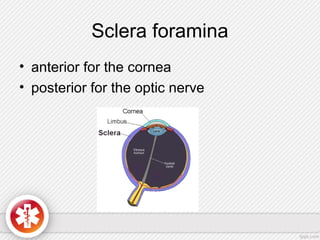
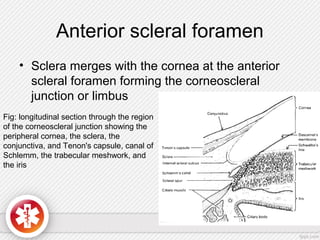
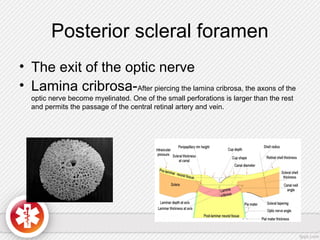
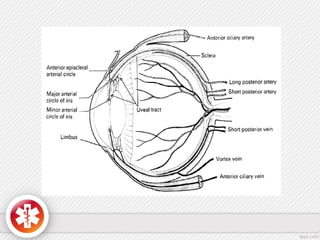
The conjunctiva is a vascularized mucous membrane that covers the anterior surface of the eyeball and posterior surface of the eyelids. It combats infection through its vascular and immunological properties. The conjunctiva has three layers - an epithelial layer, substantia propria layer, and goblet cells that secrete mucus. The sclera is the dense outer coat of the eyeball that protects its contents and maintains the globe's shape. It has three layers - episclera, scleral stroma, and lamina fusca. Both structures are supplied by arteries and veins and contain nerves to detect inflammation or eye movement.