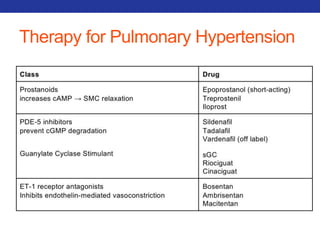
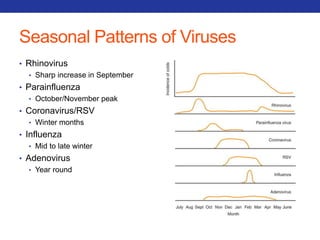
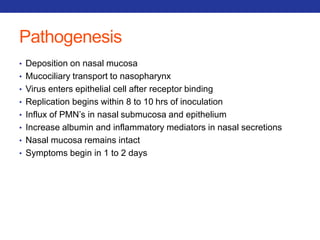
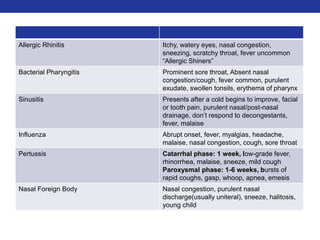
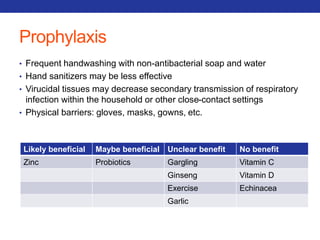
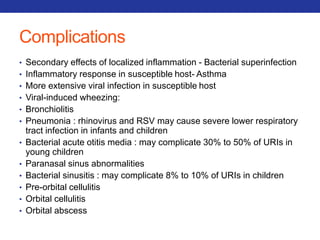
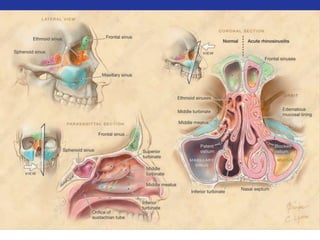
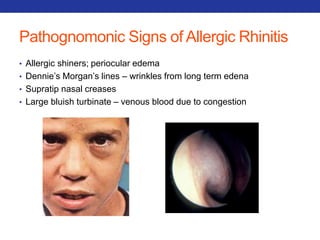
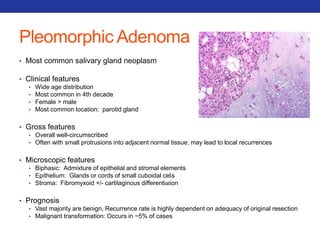
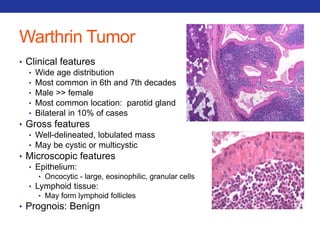
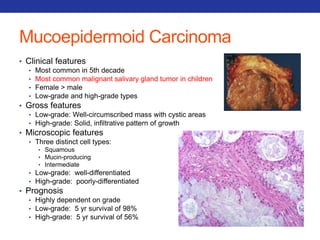
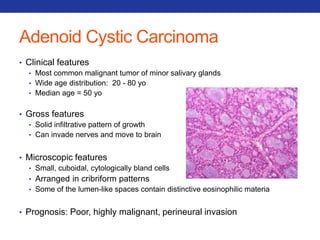
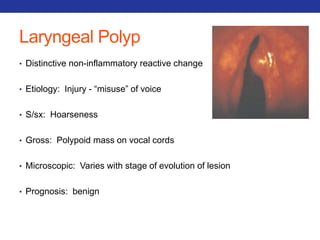
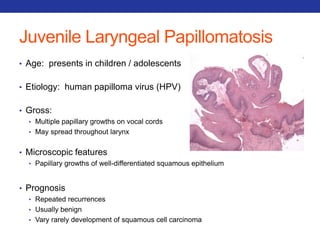
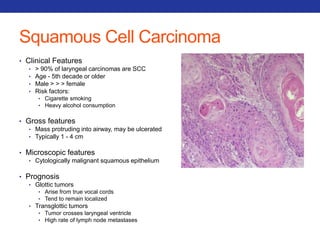
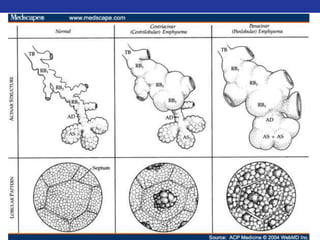
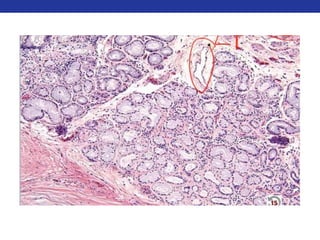
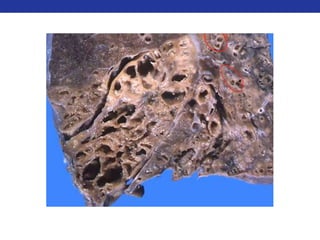
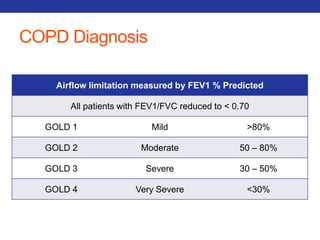
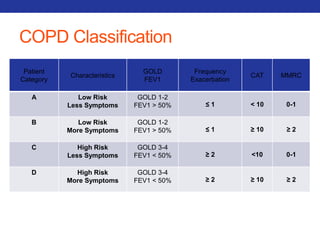
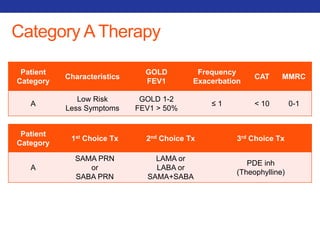
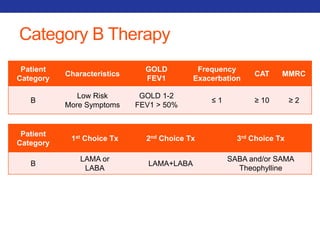
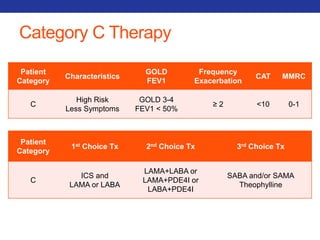
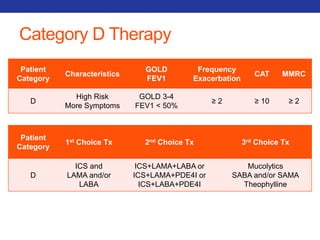
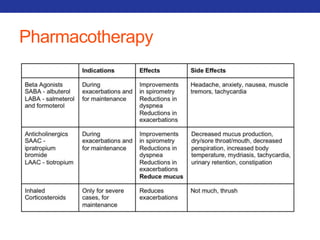
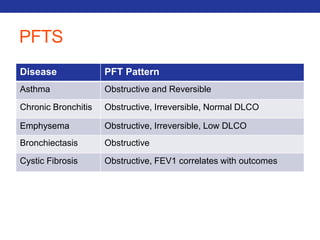
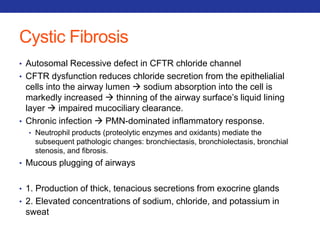
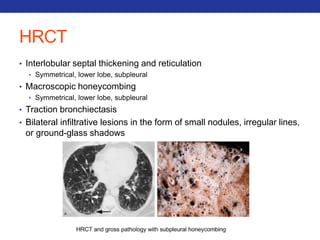
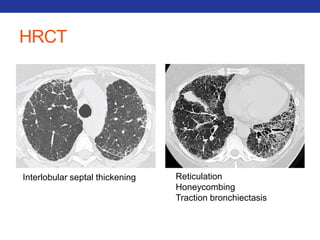
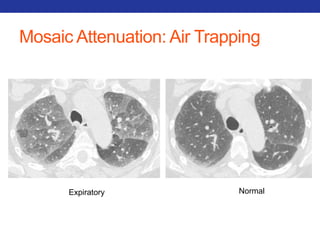
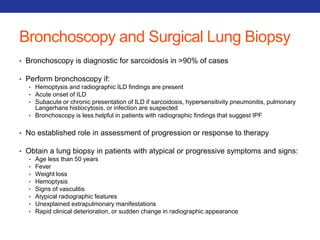
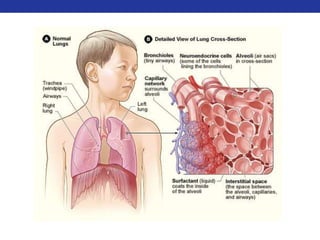
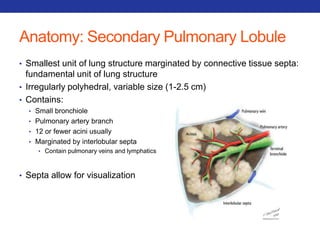
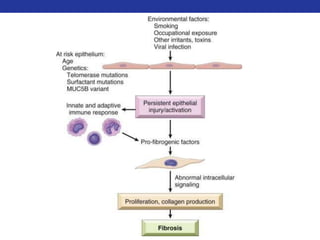
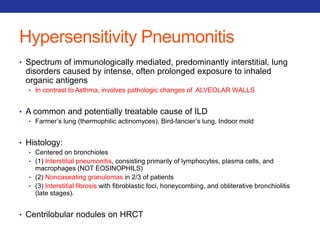
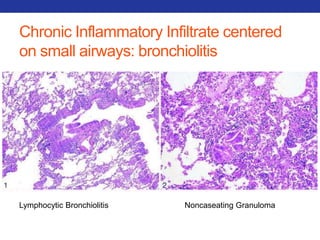
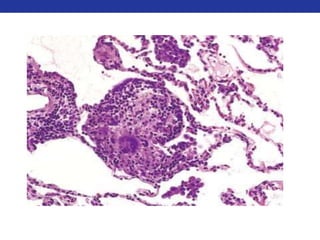
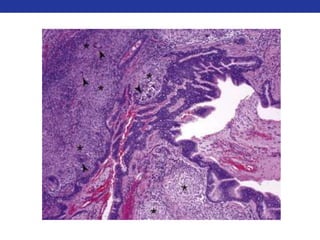
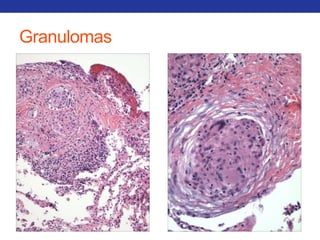
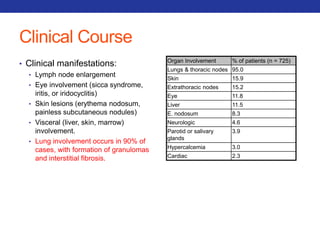
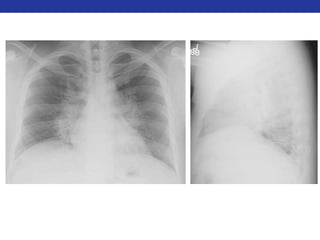
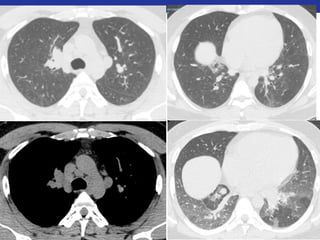
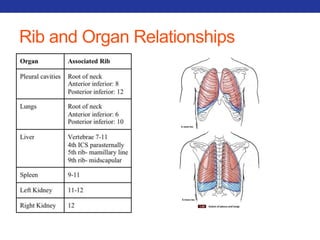
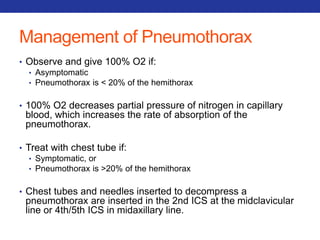
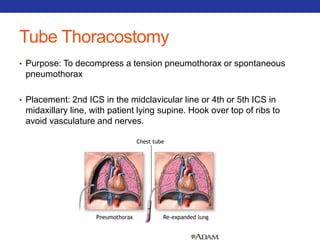
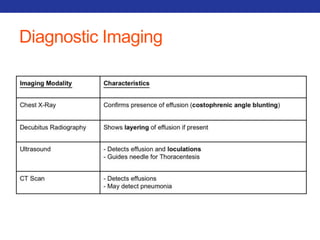
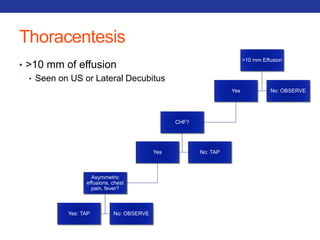
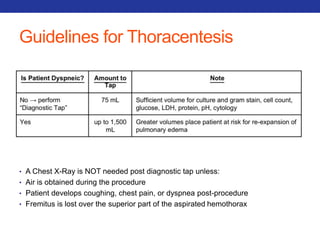
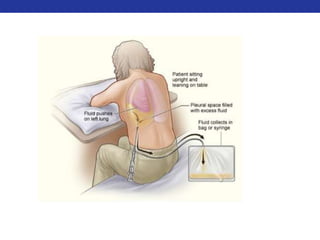
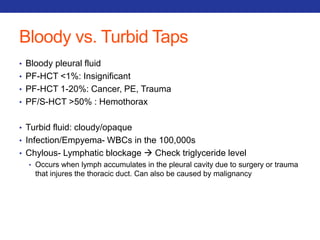
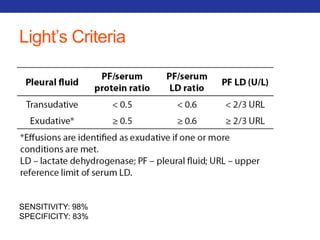
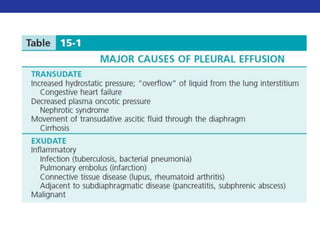
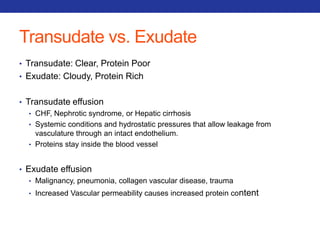
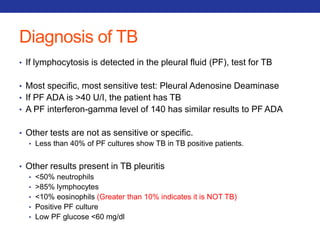
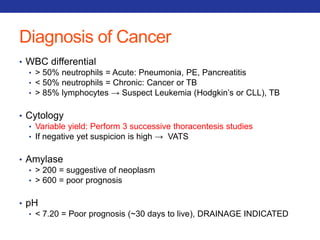
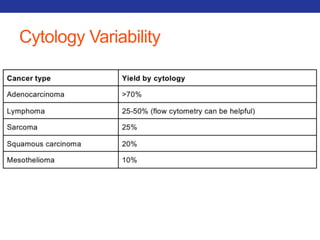
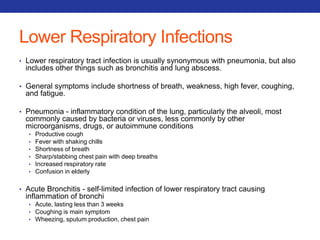
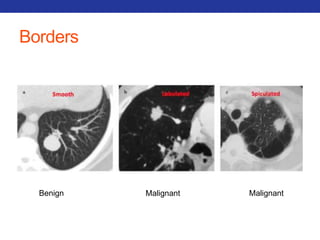
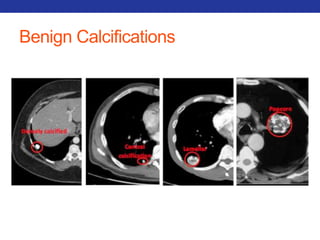
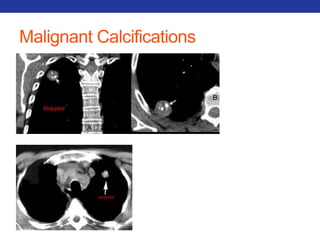
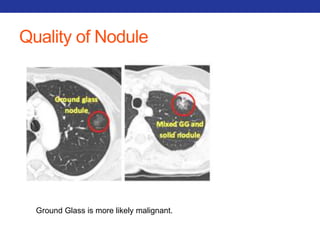
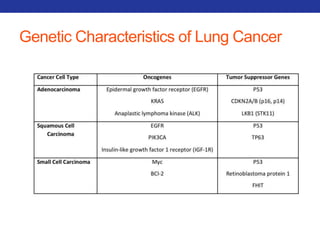
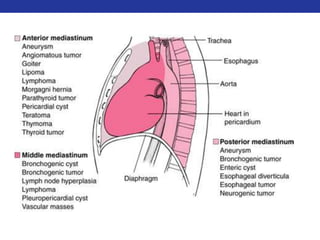
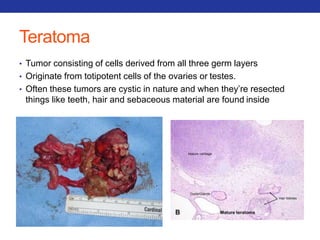
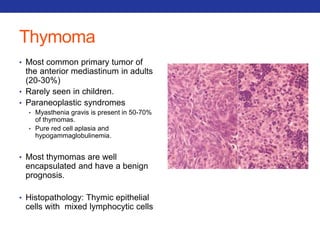
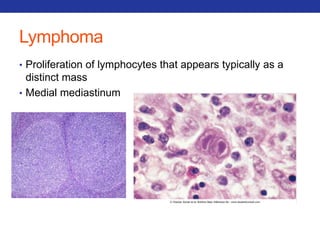
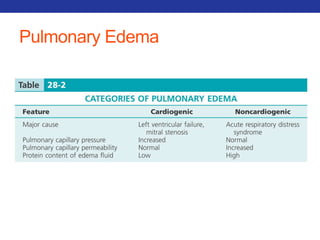
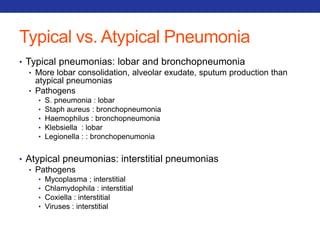
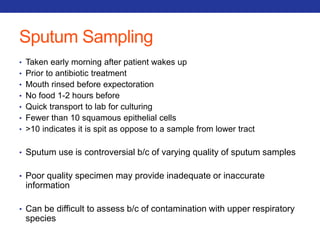
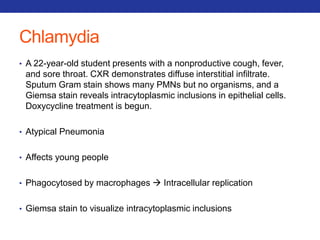
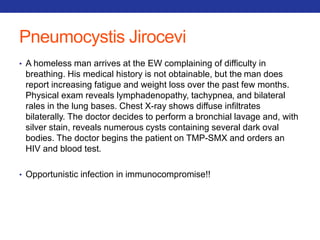
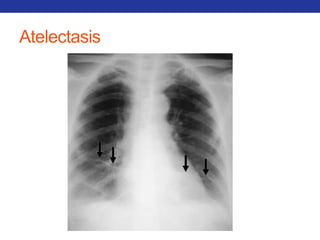
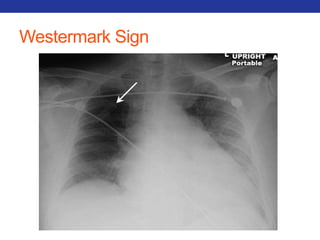
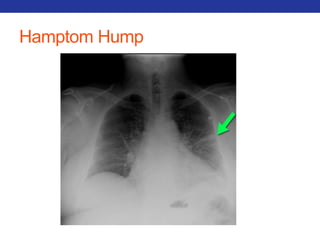
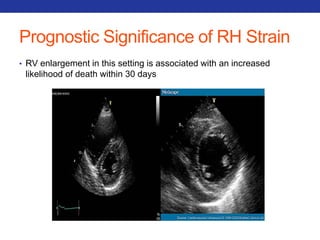
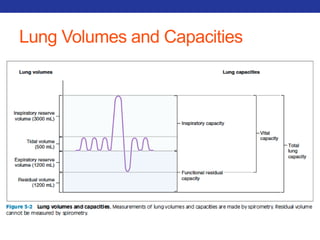
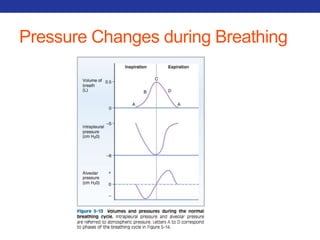
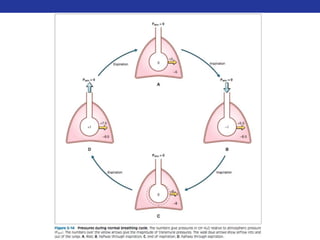
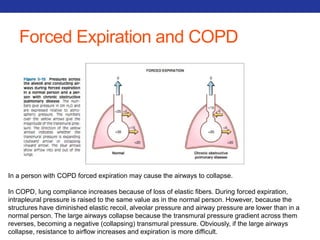
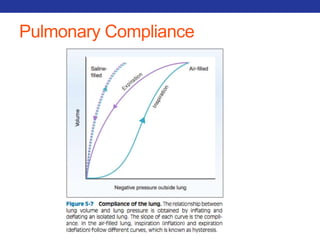
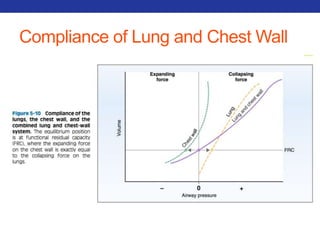
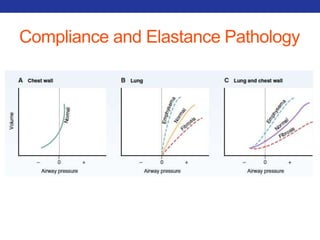
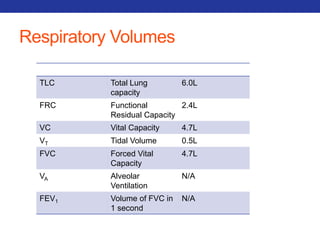
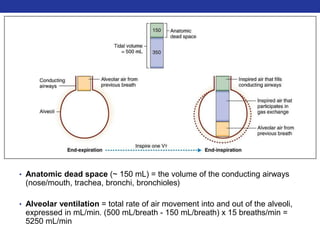
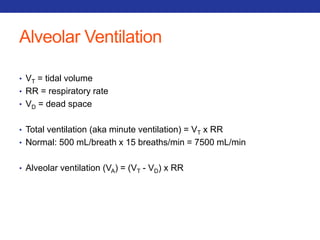
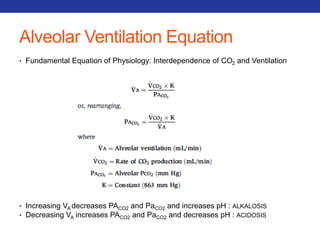
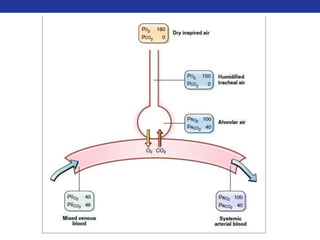
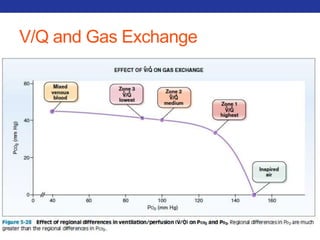
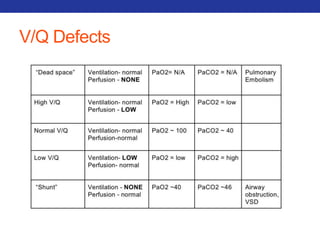
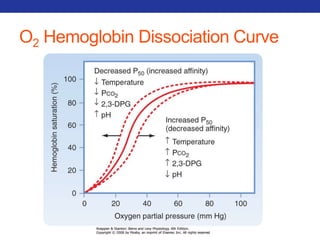
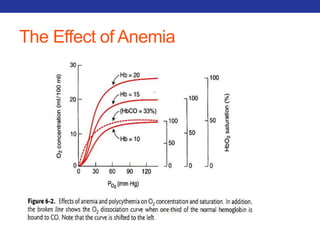
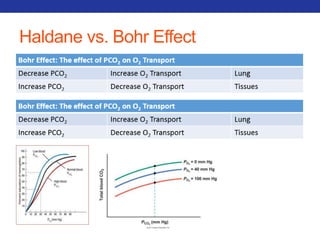
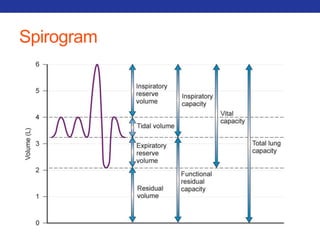
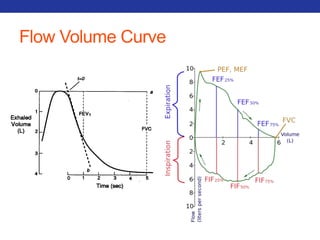
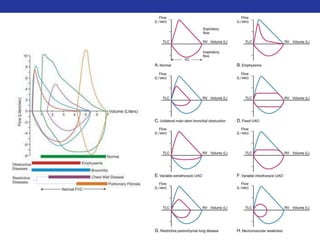
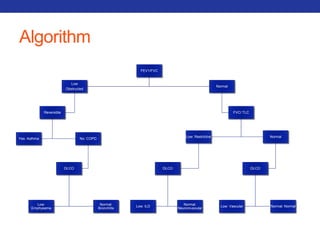
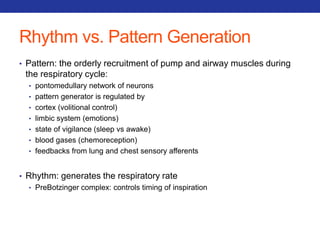
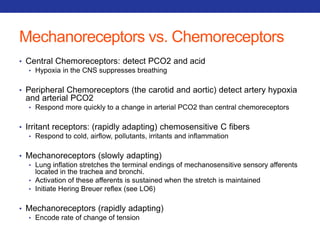
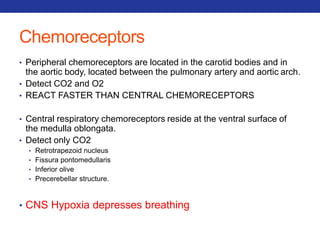
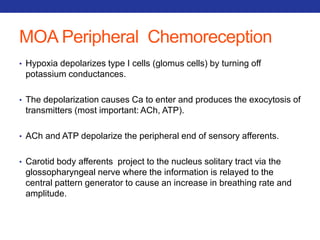
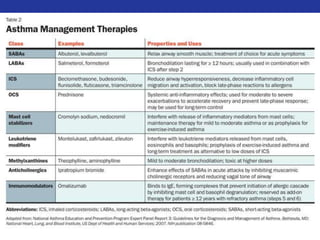
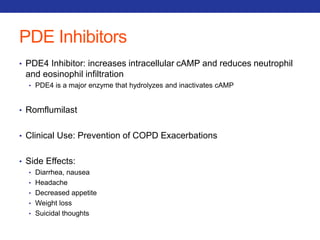
This document summarizes pulmonary physiology including mechanics of breathing, lung volumes and capacities, pressure changes during breathing, forced expiration in COPD, transmural pressures, pulmonary compliance, hysteresis, diffusion of gases, V/Q ratios, and O2 and CO2 transport. Key points include that in COPD, forced expiration can cause airway collapse due to decreased alveolar pressure, and that V/Q defects and right-to-left shunts can cause hypoxemia. O2 is transported primarily bound to hemoglobin while CO2 is transported primarily dissolved in plasma.














![A-a Gradient
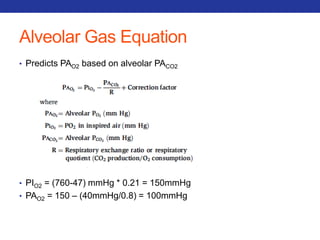
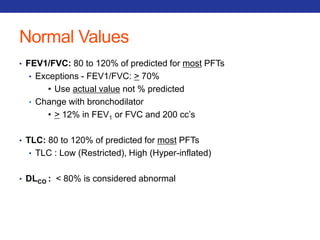
• PAO2 – PaO2
• In a normal person, the A-a difference is close to zero (but not zero),
because while O2 will equilibrate in the alveoli, there is a small
amount of blood (~2%) that bypasses the alveoli (aka the
"physiological shunt"), and PaO2 (obtained via a blood sample) is a
mixture of all blood, including shunted blood.
• To calculate the estimated normal A-a gradient : [Person’s Age/4] + 4
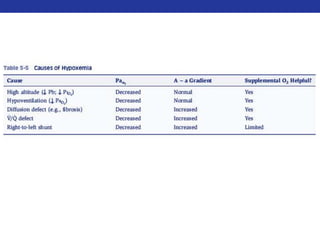
• Three scenarios that result in an increased gradient:
• Diffusion defects (e.g. fibrosis, pulmonary edema)
• V/Q defects
• Right-to-left shunts (cardiac, intrapulmonary)
• NOT Hypoventilation and High altitude](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmreview-141117134558-conversion-gate01/85/Pulmonology-Review-28-320.jpg)
















































































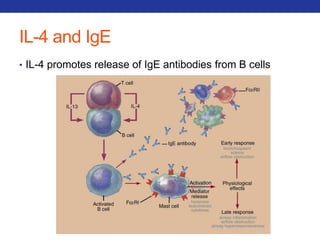




















![Mucolytics
• 1) Hypertonic Agents
• Ex: Inhaled hypertonic saline or mannitol
• MOA: Hypertonic agents draw water into the airway to lower mucus viscosity.
• Side Effects: Can cause bronchospasm therefore used following a bronchodilator
• General: cheap with good results (disadvantage: time consuming)
• 2) N-acetyl cysteine (NAC): CF and Bronchiectasis
• MOA: Lowers mucus viscosity by cleaving disulfide bonds via its free sulfhydryl group.
• Side Effects: bronchospasms (use 15 min. after bronchodilator), smells, expensive
• 3) Inhaled DNAse: CF
• MOA: Breaks down purulent sputum by cleaving DNA strands.
• Side Effects: laryngitis, pharyngitis, chest pain, conjunctivitis, dyspnea, expensive, change in
voice
• 4) Ivacaftor: CF
• MOA: CFTR protein potentiator for G551D mutation of CF. Decreases [Cl-] in sweat.
• Side Effects: Increased LFTs, rash, abdominal pain, HA, nausea, dizziness, nasal congestion,
nasopharyngitis, upper resp infxn.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmreview-141117134558-conversion-gate01/85/Pulmonology-Review-157-320.jpg)