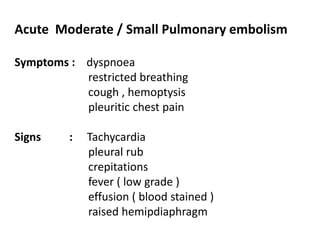
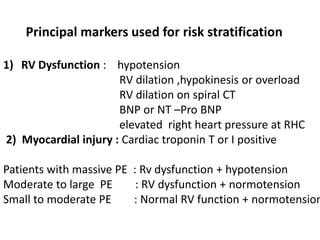
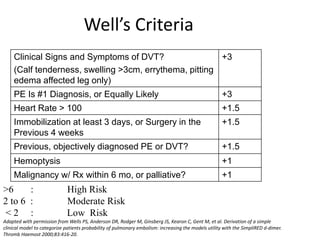
1) Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) is caused by obstruction of pulmonary vessels, usually by blood clots. Risk factors include hypercoagulability, recent surgery or trauma, pregnancy, genetic mutations.
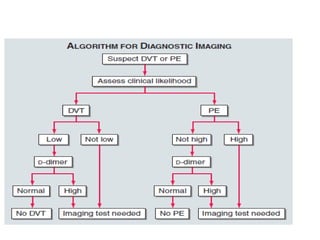
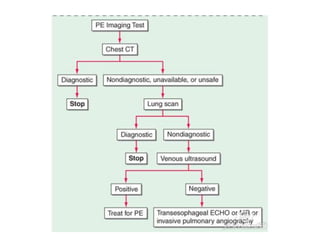
2) Diagnostic tests include D-dimer, chest CT, lung scan, echocardiogram. Chest CT has replaced lung scan as the primary imaging test.
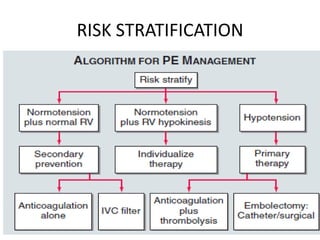
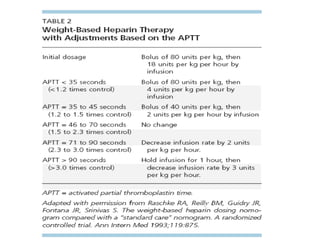
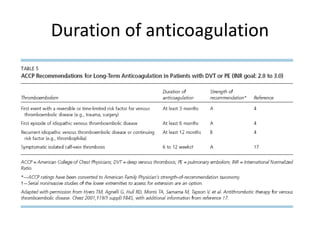
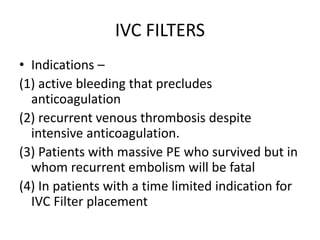
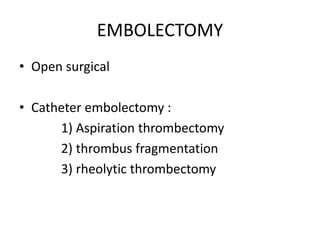
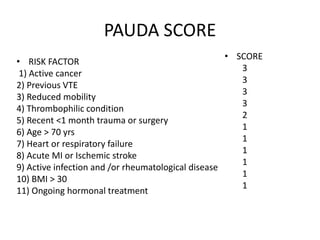
3) Treatment involves resuscitation for massive PTE, anticoagulation with heparin or low molecular weight heparin initially followed by warfarin for at least 3 months, and potentially thrombolysis for selected high-risk cases or inferior vena cava filters for recurrent clots despite


![• Venous thromboembolism[VTE]
DVT PE
Post phlebitic syndrm
chronic
thrombo embolic
pulmonary hypertension](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolism-150110023357-conversion-gate02/85/Pulmonaryembolism-3-320.jpg)