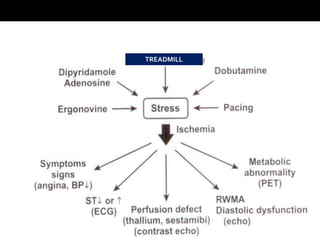
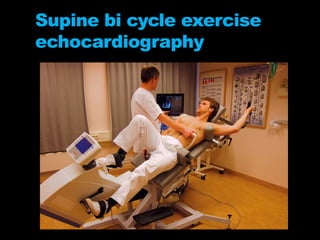
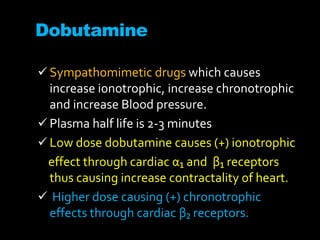
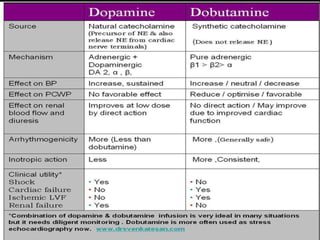
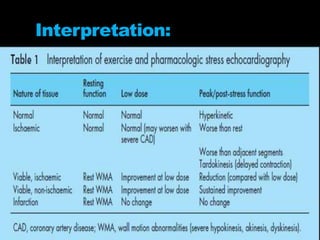
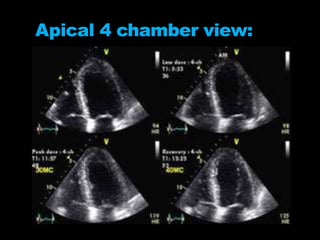
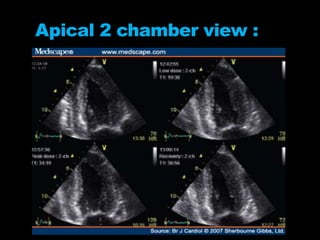
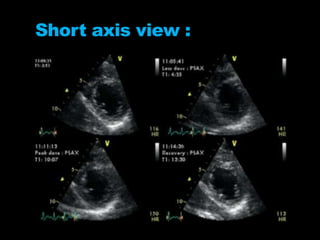
Stress echocardiography involves using cardiac ultrasound imaging along with exercise or pharmacological stressors like dobutamine to detect changes in heart wall motion that indicate reduced pumping function during stress. This can help identify blockages in the arteries to the heart. Dobutamine stress echocardiography involves gradually increasing doses of dobutamine, a drug that increases heart rate and contraction. Images are taken at each dose to detect any new wall motion abnormalities that would suggest ischemia. While it is effective for evaluating coronary artery disease, it also carries risks of side effects like arrhythmias that require emergency drugs like esmolol to reverse. Interpreting any new wall motion abnormalities seen under stress is important for diagnosis.






![Ischemic cascade
Myocardial ischemia due to coronary luminal obstruction
Decreased myocardial perfusion ――> [NS,PET,CPE]
Metabolic changes ――> [ PET scan]
Diastolic dysfunction ――> [Stress Echo]
Systolic dysfunction ――> [Stress Echo]
ECG change ――> [ECG]
Chest pain ――> [History]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stressechocardiography-140519111752-phpapp01/85/Stress-echocardiography-12-320.jpg)