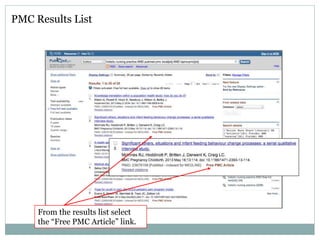
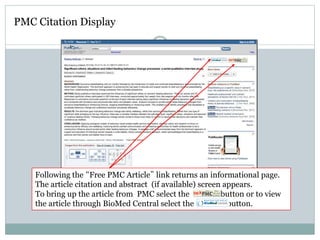
PubMed is a free database of over 23 million citations and abstracts for biomedical literature from Medline, life sciences journals, and online books. It is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM). PubMed provides bibliographic information and links to full-text content from publishers and libraries. Users can search PubMed using keywords, controlled vocabularies like MeSH, or advanced search techniques and filters to find relevant journal articles and resources.