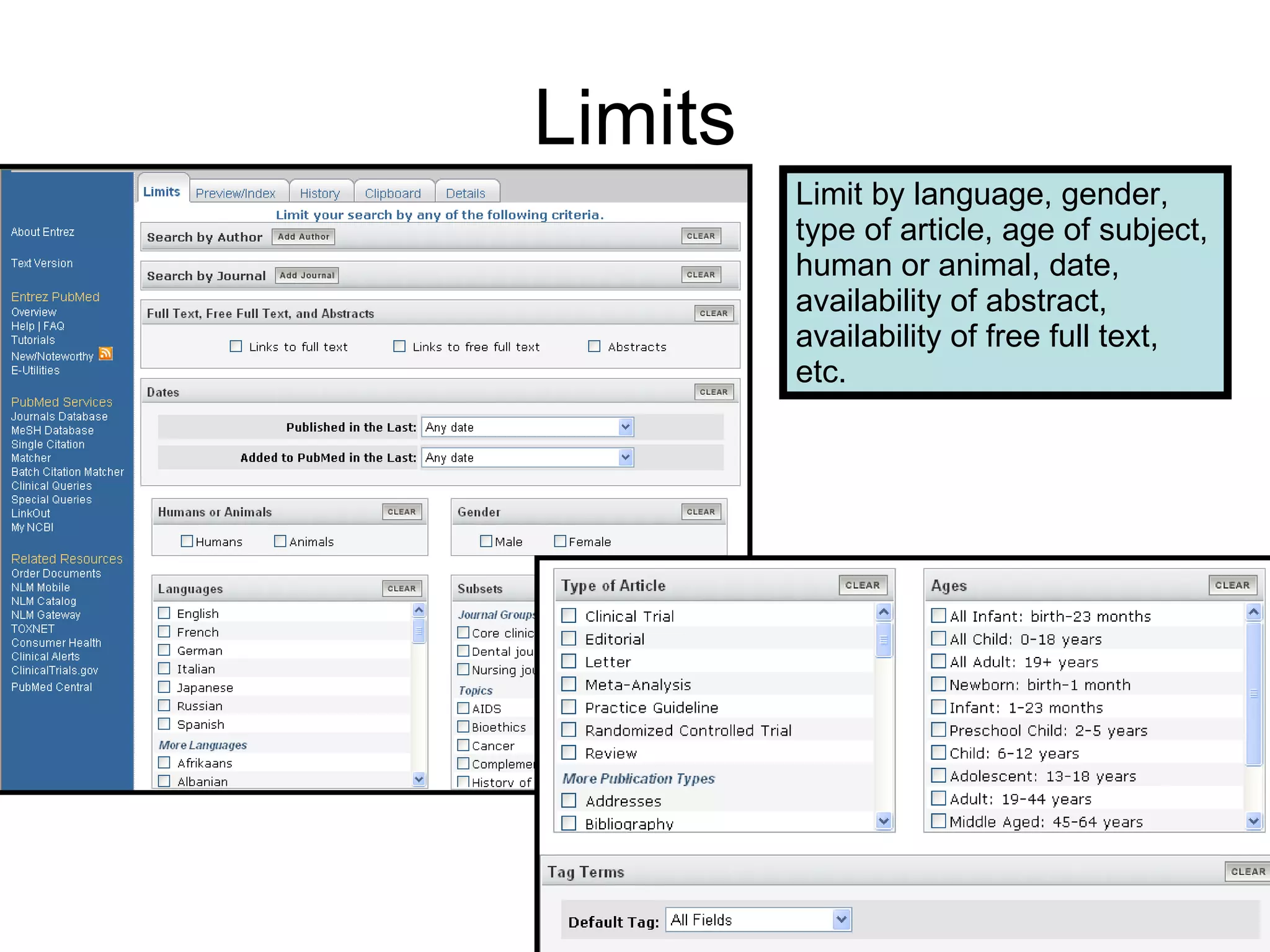
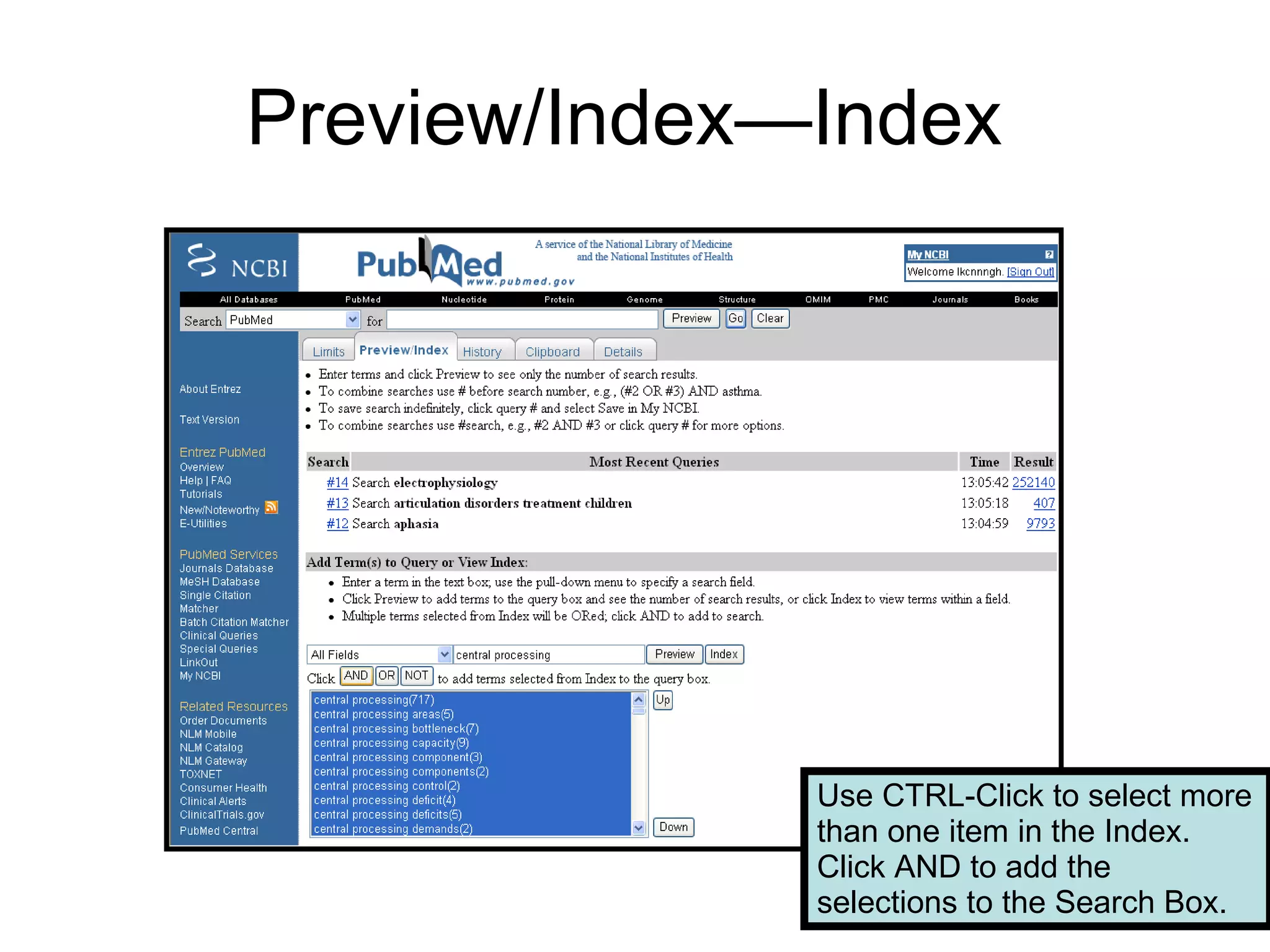
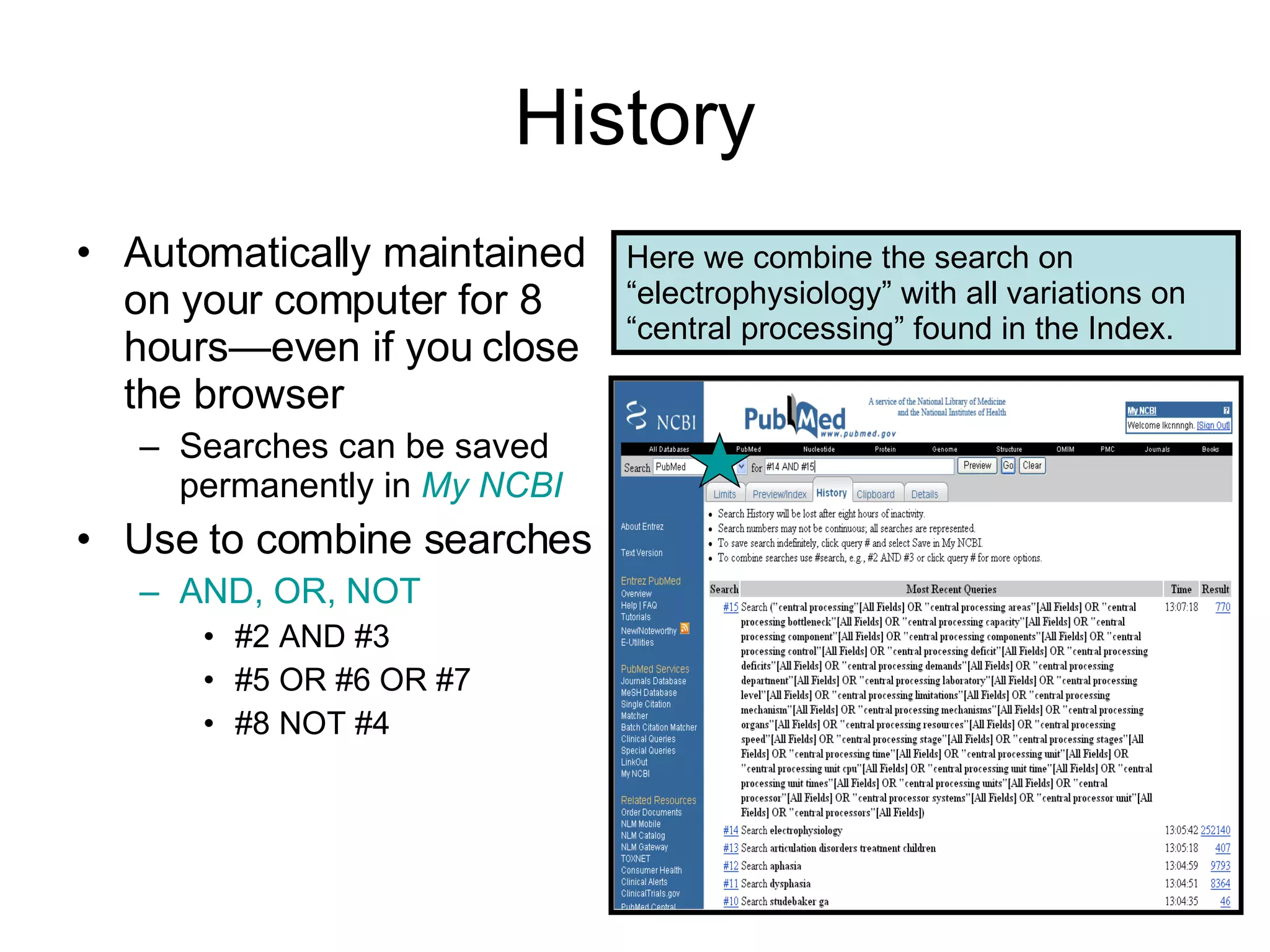
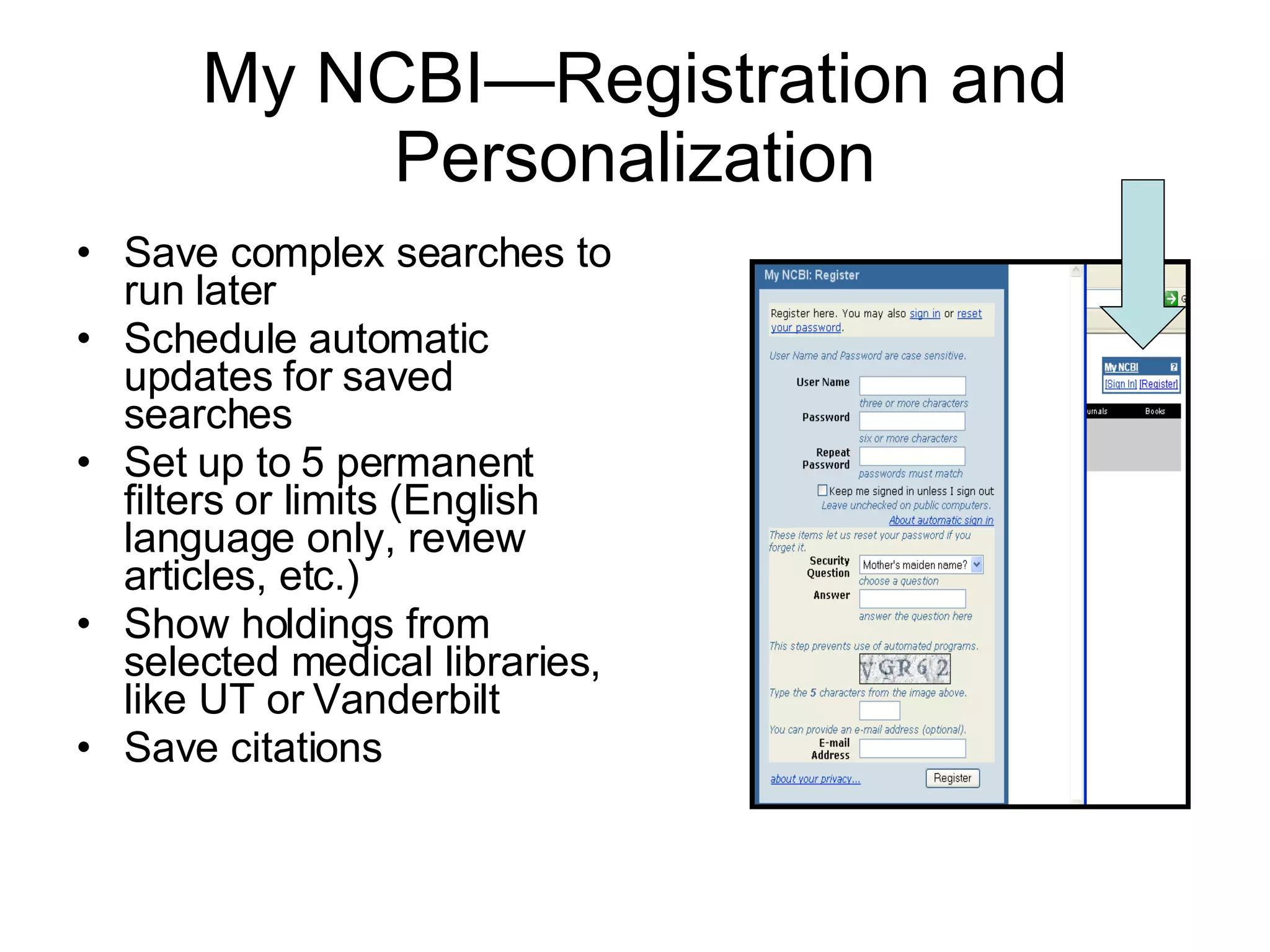
PubMed is a database that indexes biomedical literature and provides access to citations and abstracts. It contains more content than MEDLINE and is interconnected with other National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) databases. Advanced search features allow for focused searches using filters, limits, and interconnected resources. Personalization features allow users to save searches, citations, and set viewing preferences through a My NCBI account.







![Basic Search Tips Authors—last name first, at least one initial, no punctuation Example: Studebaker GA Subject/keyword concepts—string in words, no Boolean connectors Example: dysphasia children treatment (("aphasia"[TIAB] NOT Medline[SB]) OR "aphasia"[MeSH Terms] OR dysphasia[Text Word]) AND (("child"[TIAB] NOT Medline[SB]) OR "child"[MeSH Terms] OR children[Text Word]) AND ("therapy"[Subheading] OR ("therapeutics"[TIAB] NOT Medline[SB]) OR "therapeutics"[MeSH Terms] OR treatment[Text Word]) TRANSLATION=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ausppubmed2008-1226454712036162-8/75/PubMed-AUSP-2008-9-2048.jpg)