Embed presentation
Download to read offline




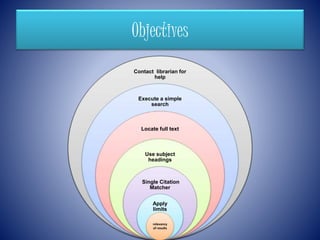
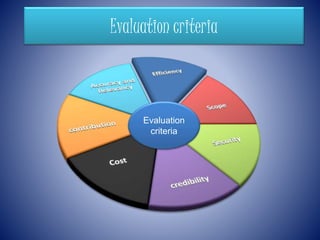
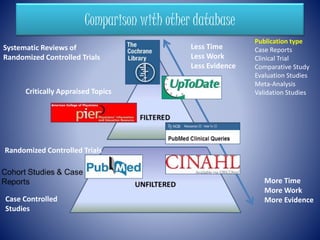




PubMed is a free resource developed and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information that covers journal articles in medicine, nursing, dentistry, veterinary medicine, and healthcare. It contains over 24 million citations for biomedical literature from 5,200 medical journals in 40 languages dating back to 1949 and is updated daily. PubMed also provides links to other relevant websites and the NCBI's molecular biology resources.









