This document provides an overview of searching PubMed, including:
I. PubMed searches the MEDLINE database and provides access to over 21 million records and abstracts indexed with Medical Subject Headings (MeSH).
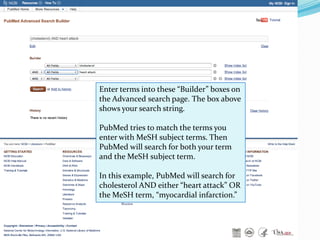
II. MeSH terms standardize topics across articles and help retrieve related articles that use different terminology for the same concept.
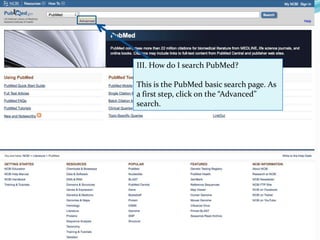
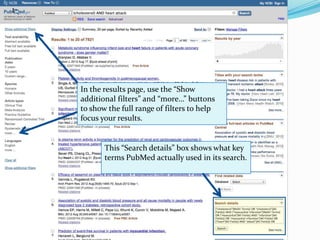
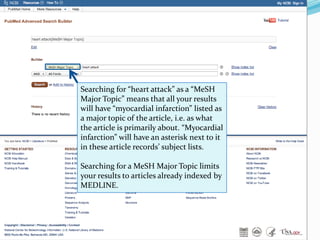
III. Searching PubMed involves using keywords that are matched to MeSH terms, and filters can then focus results; searching for a term as a "MeSH Major Topic" limits to articles where it is a primary topic.
IV. Full text of articles can be accessed through setting preferences in a NCBI account, using the UST OneSearch database which includes Pub