Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times



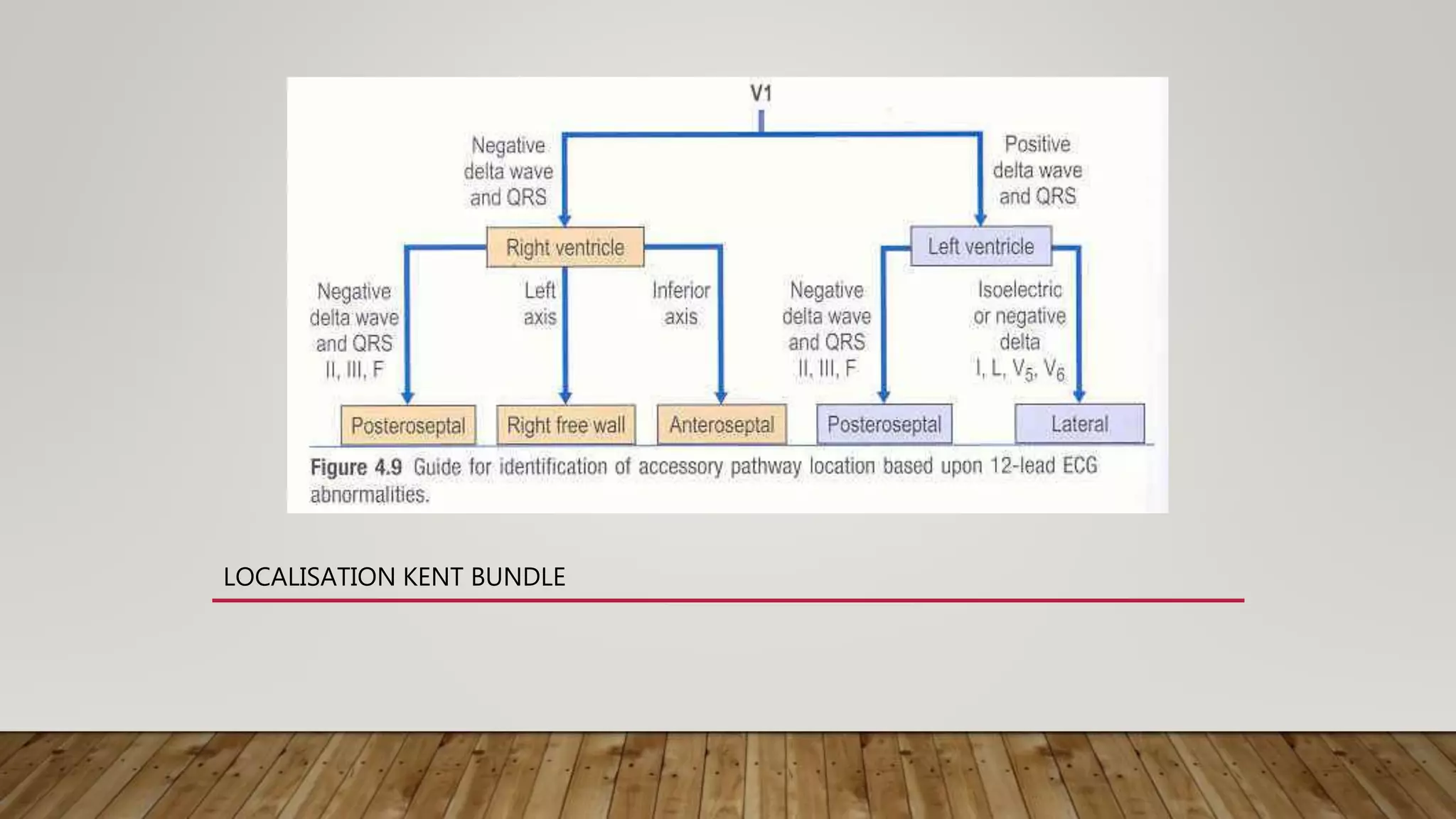



The document discusses conditions that can mimic myocardial infarction through changes in ECG readings, including WPW preexcitation, IHSS, LVH, and others. A case vignette illustrates a 62-year-old woman with a unique ECG pattern indicative of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. The document emphasizes the importance of accurate ECG interpretation to differentiate these conditions.





