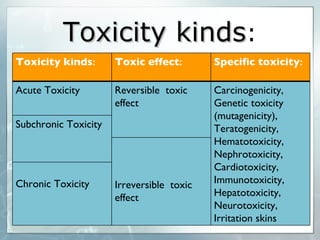
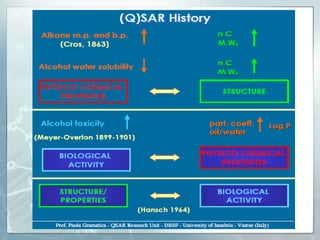
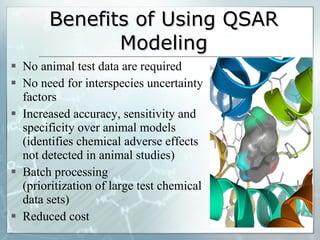
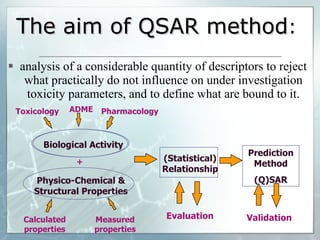
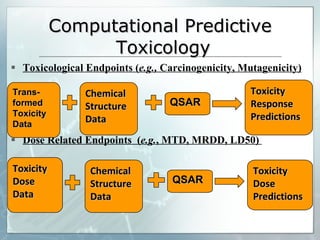
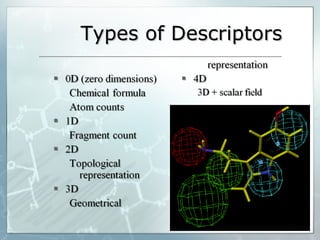
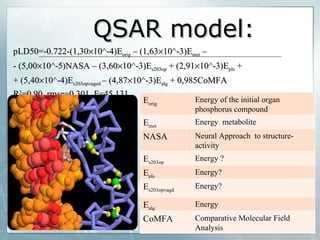
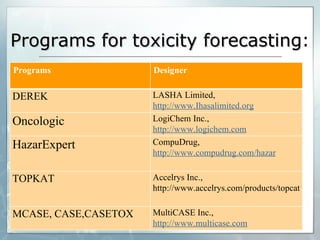
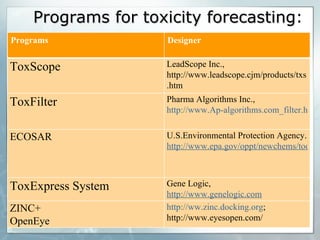
The document discusses computer-aided prediction of chemical toxicity. It defines key terms like toxicology, toxicity, and xenobiotics. It then describes using quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling and molecular descriptors to predict toxicity without animal testing. This allows prioritizing chemicals for safety assessment and identifies effects not seen in animal studies. It lists several software programs that use these methods for predictive toxicology.