Embed presentation
Downloaded 36 times


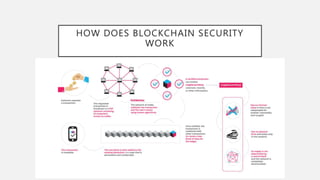
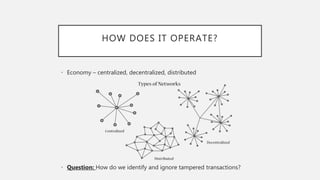
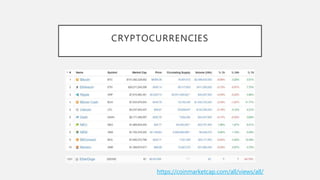

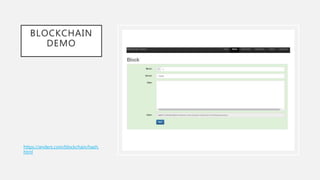
Blockchain security works by having each transaction verified as a digital "block" before entering the system. Computers on the network compete to solve cryptographic puzzles to validate blocks and add them to the blockchain in a verifiable order. This process cuts down on fraud while allowing transactions to occur safely and quickly in a decentralized way. Blockchain has many uses including cryptocurrency, supply chains, financial services, and more.










