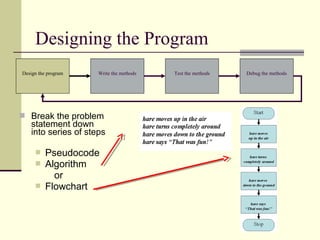
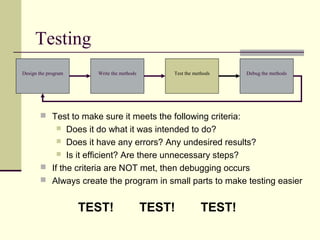
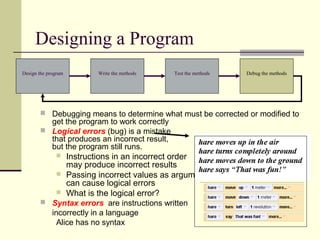
The document outlines the program development cycle, which involves designing the program, writing methods to implement the design, testing the methods, and debugging any errors found. It describes each step in more detail: in the design step, the problem is broken down into a series of steps using pseudocode or a flowchart; methods are then written to reflect these steps; testing ensures the program meets its intended purpose without errors or inefficiencies; and debugging identifies and corrects any logical errors in the program's instructions or implementation.