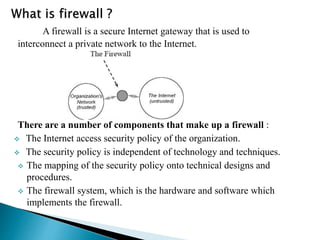
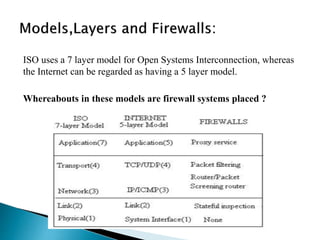
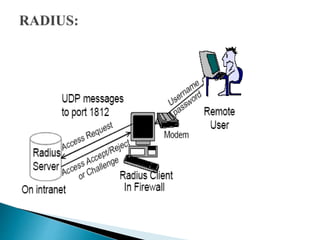
Firewalls are used to securely interconnect private networks to the Internet and protect them from external threats. They implement an organization's security policy by filtering network traffic and only allowing authorized connections based on properties like source/destination addresses and ports. There are different types of firewalls that operate at various layers of the network model and use techniques like packet filtering, application proxies, authentication, and content inspection to enforce security. Organizations should choose a firewall configuration based on their specific security needs, from dual-homed gateways to screened subnets in demilitarized zones.