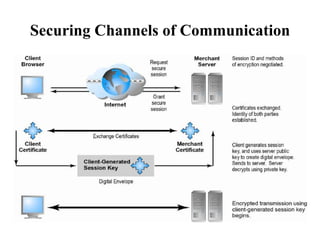
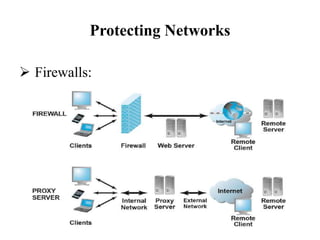
This document discusses security measures for e-commerce, including securing communication channels through SSL/TLS and VPNs, protecting networks with firewalls and proxy servers, and protecting servers and clients with operating system security enhancements and anti-virus software. It provides details on how these technologies establish secure connections, filter traffic, prevent unauthorized access, and protect against viruses and hackers. The goal is to secure e-commerce transactions and sensitive information from interception or modification during transmission.