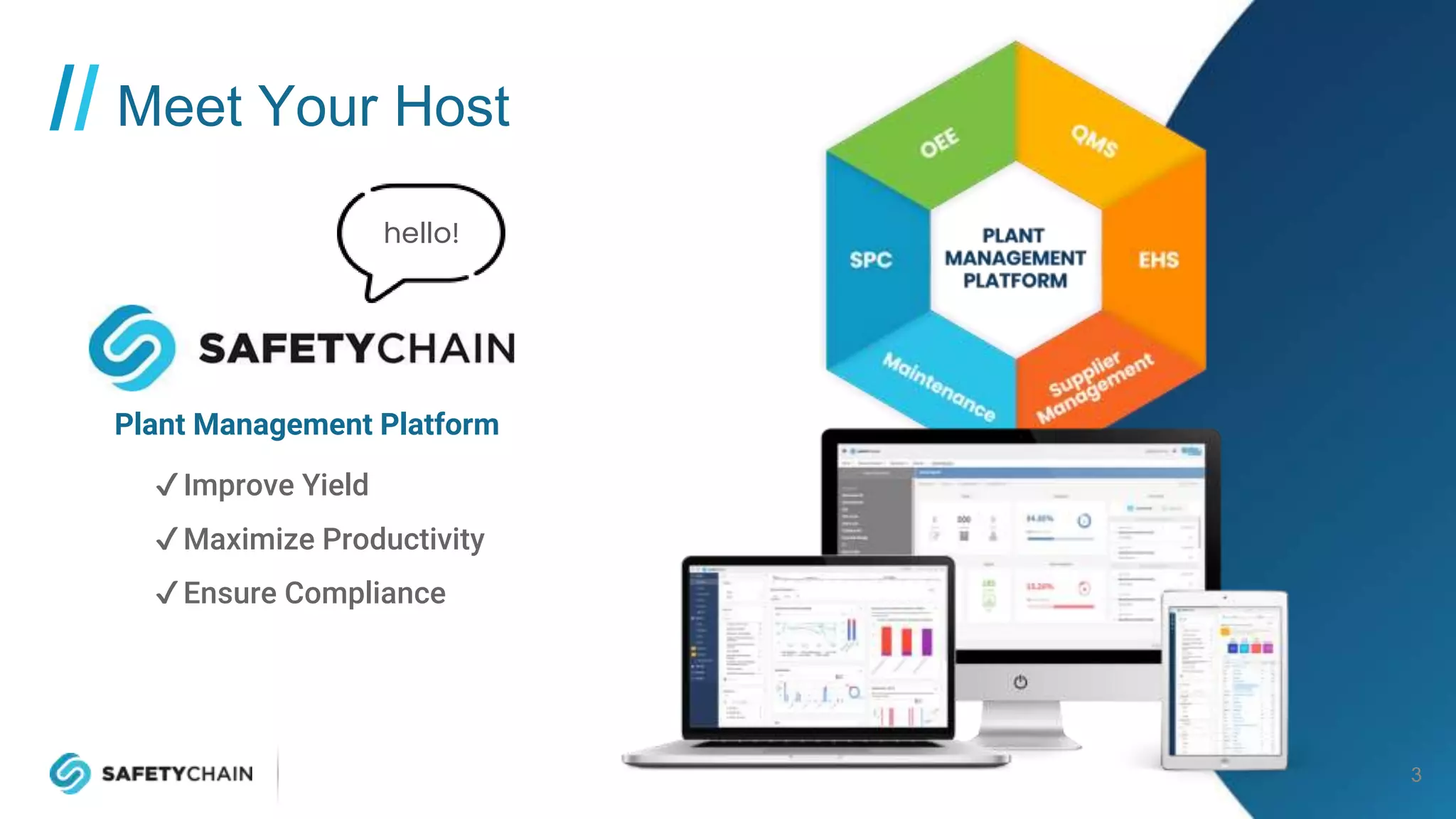
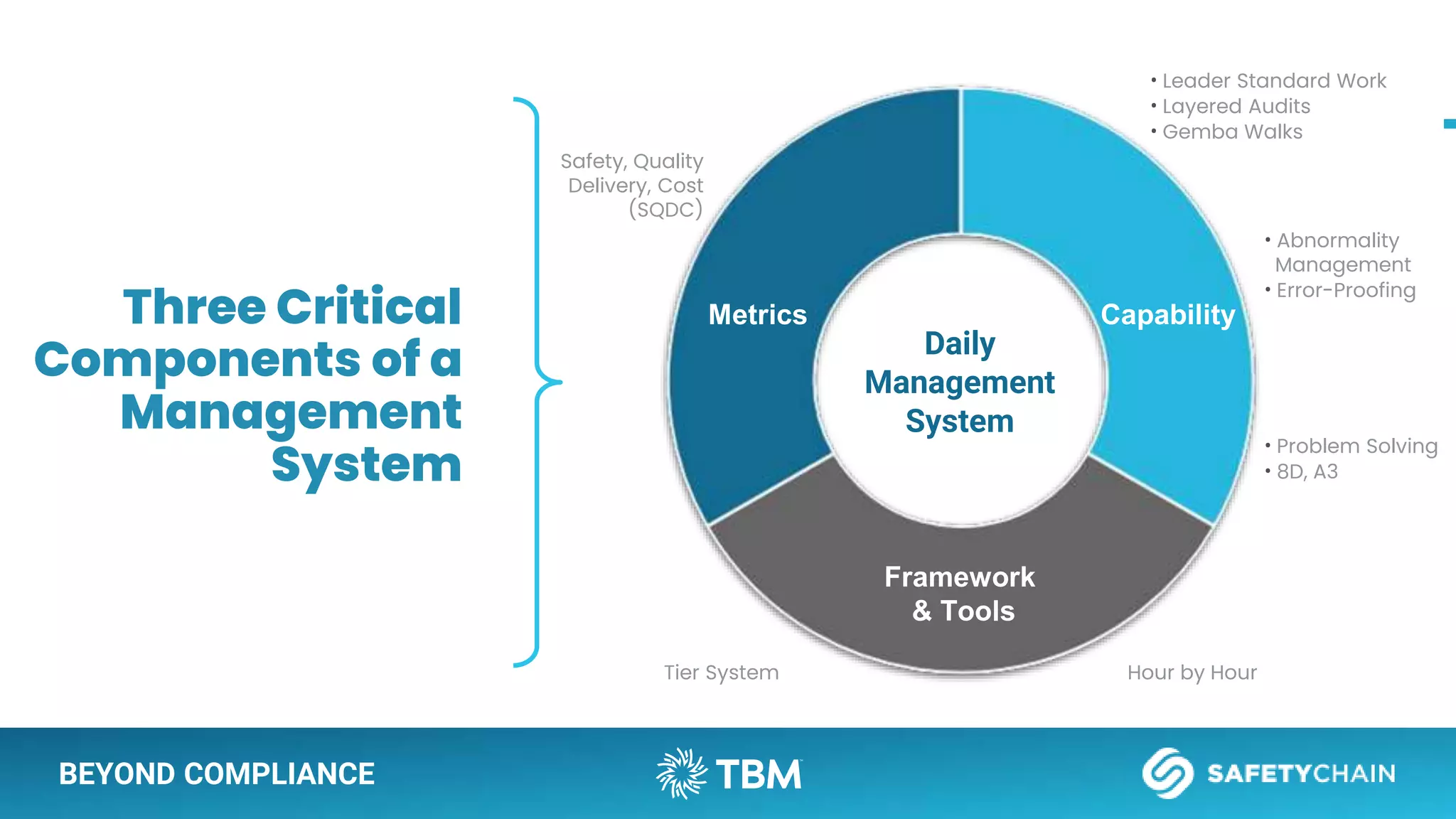
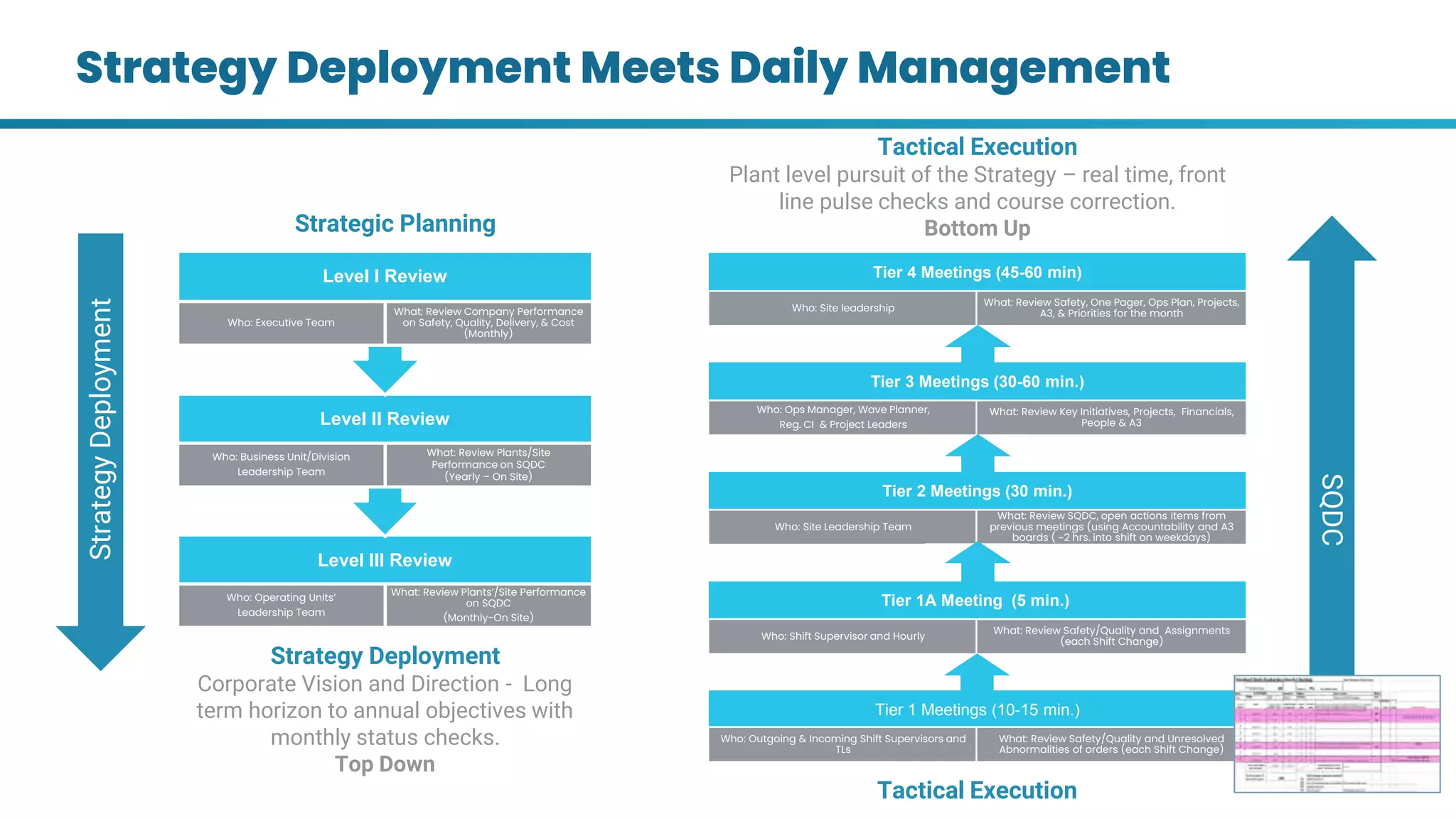
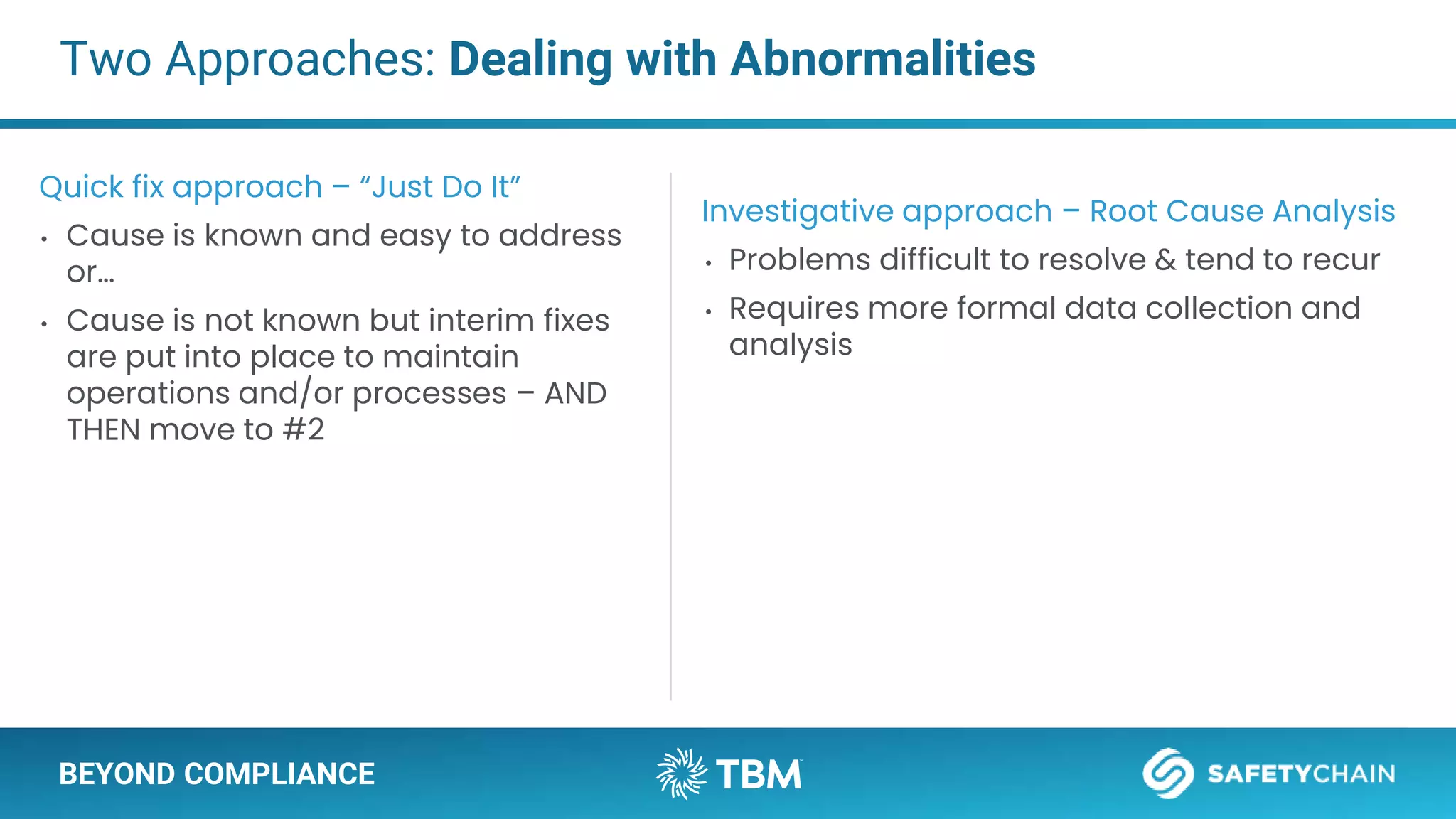
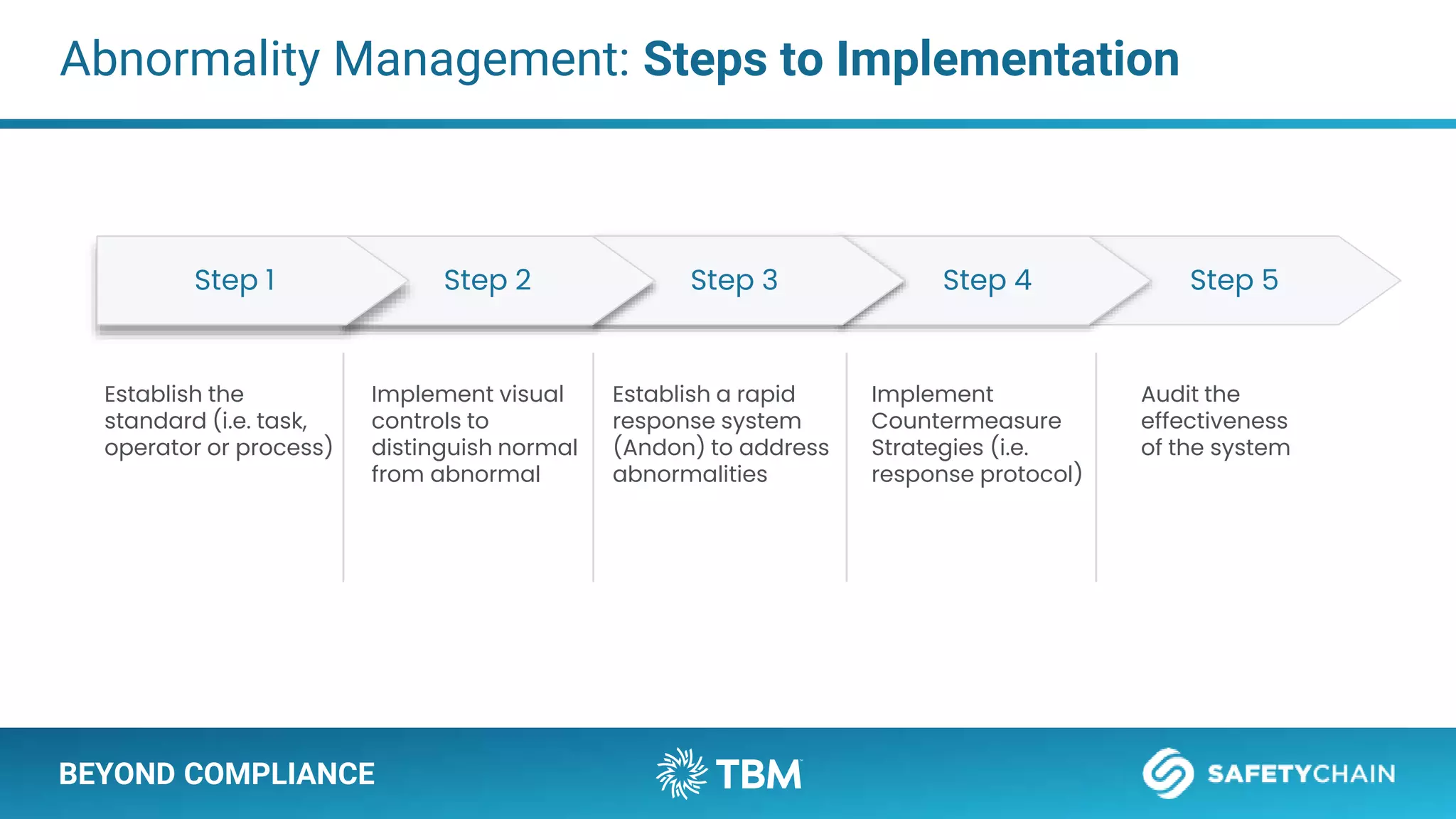
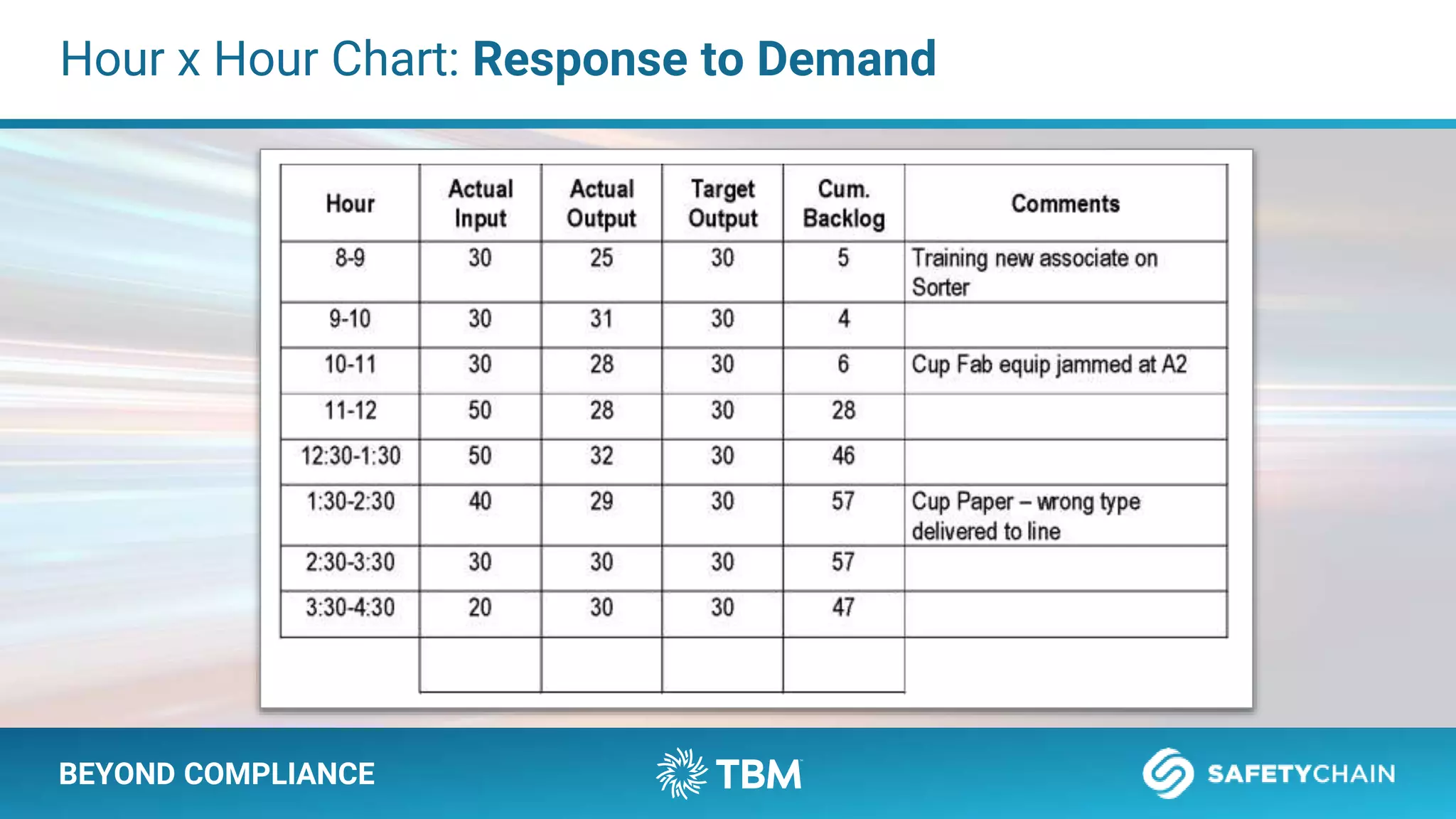
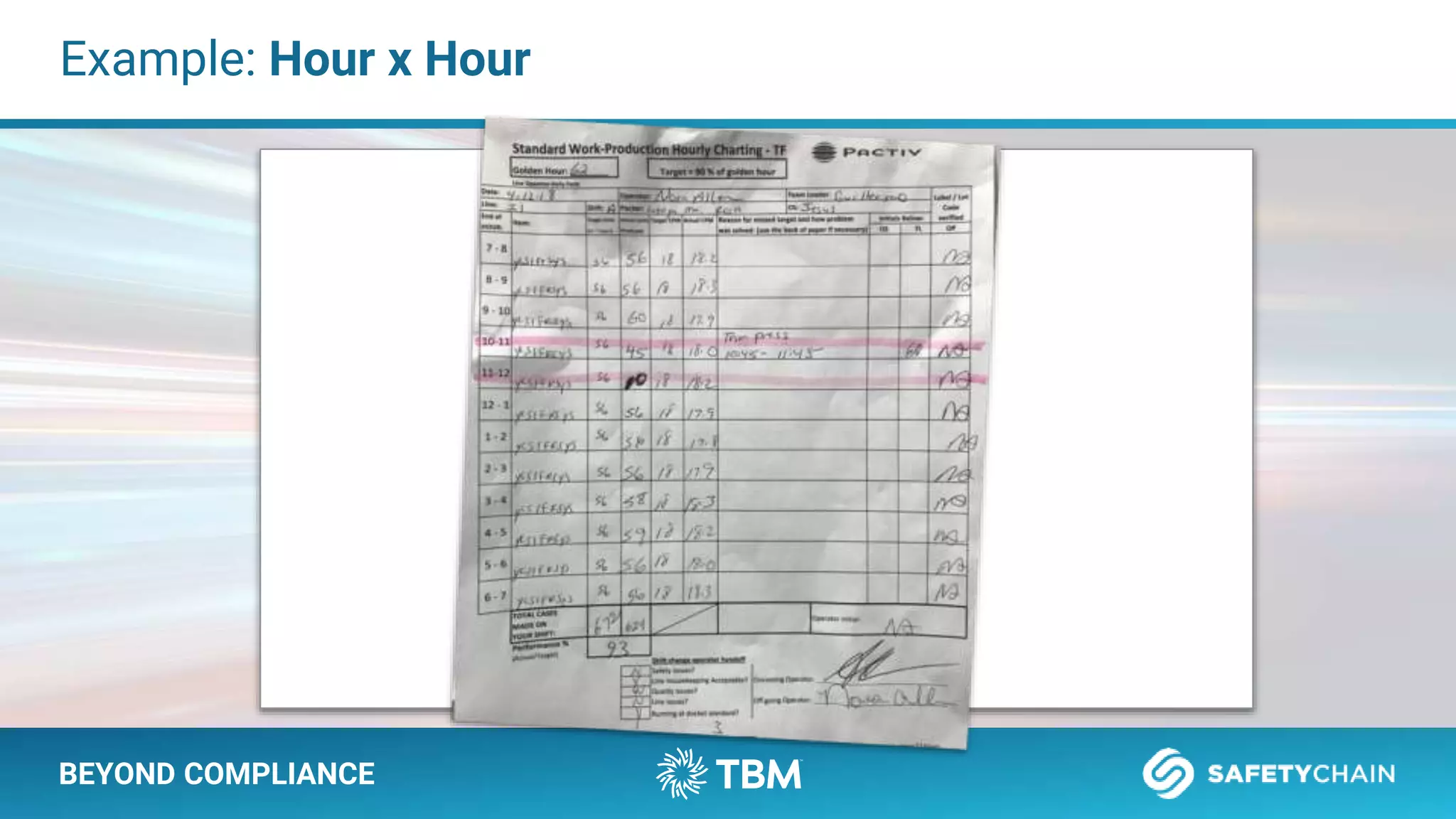
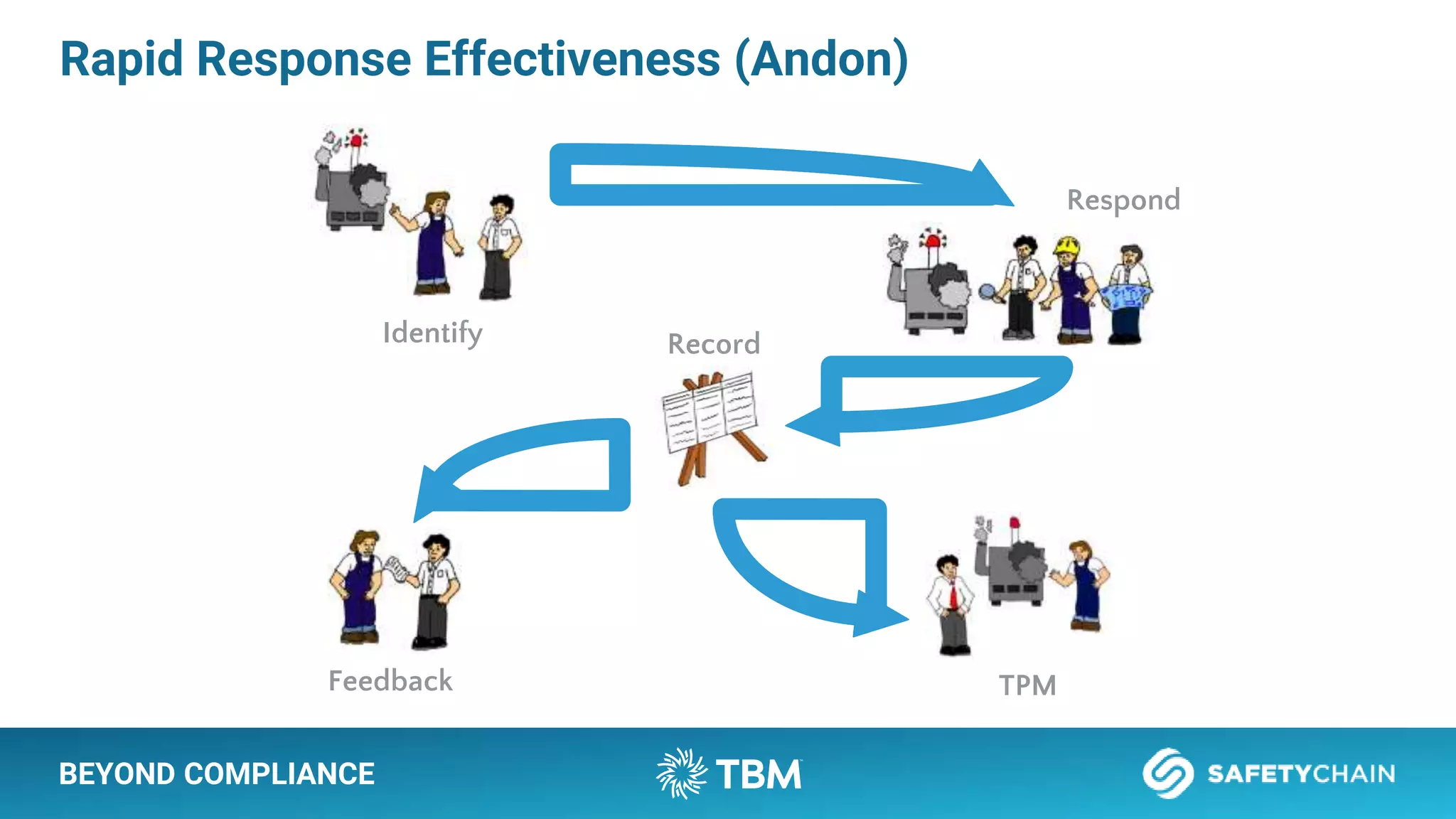
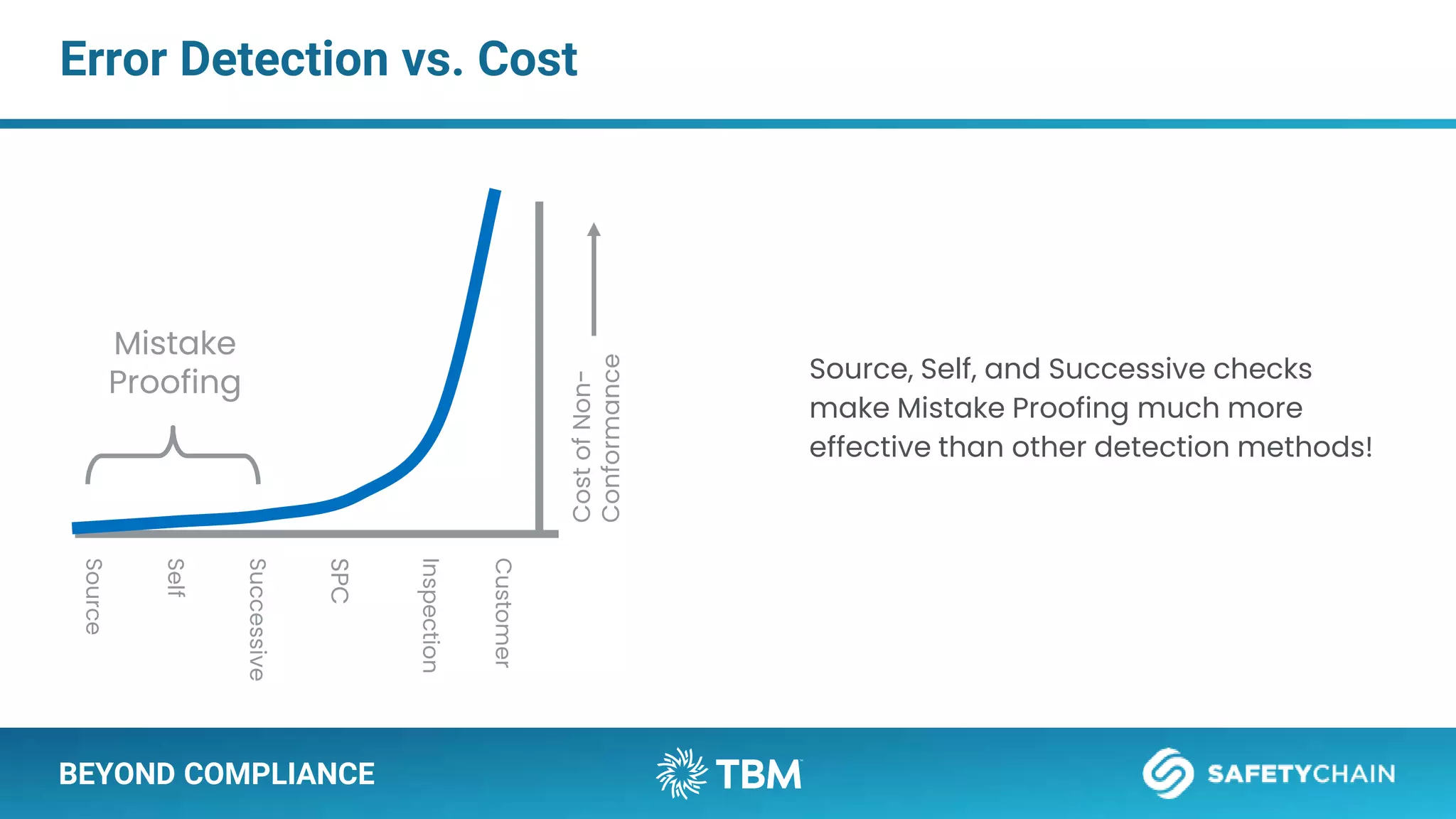
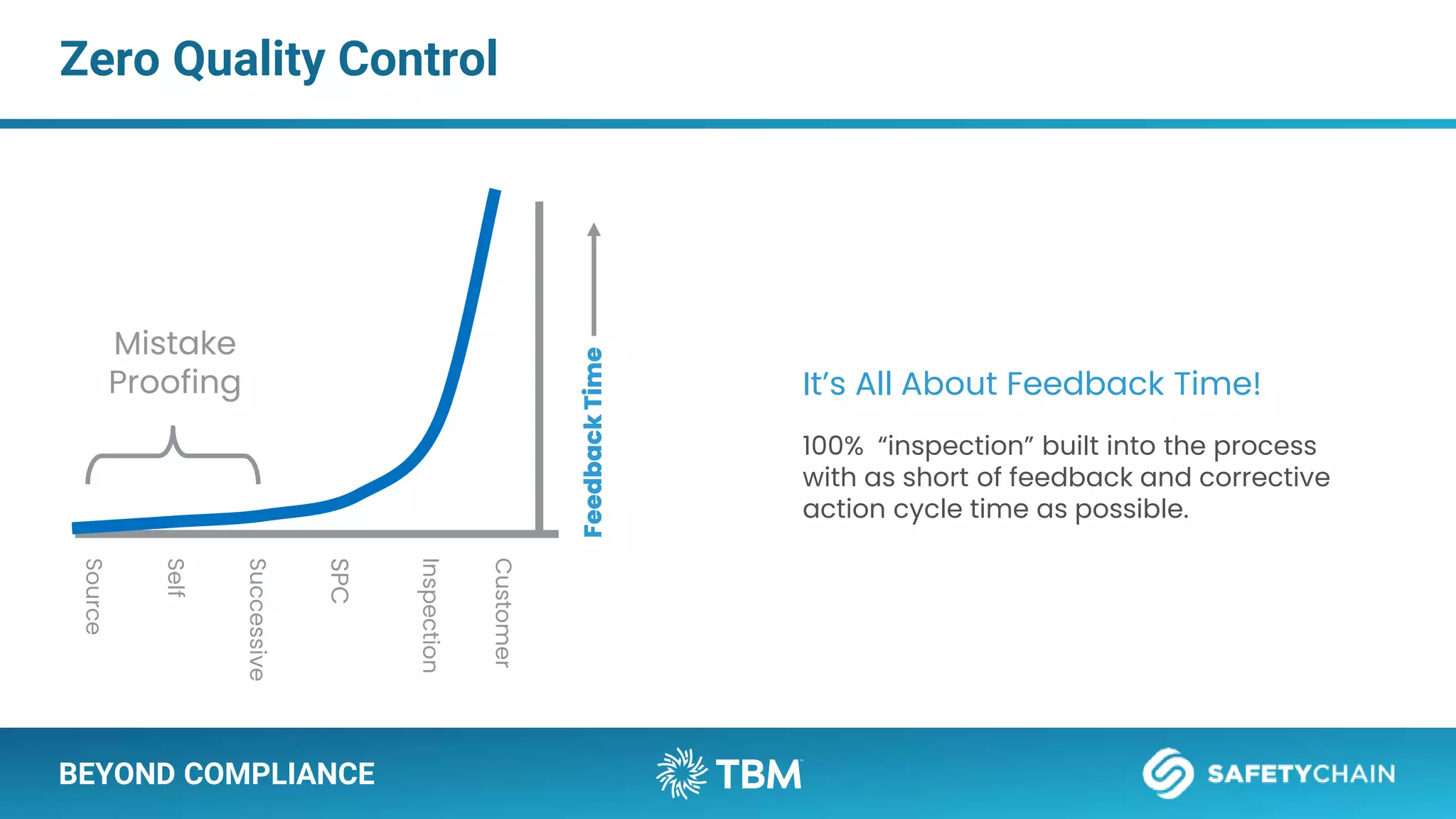
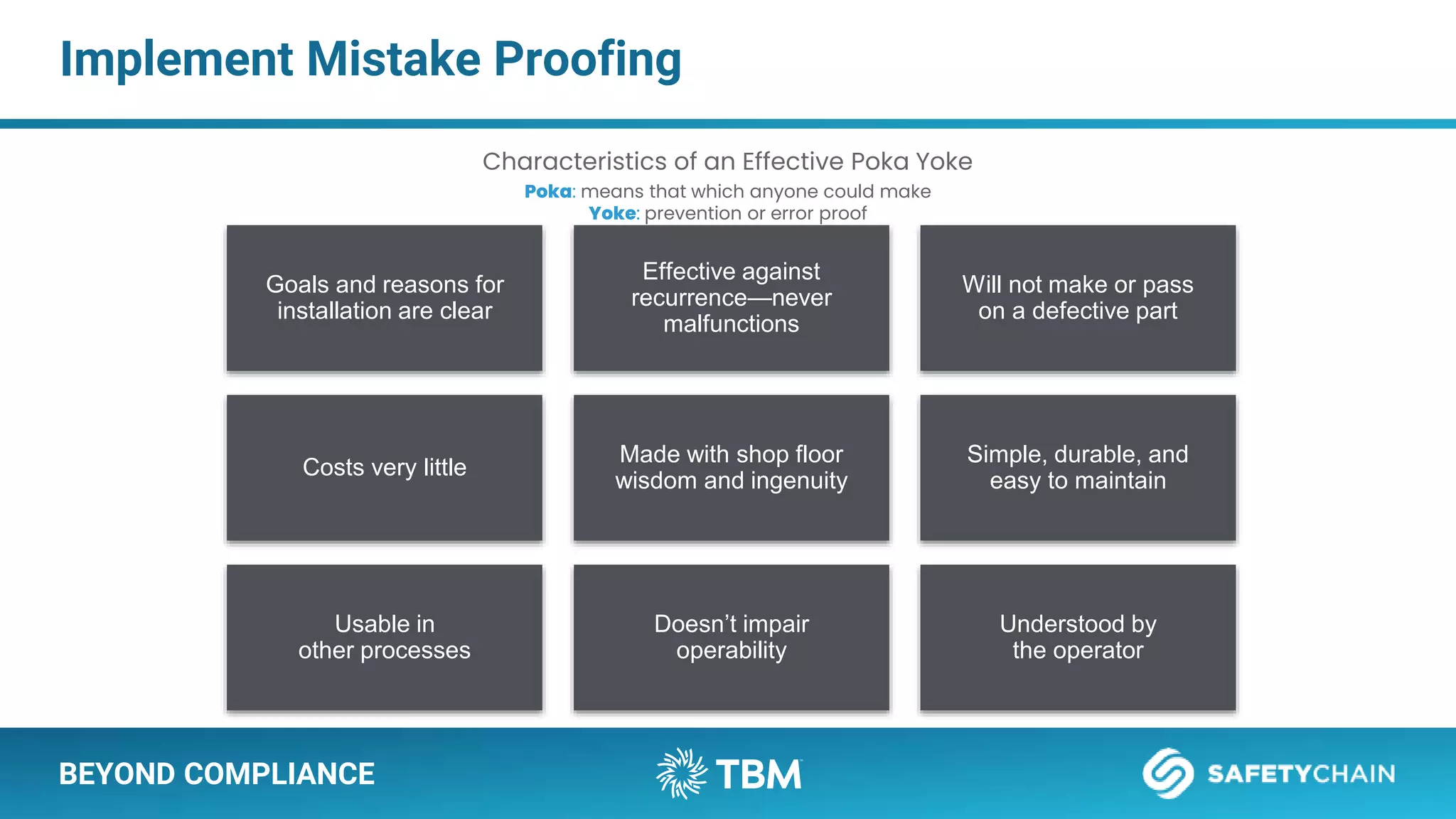
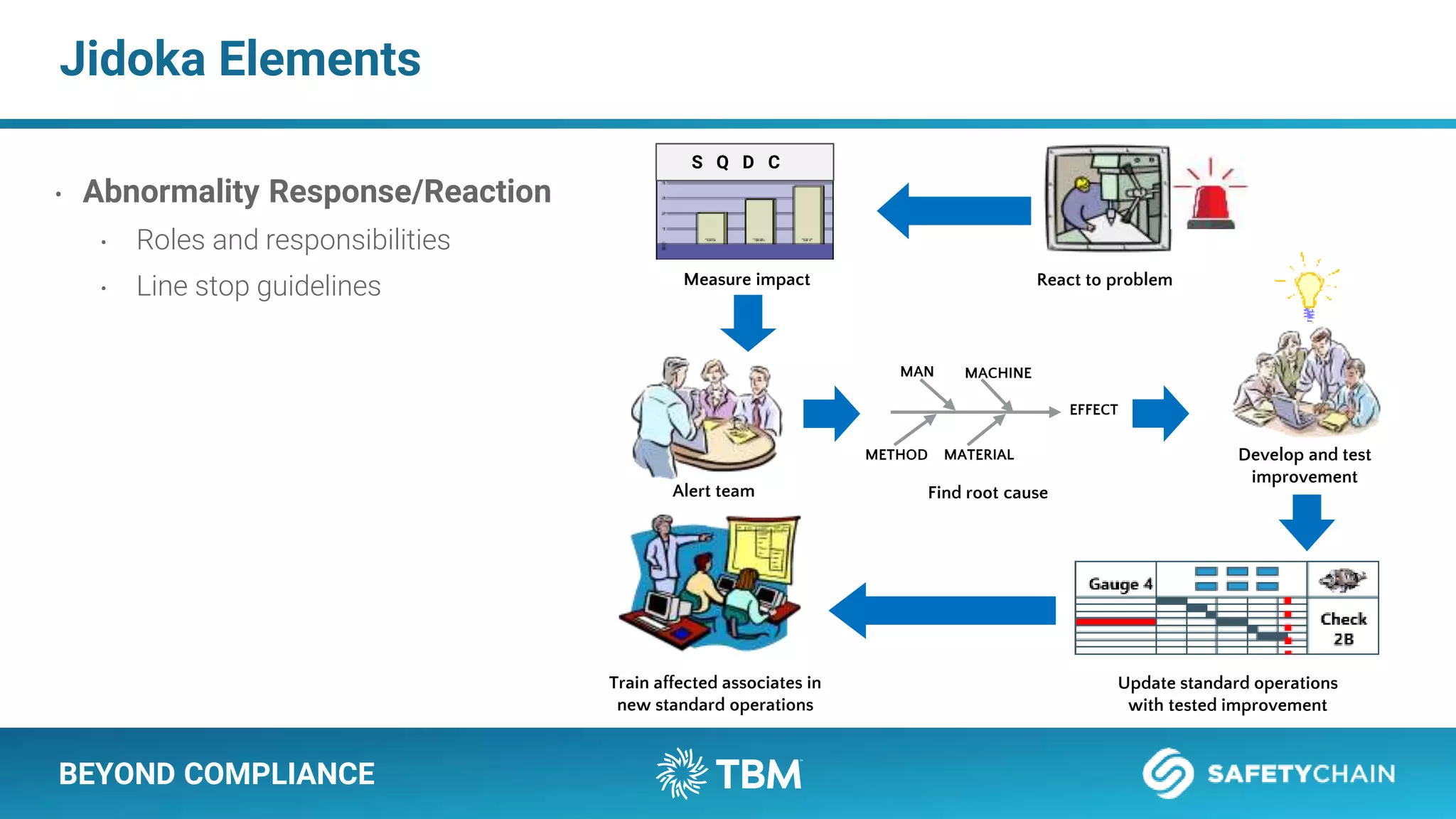
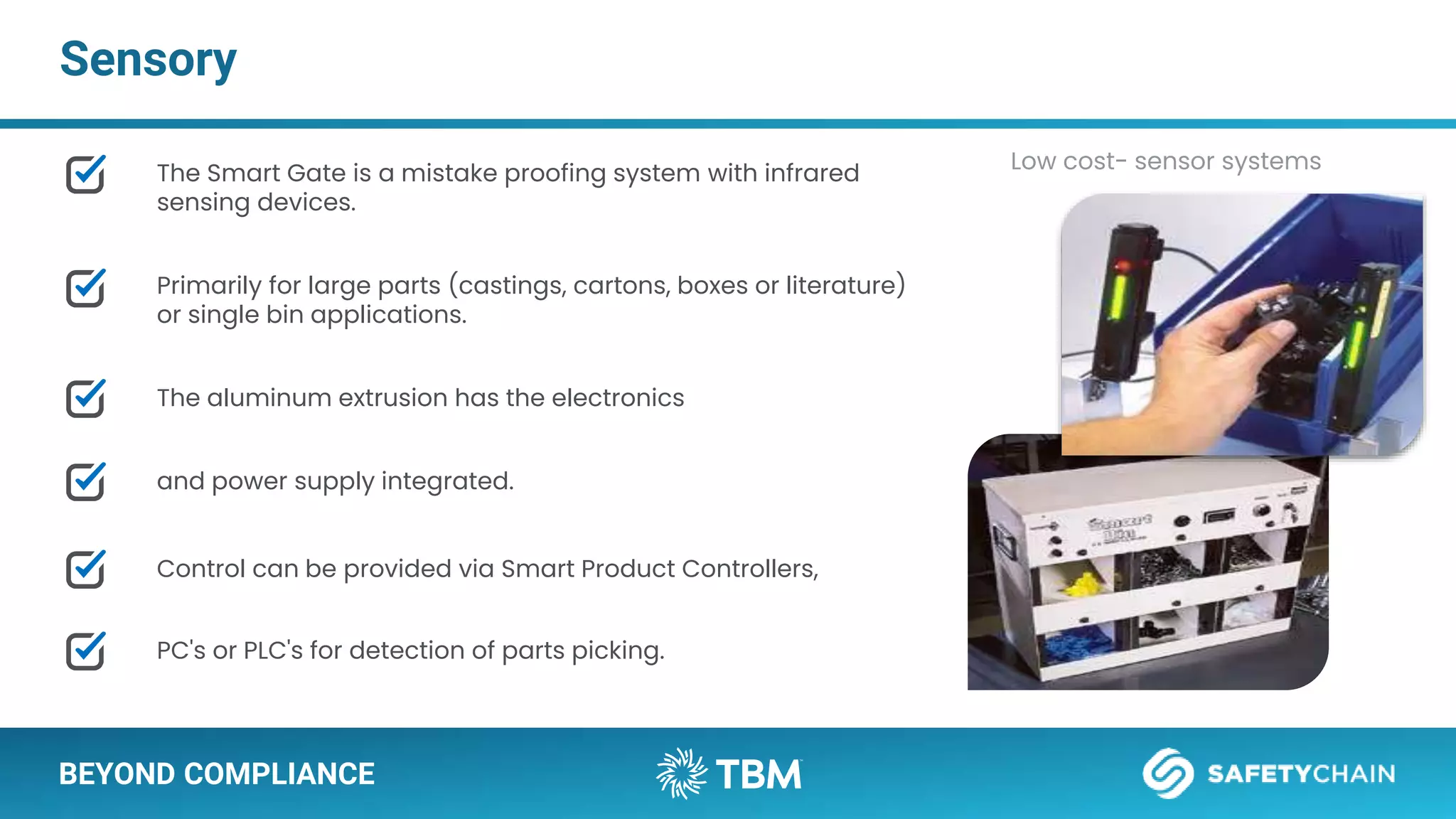
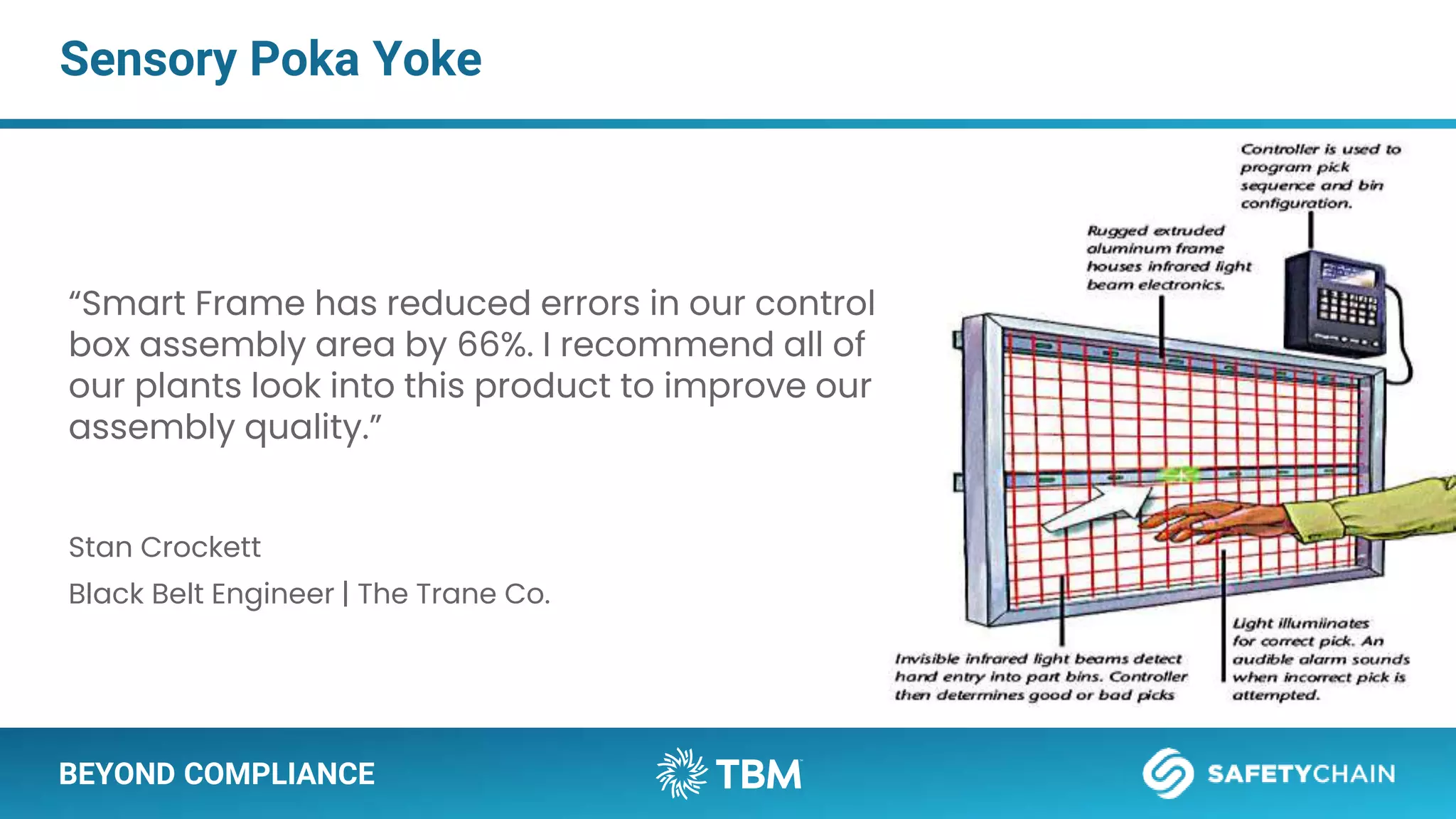
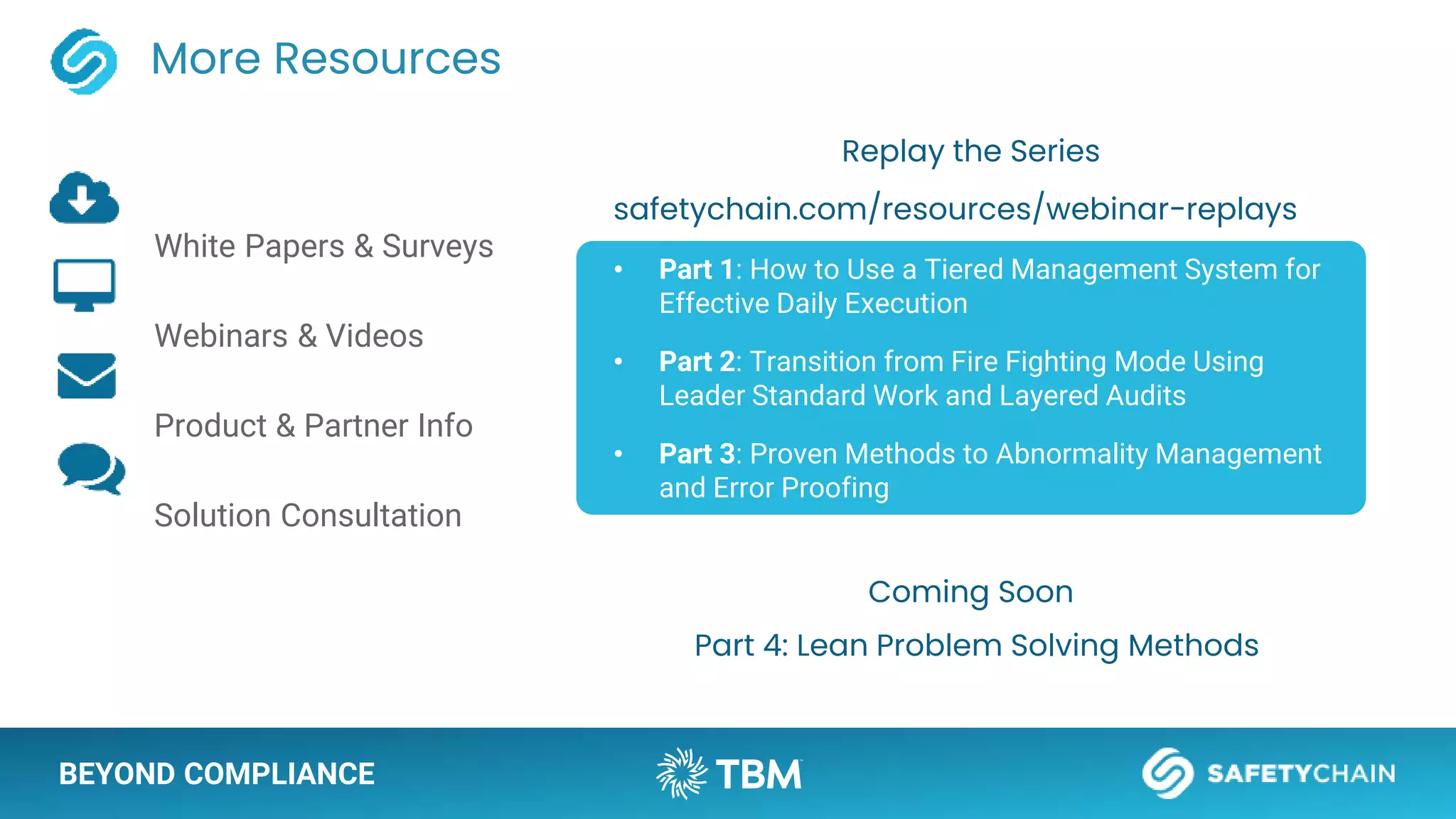
The document outlines a webinar and podcast series focused on proven methods for abnormality management and error-proofing in process manufacturing. It details the roles of experienced consultants, a comprehensive management system, and strategies for improving operational efficiency and compliance through tiered management systems and visual controls. The content emphasizes the importance of rapid response systems, mistake-proofing techniques, and the continuous improvement culture to enhance productivity and minimize errors.