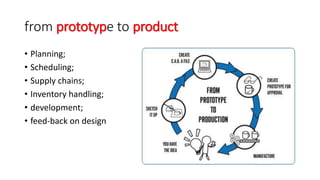
The document discusses the process of rapid prototyping in engineering design, emphasizing its role in evaluating, modifying, and finalizing product designs. It highlights the importance of testing prototypes for functionality and design viability, and how early design modifications can reduce costs. Additionally, it addresses engineering design as a method for problem solving, incorporating planning, scheduling, and supply chain management.