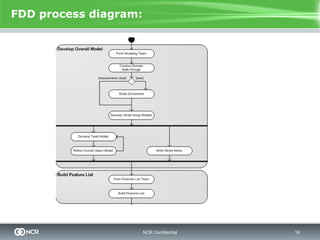
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is an agile software development process that focuses on developing features according to a list prioritized by business value. It involves short iterative development cycles where a feature is designed, built, and tested within a time-boxed iteration. Key aspects of FDD include feature teams made up of different roles that work together to implement features, with activities like design reviews, coding reviews, and release meetings. FDD aims to provide predictability through tracking progress at the feature level.