Vancomycin is used to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus when other antibiotics cannot be used. It works best when maintained above the minimum inhibitory concentration for the target bacteria. Vancomycin should be administered intravenously in dilute solution at a slow rate to avoid infusion reactions and tissue damage from extravasation. Dosing is based on creatinine clearance and weight, with levels monitored regularly due to risks of toxicity, especially to the kidneys.




![Dose Calculations
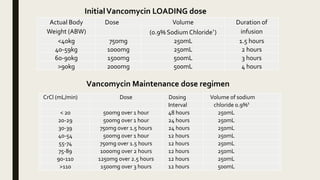
■ Calculate loading dose and maintenance dose based on creatinine clearance (CrCl)
using online calculator
■ If CrCl is not known use actual body weight for calculating initial loading dose.
Calculate maintenance dose after calculatingCrCl
‘Cockcroft Gault’ equation can be used to estimate creatinine clearance (CrCl)
CrCl = [140-age (years)] x weight(kg) x 1.23 (male) or 1.04(female)
(mL/min) serum creatinine(μmol / L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protocolofuseforvancomycin-170427034015/85/Protocol-of-use-for-vancomycin-5-320.jpg)