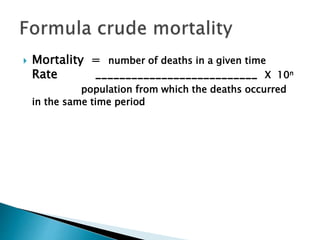
This document discusses various health indicators that can be used to measure and evaluate health status at the community and country level. It describes demographic indicators like mortality rates (crude death rate, infant mortality rate, child mortality rate, maternal mortality rate), life expectancy, and proportional mortality rate. It also discusses health service indicators like population to healthcare resource ratios and immunization coverage rates. Overall, it recommends using multiple indicators together to comprehensively evaluate health status.