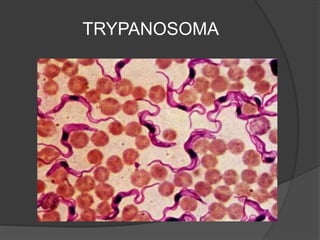
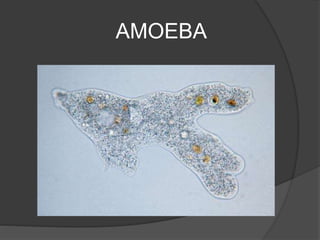
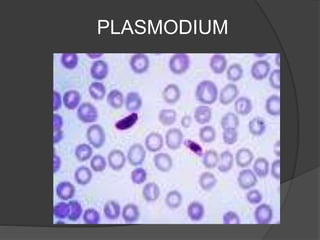
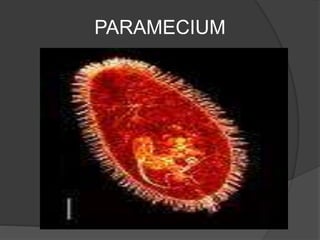
Protists have more complex structures and functions than bacteria, including specialized organelles. They can be classified as plantlike, funguslike, or animal-like. Three groups of algae - green algae, kelp, and red coral algae - are considered plantlike protists. Plantlike protists also include phytoplankton like euglena and diatoms that provide food for aquatic animals. Funguslike protists break down dead organic matter as saprophytes. Animal-like protists, also called protozoans, are heterotrophic and include zooflagellates, sporozoa, and ciliates like trypanosoma, amoeba, plasmodium,