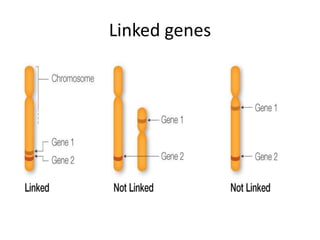
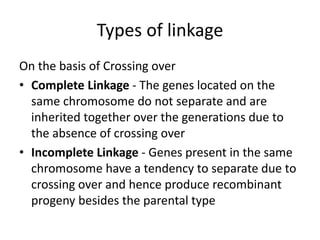
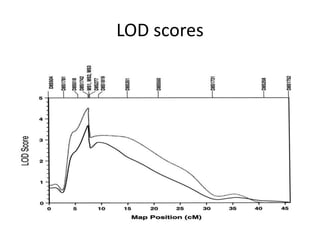
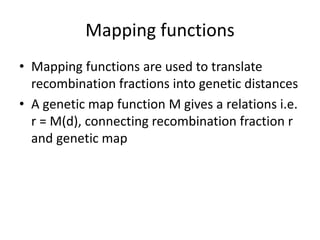
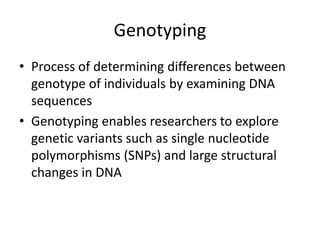
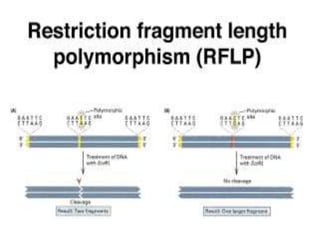
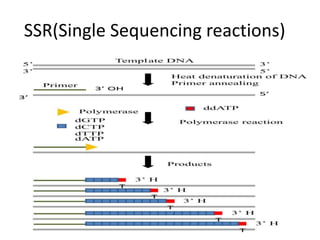
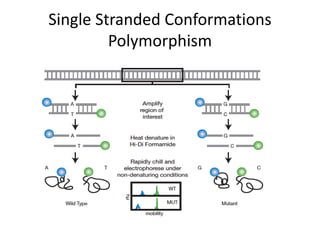
Genetic linkage analysis and genotyping techniques are used to map disease genes to their chromosome locations. Linkage describes how closely linked genes are inherited together on a chromosome. Complete linkage means genes do not cross over, while incomplete linkage means genes can separate during crossing over. Linkage analysis uses techniques like recombination fraction, LOD scores, and Haldane mapping functions to statistically map traits to chromosomes. Genotyping determines genetic differences by examining DNA sequences, and can analyze whole genomes, targeted regions, or custom panels of variants. It enables studying SNPs, CNVs, and structural variants.