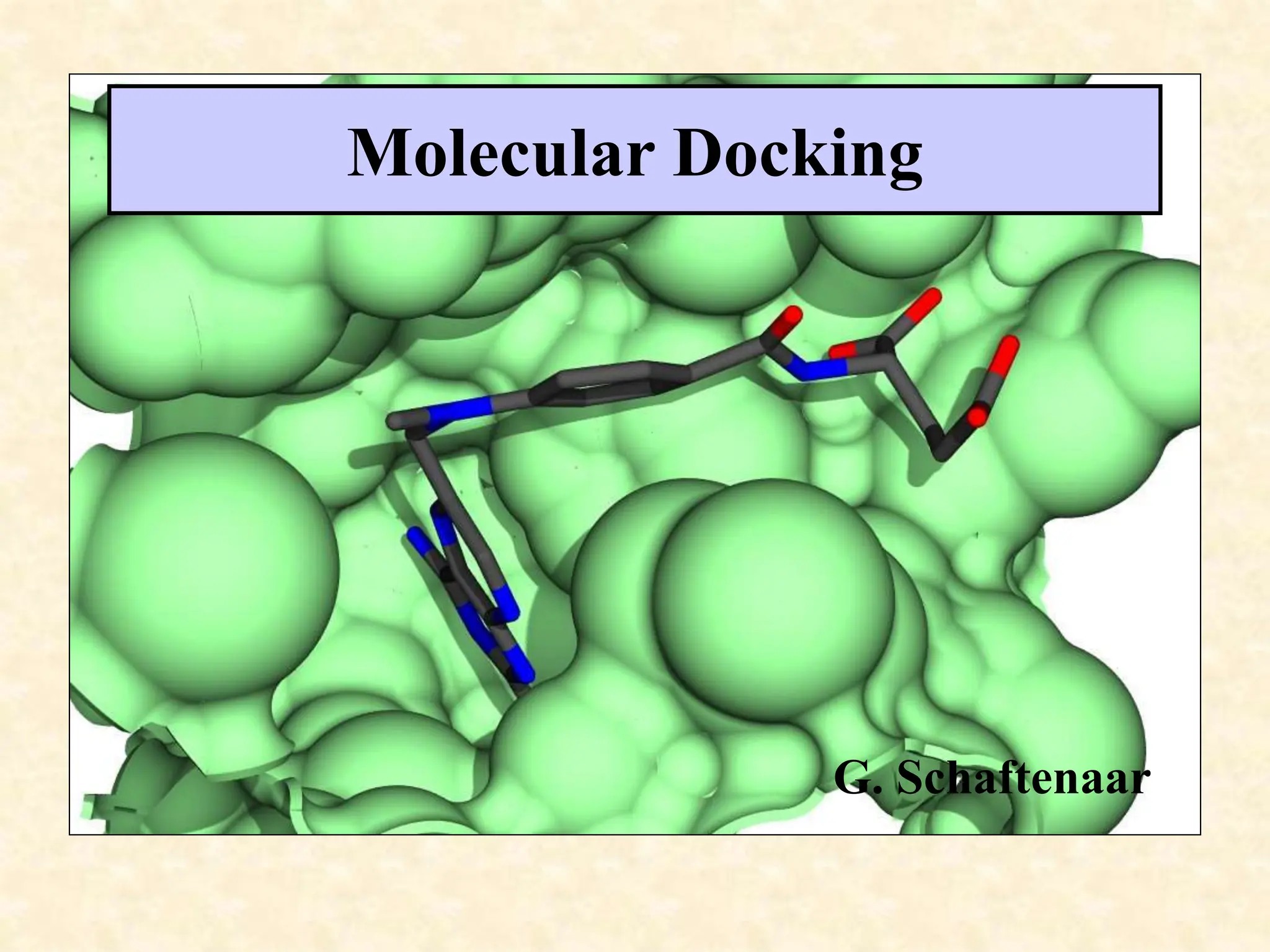
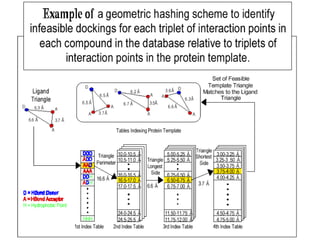
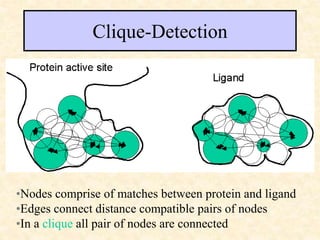
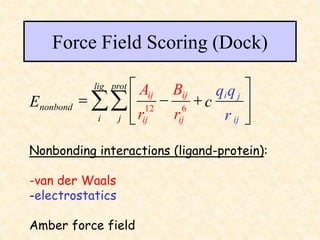
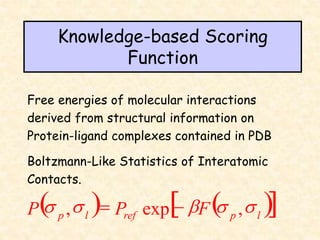
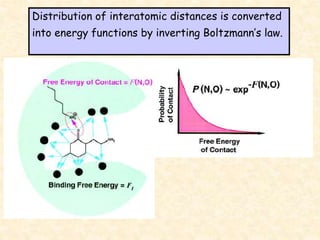
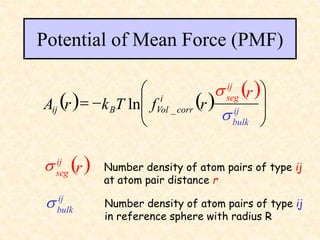
This document discusses molecular docking techniques. It describes two main tasks of docking tools: sampling conformational ligand space and scoring protein-ligand complexes. It outlines early rigid-body docking approaches and introduces flexibility through methods like Monte Carlo, molecular dynamics, and genetic algorithms. It also discusses fragment-based docking and techniques for placing fragments and rigid molecules like geometric hashing, pose clustering, and clique detection. The document compares scoring functions including shape complementarity, empirical, force field, knowledge-based, and consensus scoring. It notes that while docking reliability is limited, it can provide new suggestions and that consensus scoring may reduce false positives.