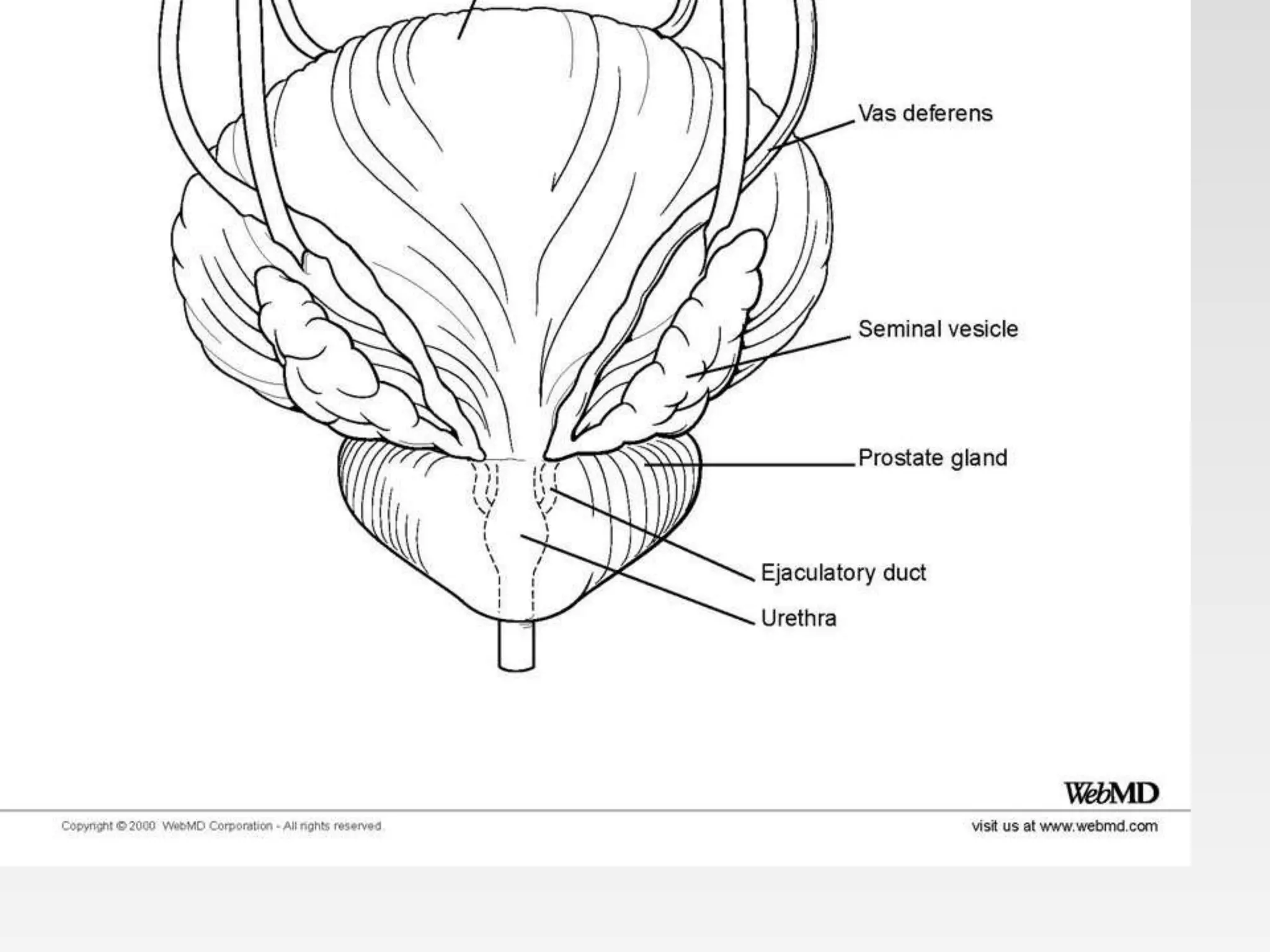
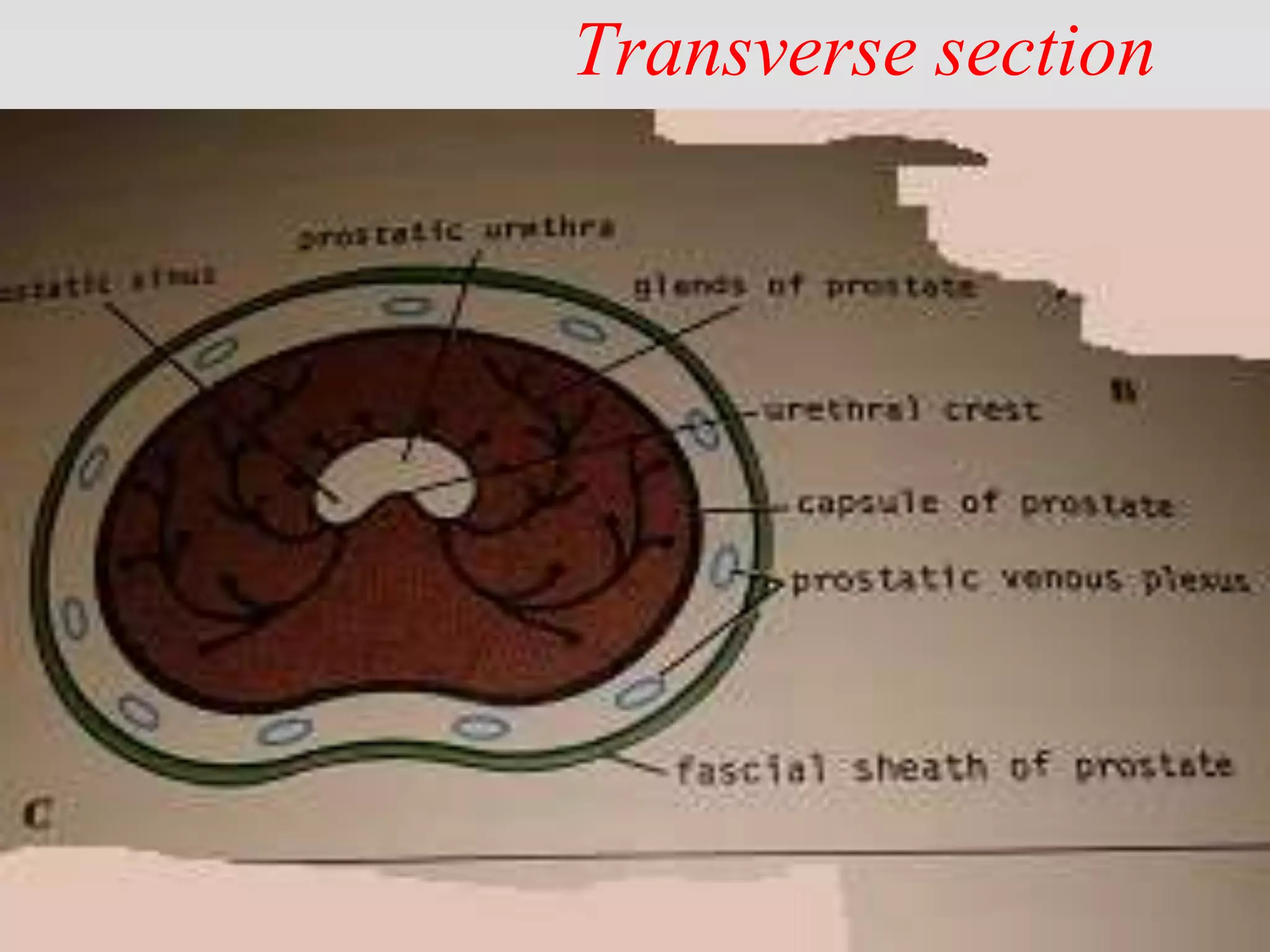
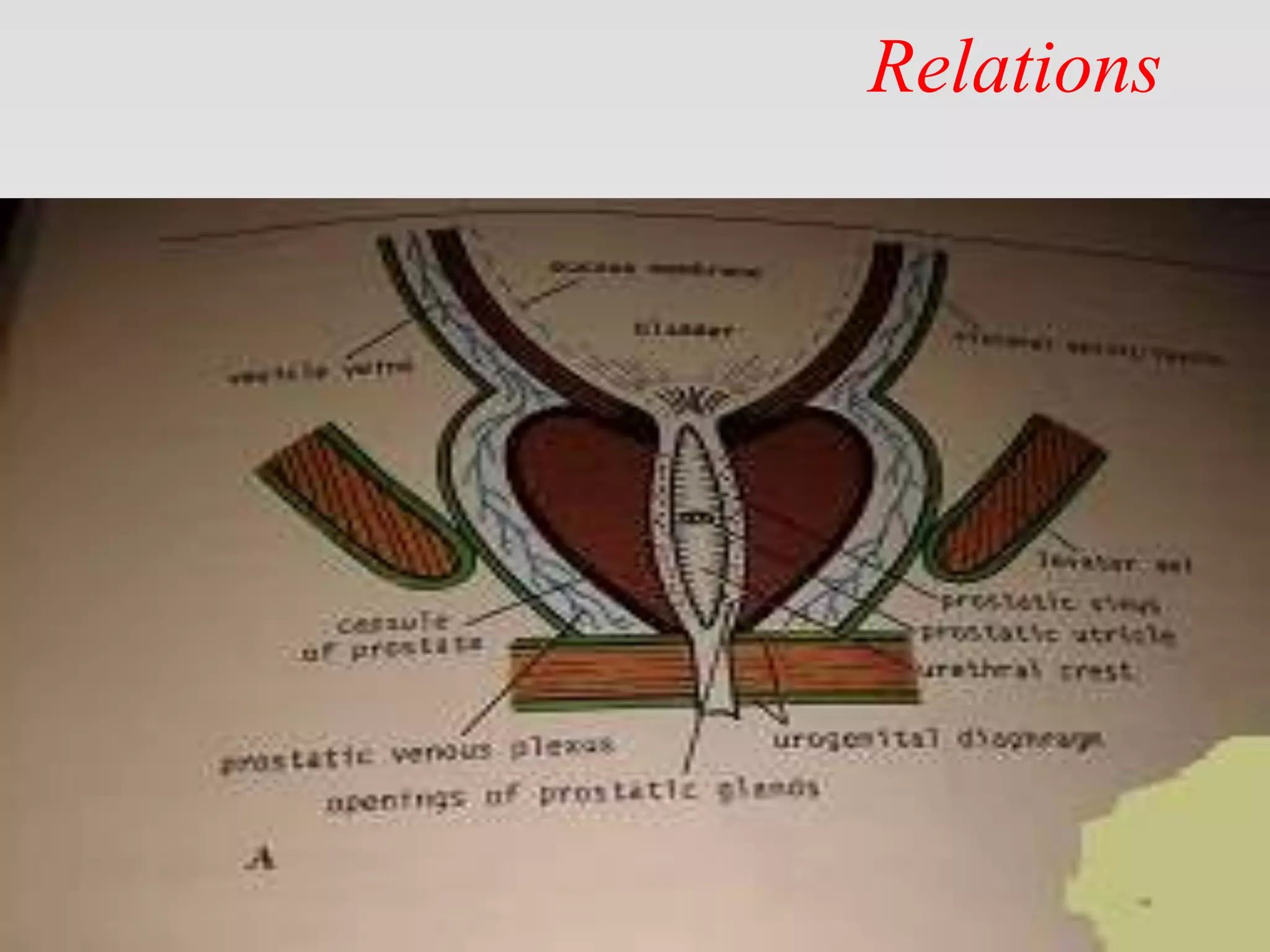
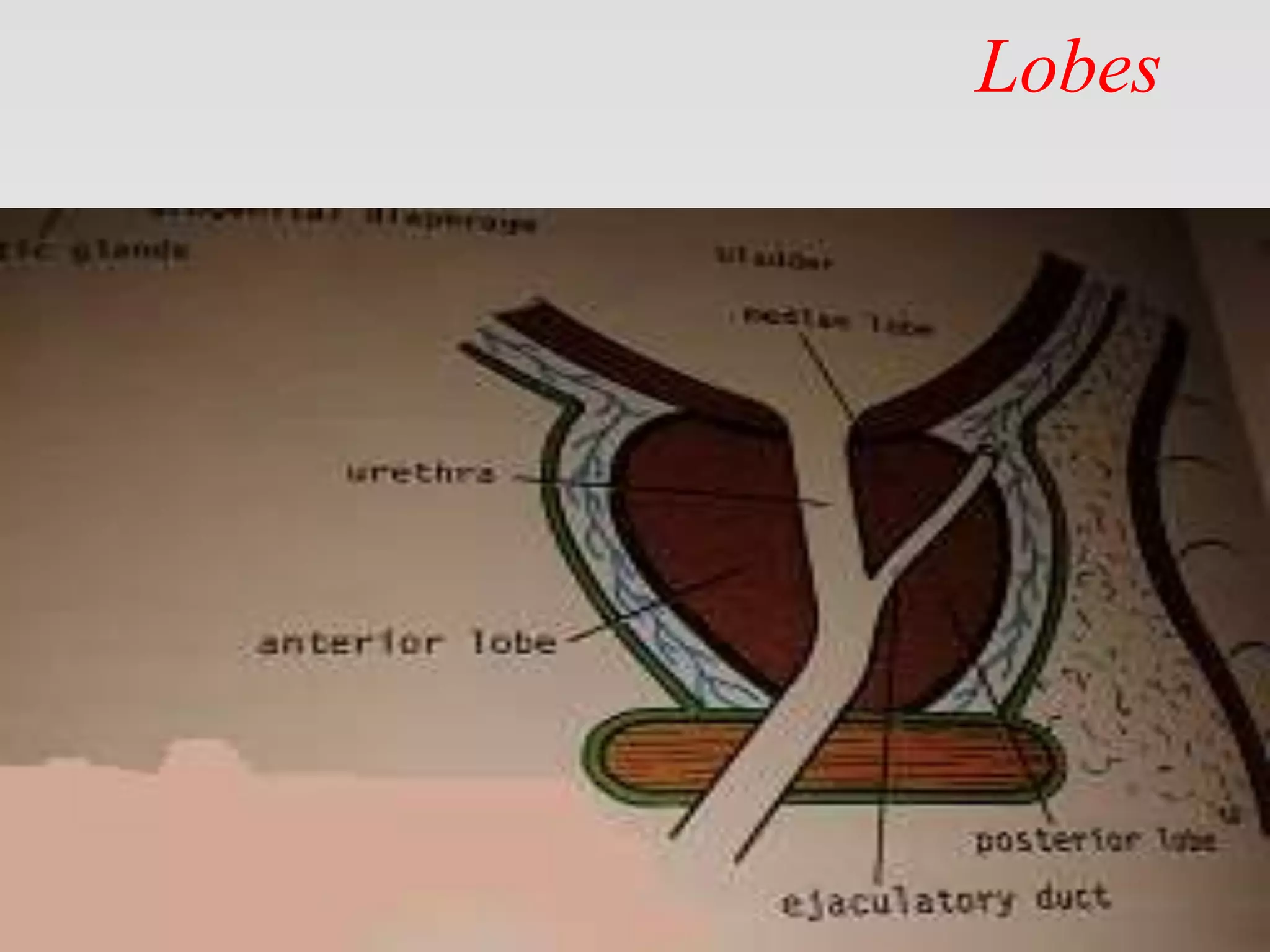
This document provides tips for using a PowerPoint presentation on prostate anatomy and physiology. It recommends freely editing the slides and asking students questions about blank slides to promote active learning. Reviewing blank slides before showing content engages students to think about what they know. The presentation is suitable for self-study by viewing a blank slide, thinking about the topic, and then reading the next slide. It aims to facilitate learning through three revisions of this interactive process.