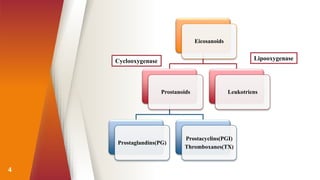
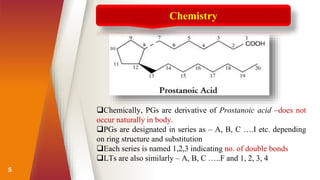
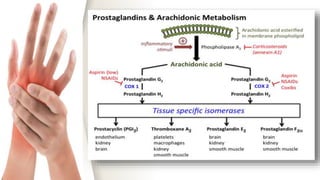
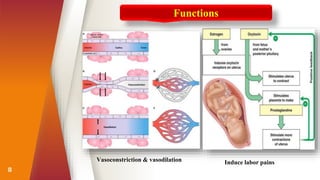
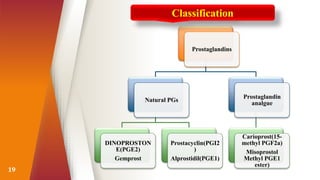
Prostaglandins were discovered in the 1930s and are locally acting lipid compounds derived from fatty acids. They include prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Prostaglandins have diverse physiological functions such as regulating inflammation, inducing labor pains, vasodilation/constriction, and sensitizing neurons to pain. They are synthesized through the cyclooxygenase pathway from arachidonic acid and act through G-protein coupled receptors on target cells. Common therapeutic uses of prostaglandins include induction of labor, treatment of hypertension and peripheral vascular diseases.