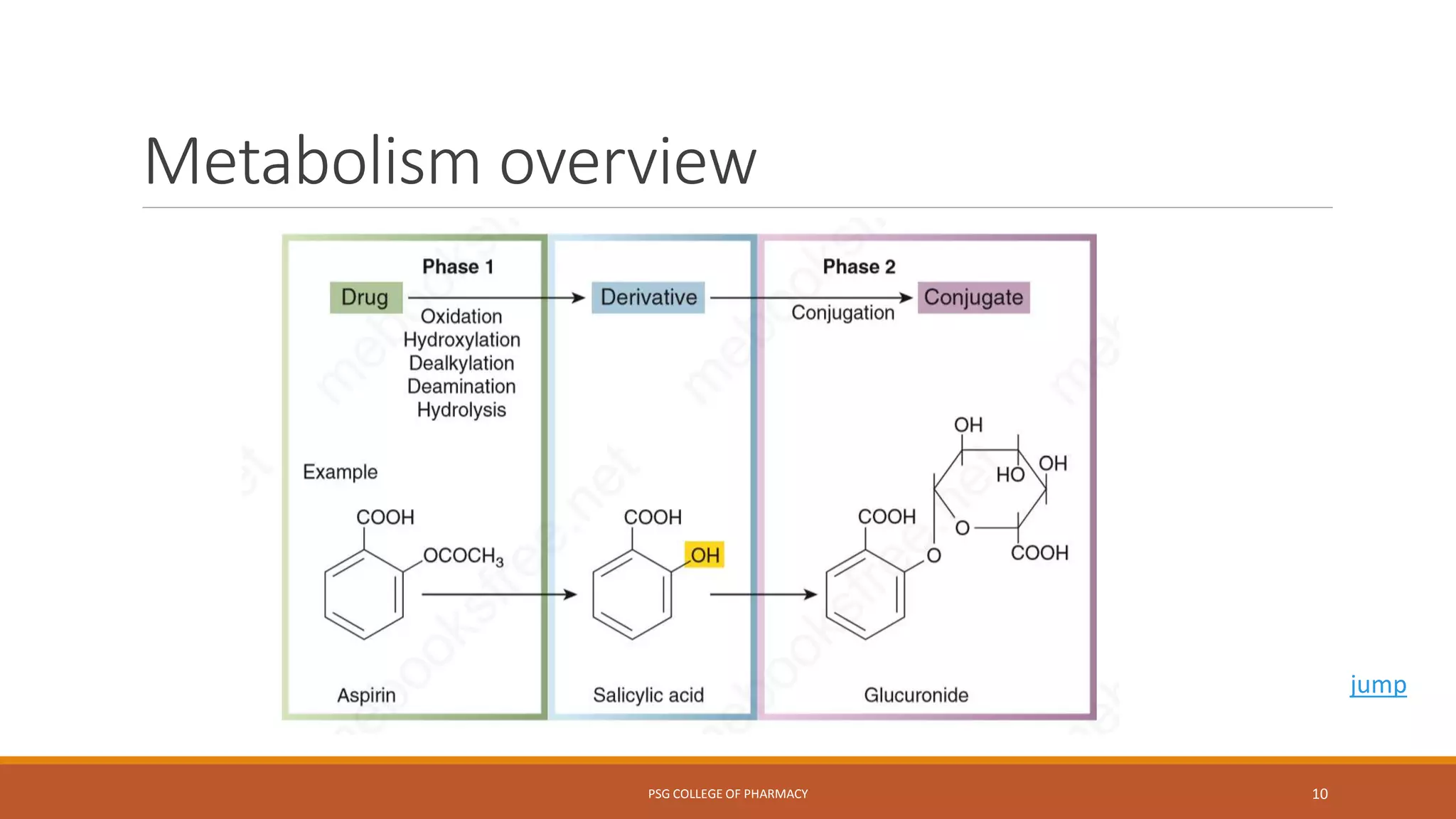
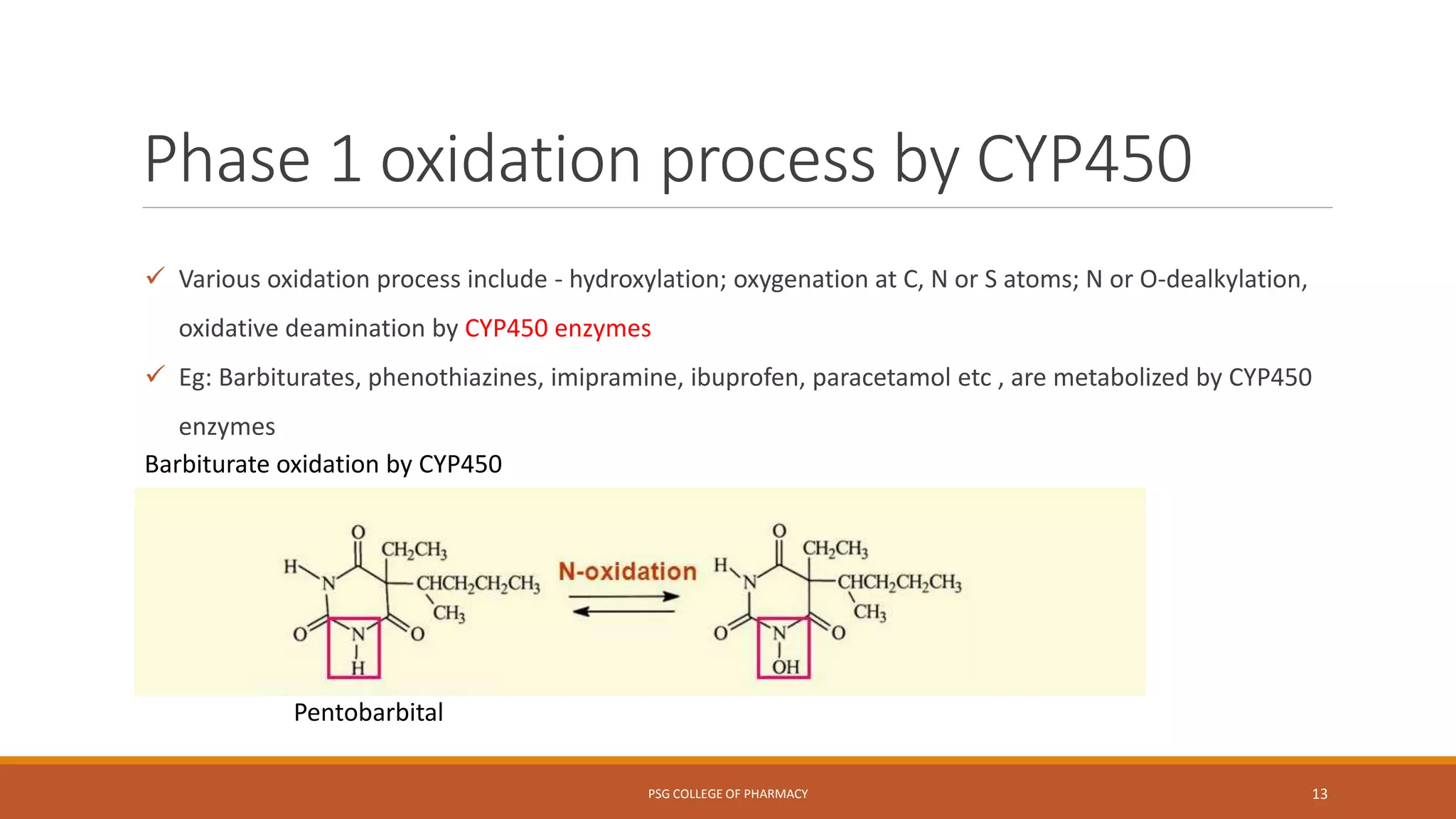
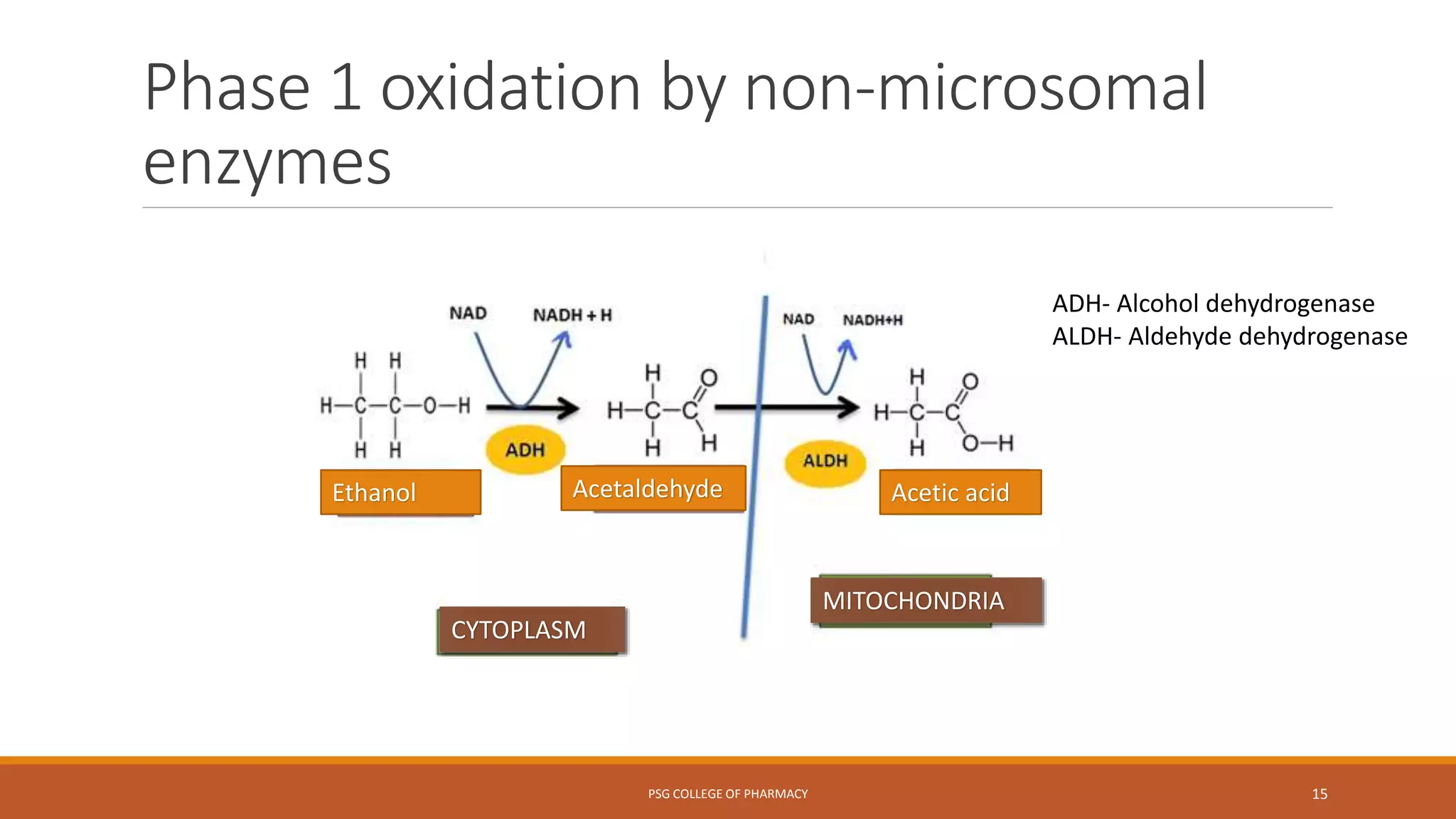
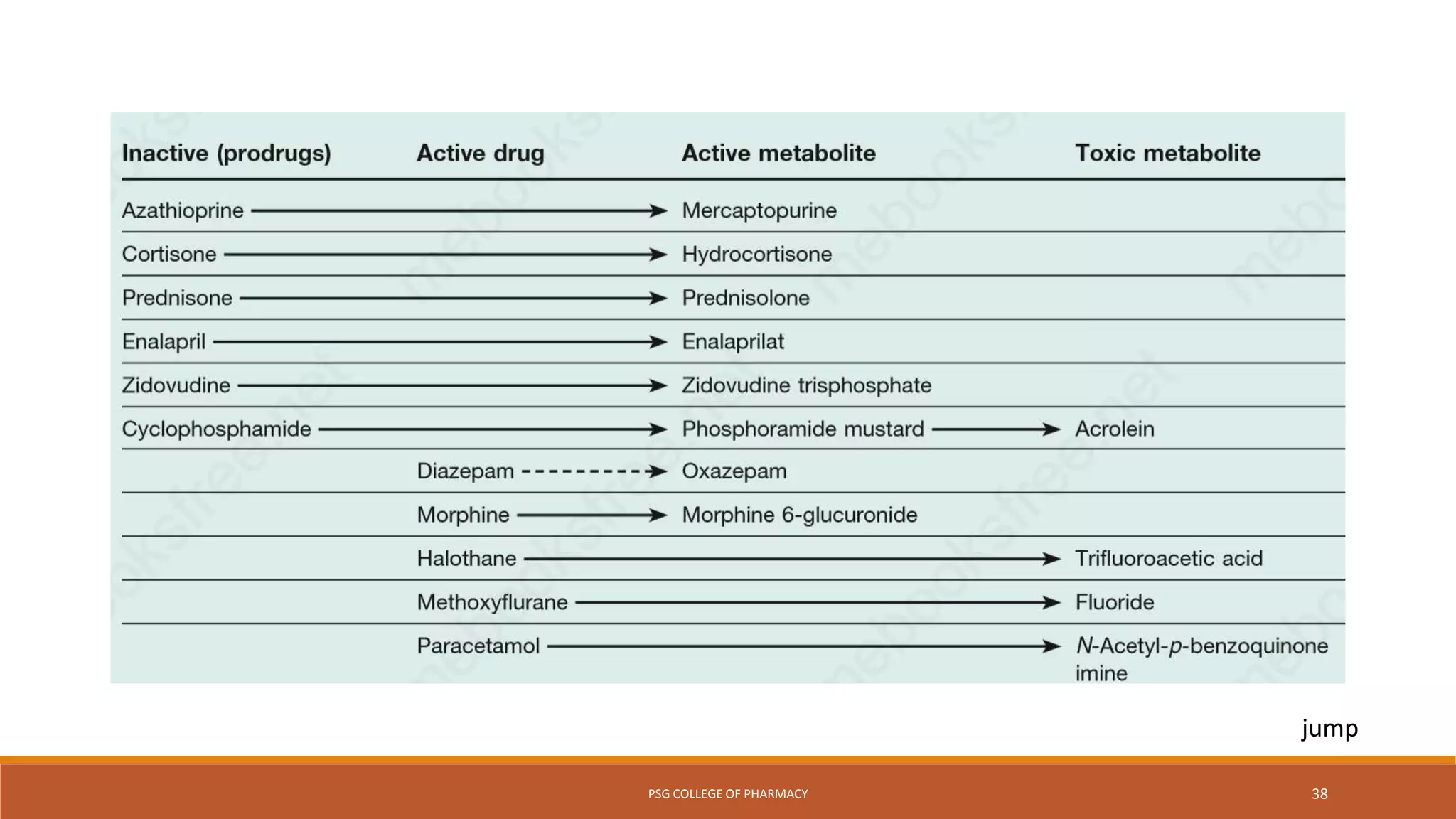
This document provides an overview of biotransformation (metabolism) through phases 1 and 2. Phase 1 reactions like oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, cyclization and decyclization make drugs more polar through functional group changes. Phase 2 then involves conjugating reactions like glucuronidation, acetylation, methylation, sulfation and glutathione conjugation to make drugs more hydrophilic for excretion. The liver is a major site of biotransformation through microsomal and non-microsomal enzymes. First pass metabolism reduces bioavailability of orally administered drugs. Biotransformation is important for drug clearance, detoxification and activation of certain drugs for their actions.