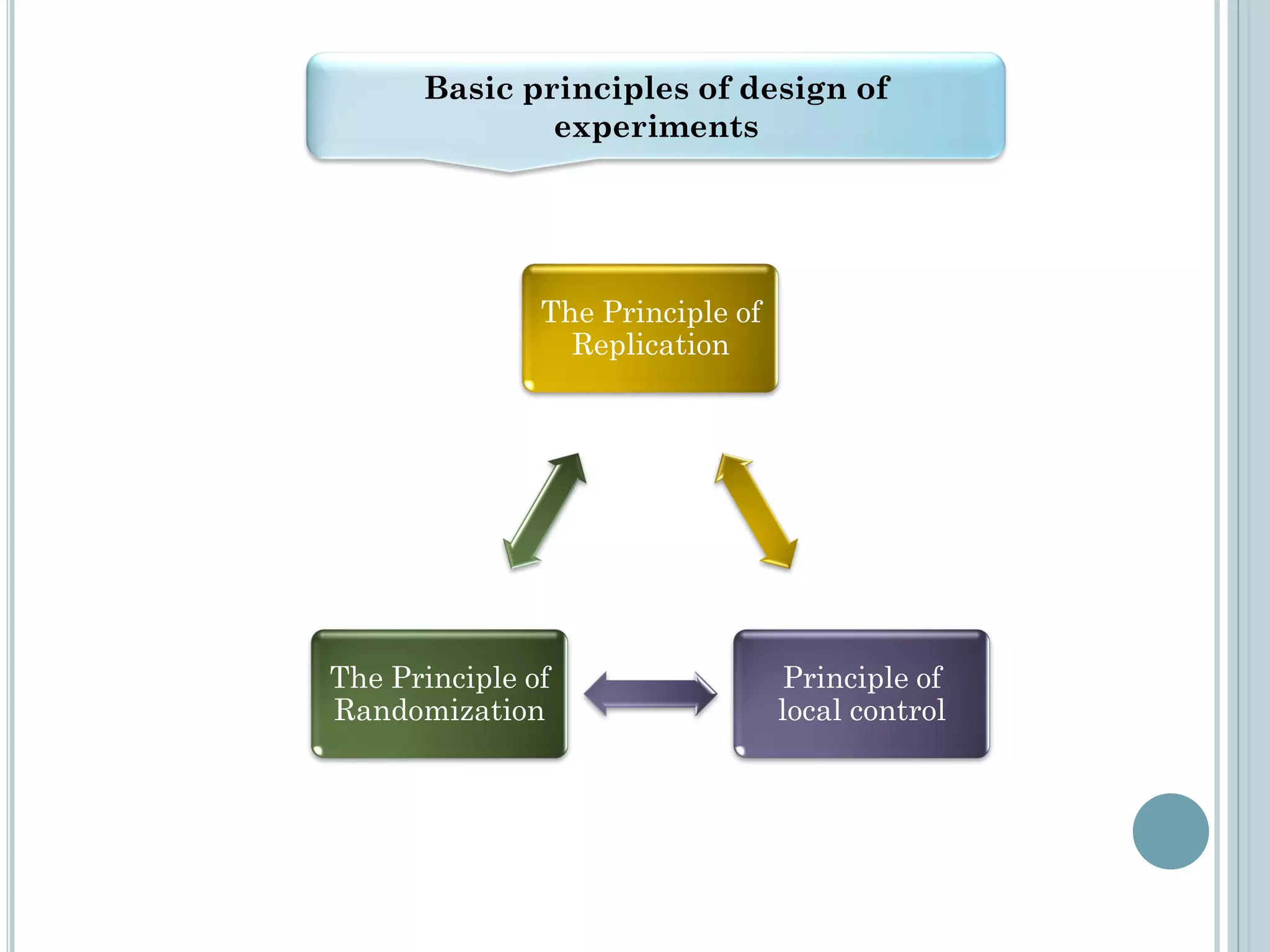
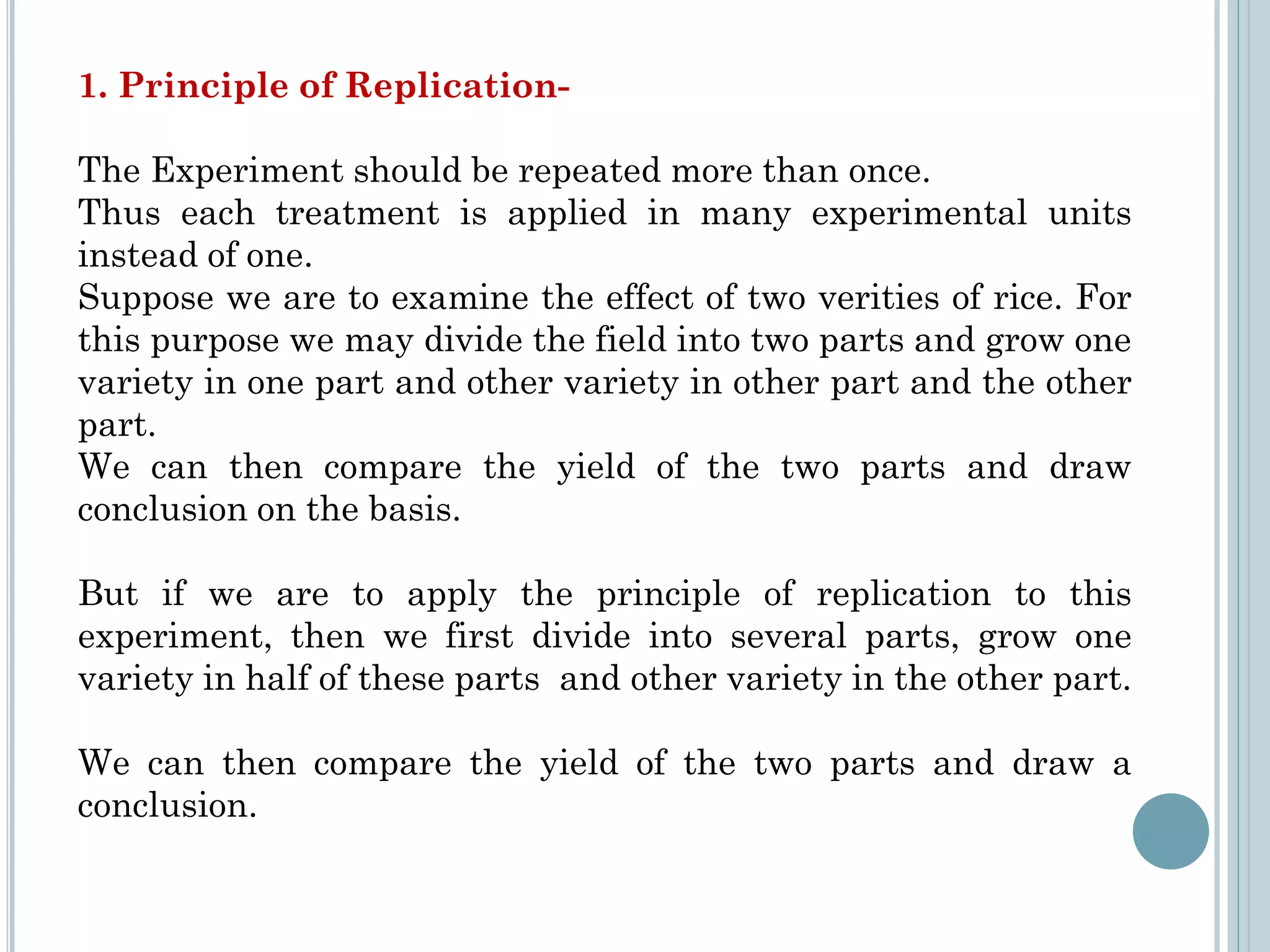
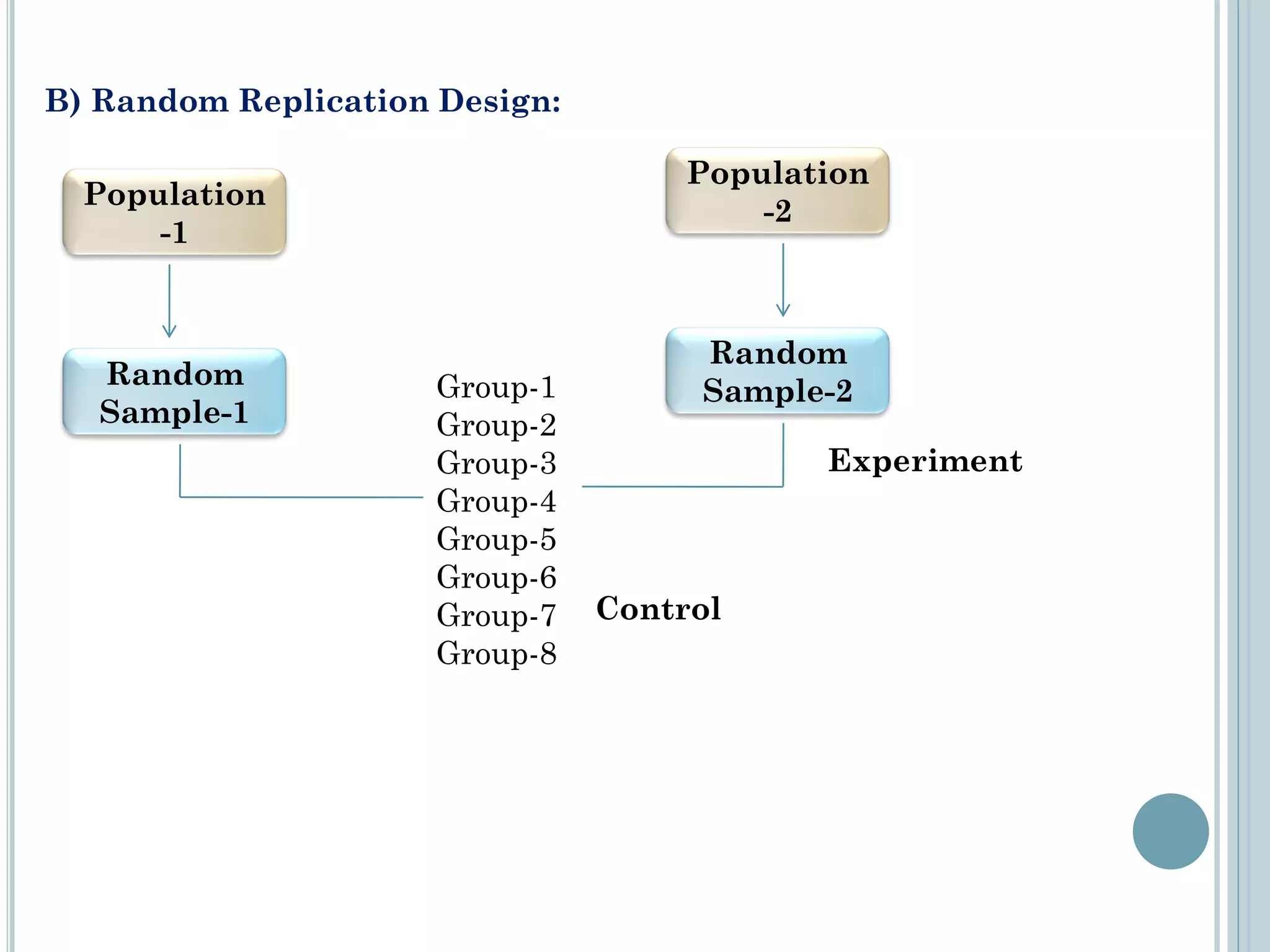
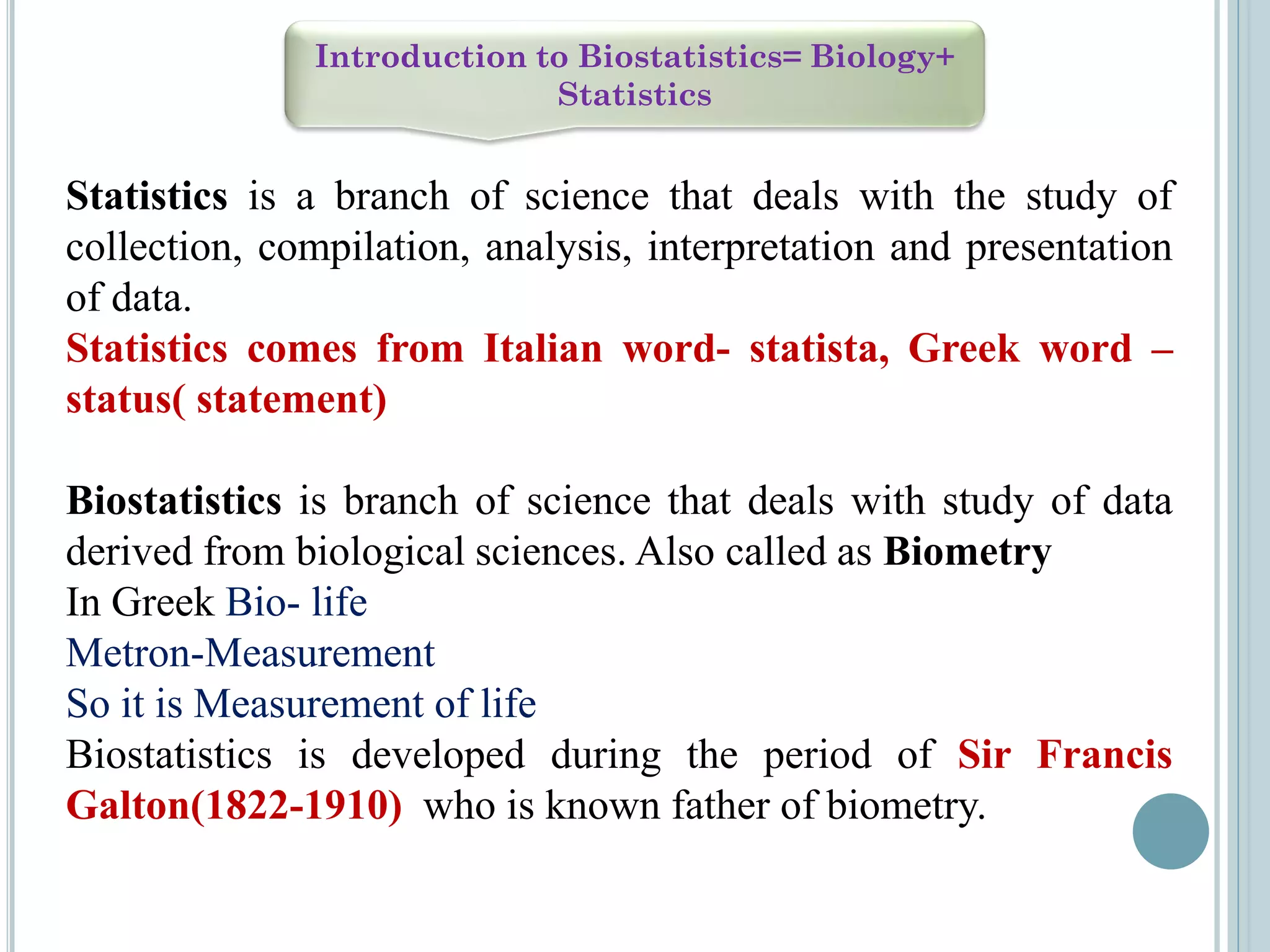
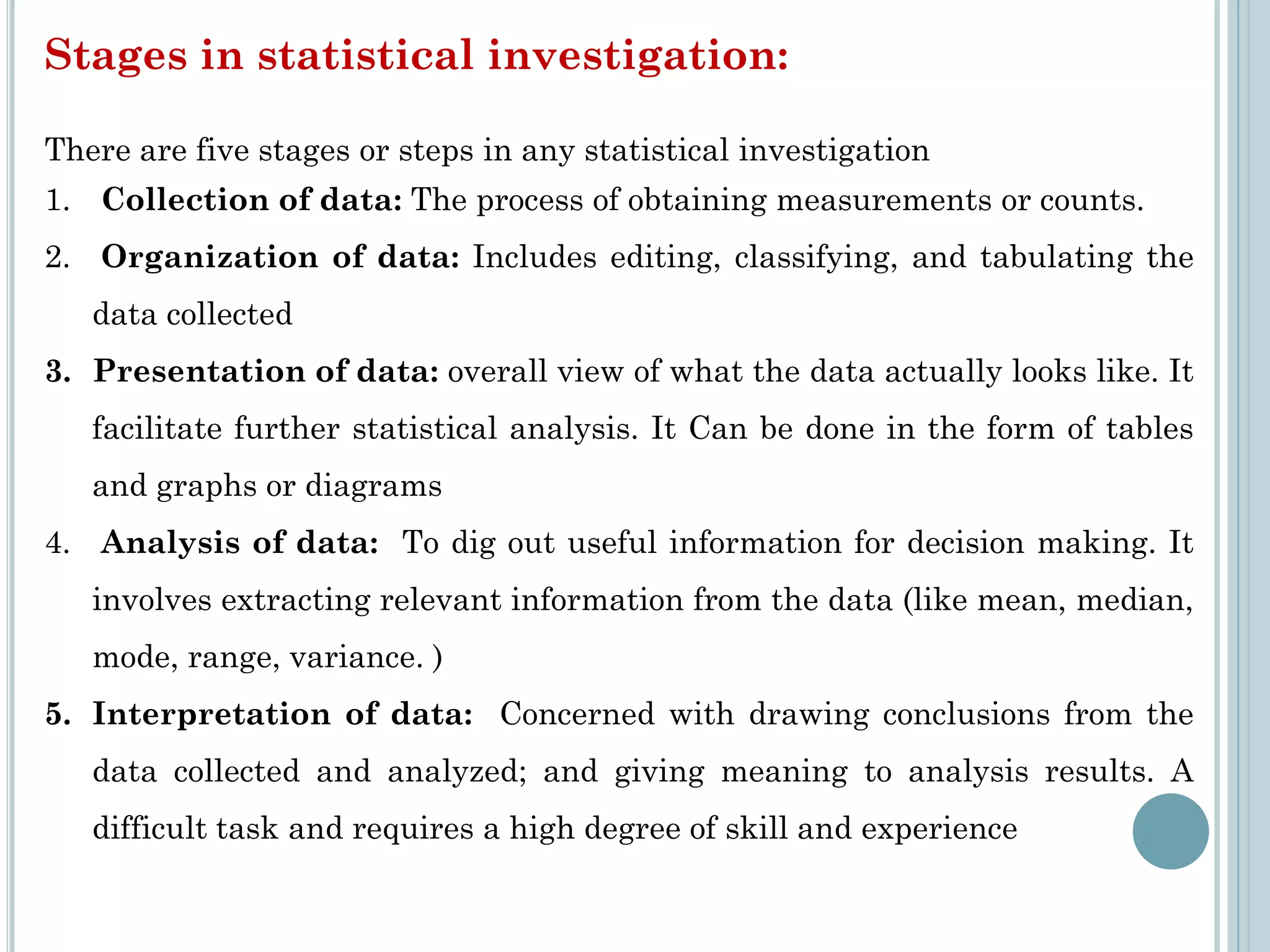
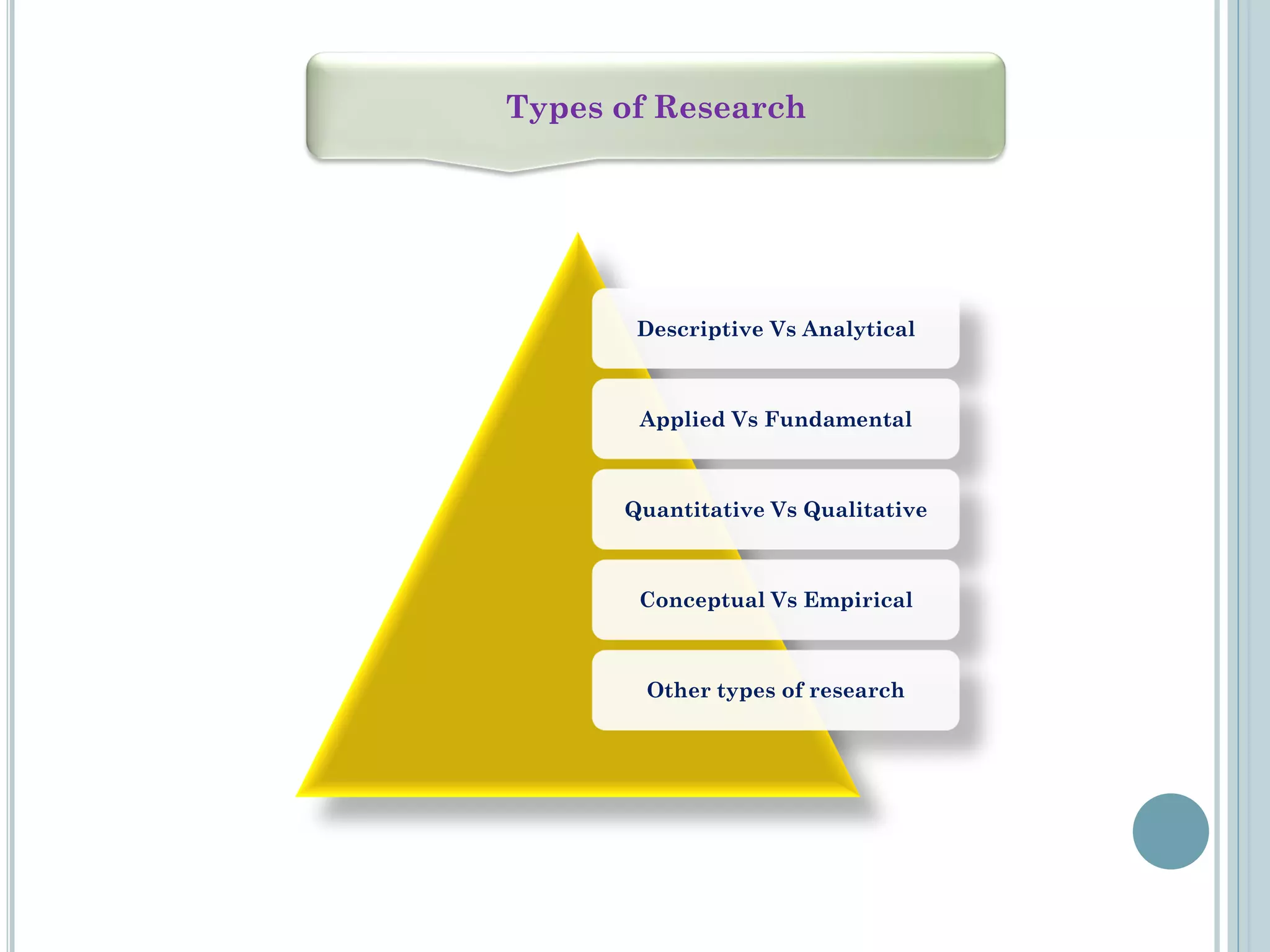
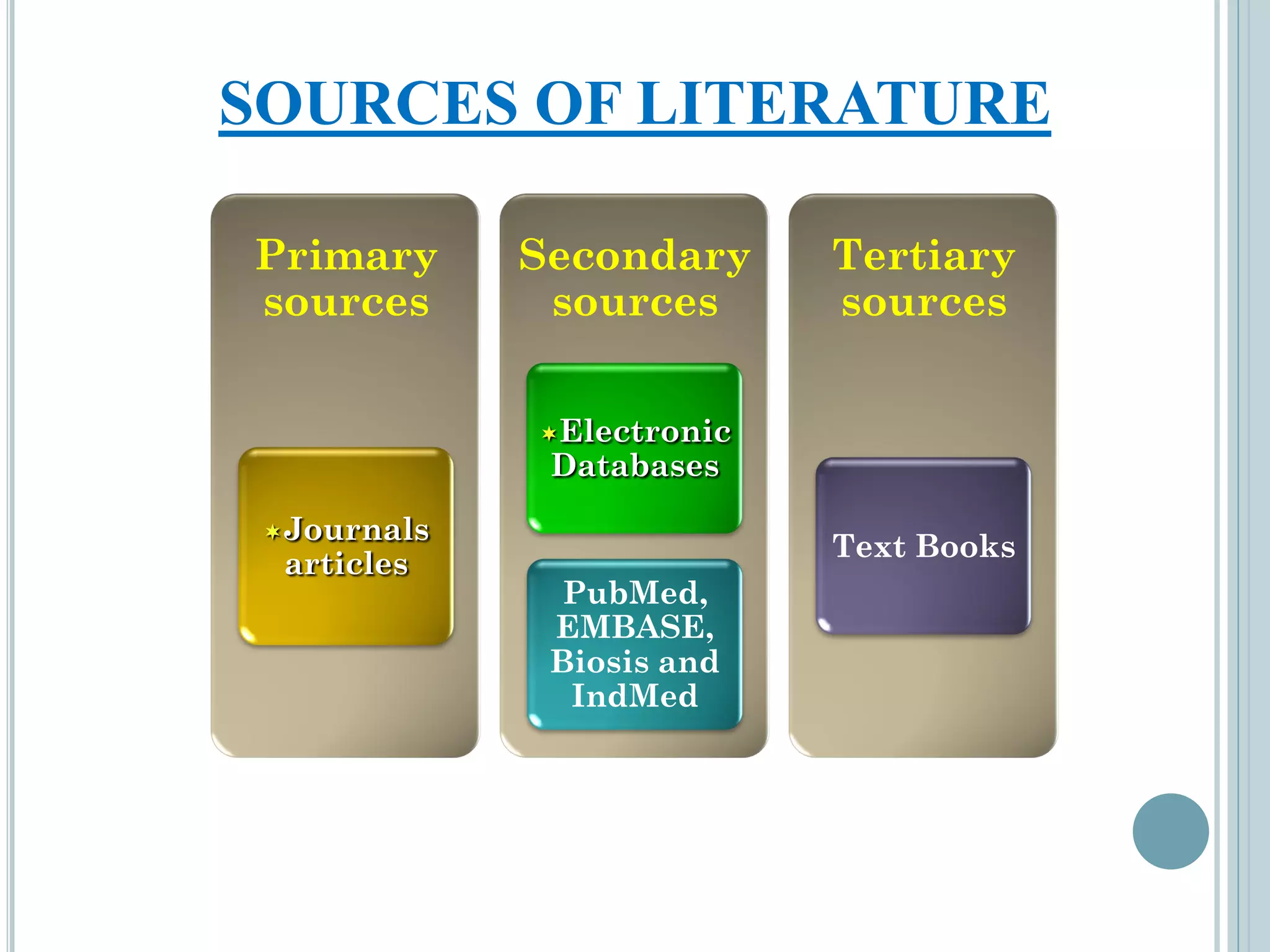
This document provides an overview of biostatistics and research methodology. It defines what research is, the objectives and importance of research, and the different types of research. The key stages of the research process are described, including defining the research problem, reviewing relevant literature, and formulating hypotheses. Statistical concepts like variables, frequency distributions, and hypothesis testing are also introduced. The roles of biostatistics in research applications and data presentation are discussed.











































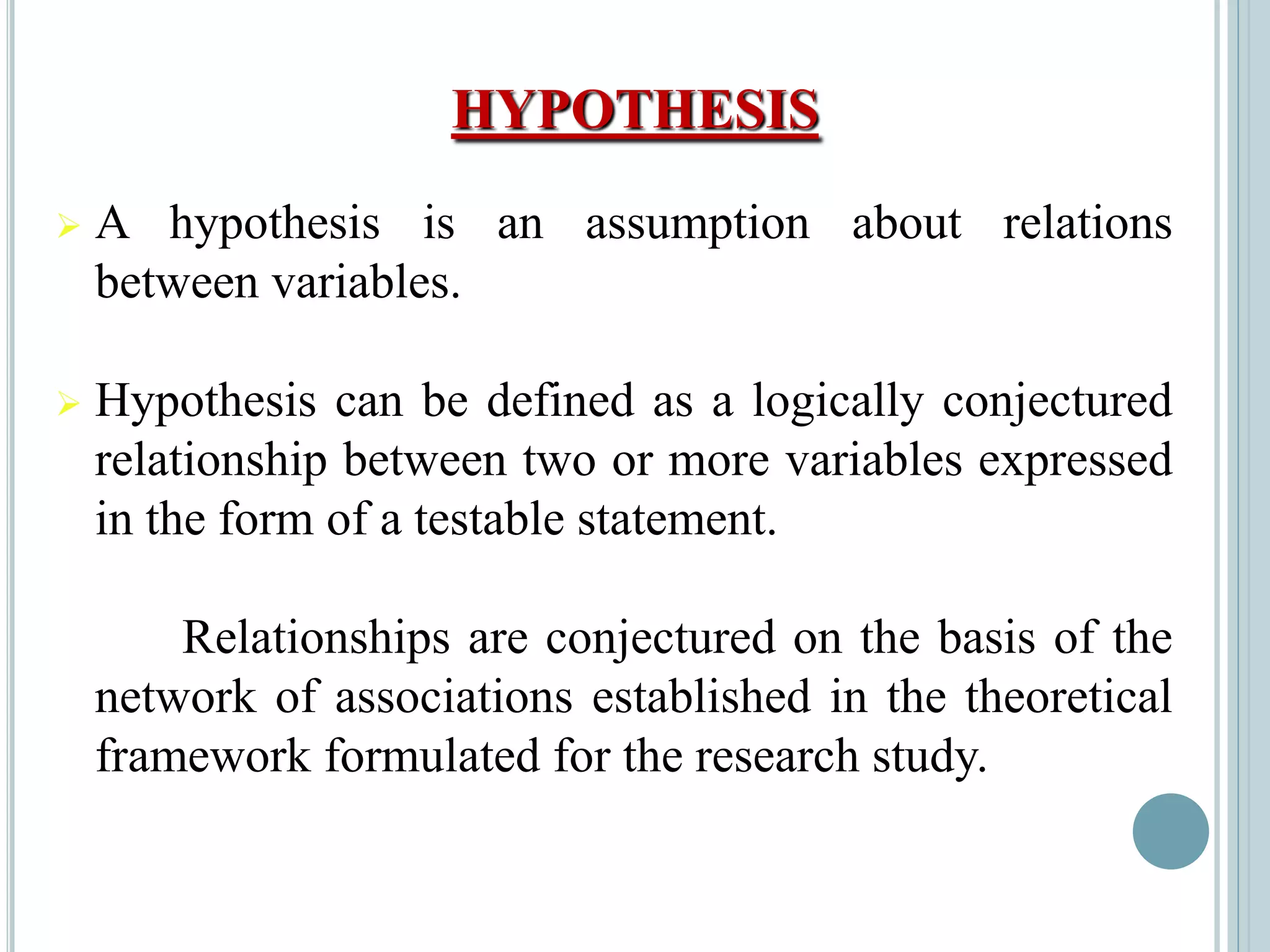










![Relational Hypothesis [Explanatory Hypothesis]
These are assumptions that describe the relationship
between two variables. The relationship suggested may be
positive, negative or causal relationship.
Examples:
“Families with higher incomes spend more for recreation”.
Causal Hypothesis state that the existence of or change
in one variable causes or leads to an effect on another
variable. The first variable is called the independent
variable and the latter is the dependant variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biostaticsandresearchmethodology-230822062622-47cf95ac/75/Biostatics-and-Research-Methodology-59-2048.jpg)